If we use JSON files as configuration for our Web App, we can use fetch() or import to read JSON files in the Browser.
Version
Brave 1.45.123
JSON File
data.json
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Sam"
}
- Standalone
data.jsonfile for configuration
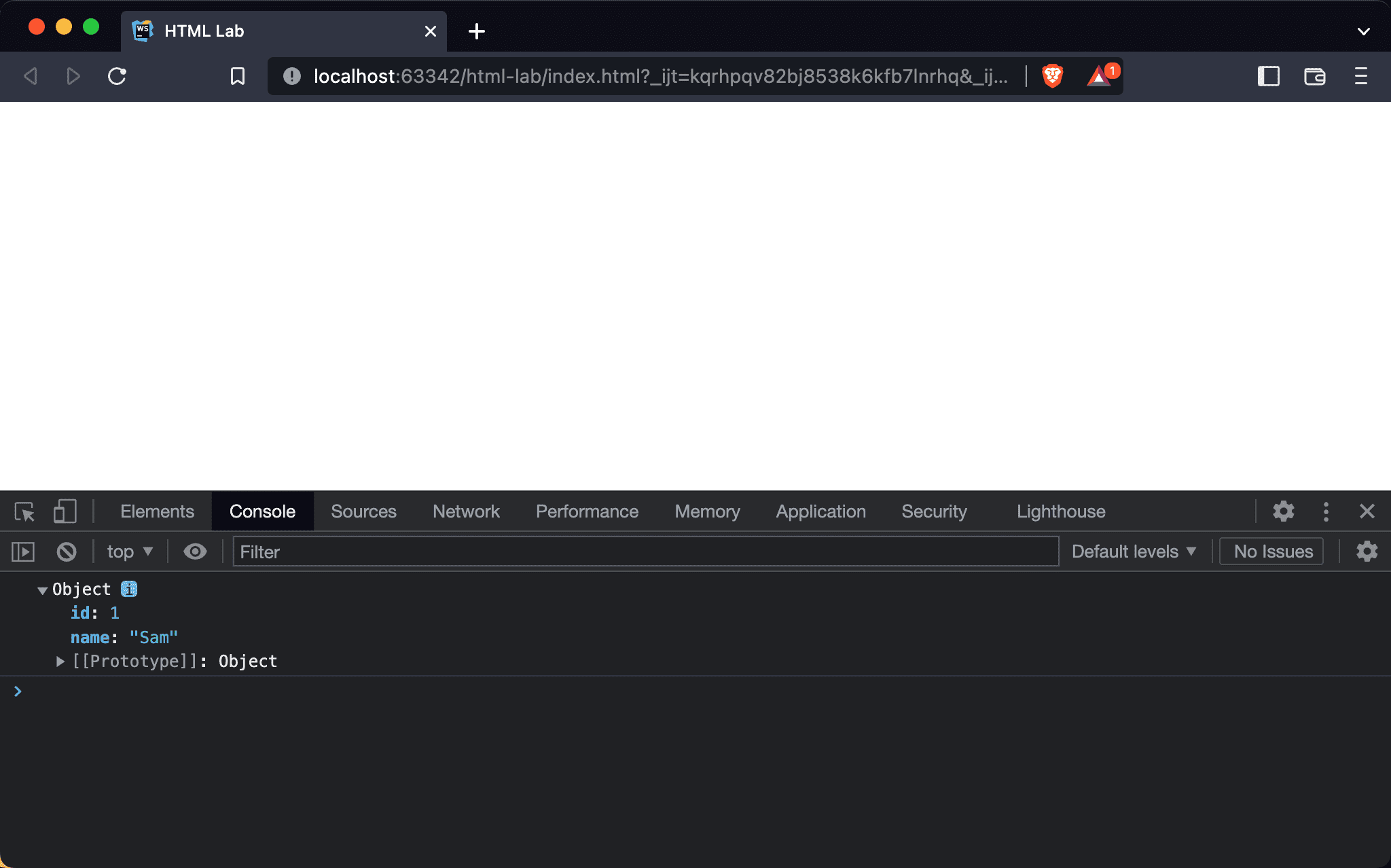
data.jsoncan be read as an Object
fetch()
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>HTML Lab</title>
</head>
<script>
fetch('./data.json')
.then(x => x.json())
.then(console.log)
</script>
</html>
Line 9
fetch('./data.json')
.then(x => x.json())
.then(console.log)
- The JSON file can be read by
fetch() - Since
fetch()returns Promise, we can use Promise Chain to handle JSON files.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>HTML Lab</title>
</head>
<script>
;(async () => {
let res = await fetch('./data.json')
let data = await res.json()
console.log(data)
})()
</script>
</html>
Line 9
;(async () => {
let res = await fetch('./data.json')
let data = await res.json()
console.log(data)
})()
- Since
fetch()returns Promise. We can also useasync-awaitto handle Promise - Top-level await is not supported by Browser now; what we can do is use async IIFE to simulate top-level await
ES Module
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>HTML Lab</title>
</head>
<script type="module">
import data from './data.json' assert { type: 'json' }
console.log(data)
</script>
</html>
Line 8
<script type="module">
- We have to add
type="module"on<script>to enable ES module
Line 9
import data from './data.json' assert { type: 'json' }
console.log(data)
- Use
importstatement to import the JSON file - Assert the file format is JSON type
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>HTML Lab</title>
</head>
<script type="module">
let { default: data } = await import('./data.json', {
assert: {
type: 'json',
},
})
console.log(data)
</script>
</html>
Line 8
<script type="module">
- We have to add
type="module"on<script>to enable ES module
Line 9
let { default: data } = await import('./data.json', {
assert: {
type: 'json',
},
})
- We can also use
import()to dynamically import JSON file import()returns Promise
Conclusion
- We can use
fetch()to read JSON files, but asynchronously - We can also use
importto read JSON files synchronously or asynchronously