We can login to Ubuntu without any password by storing the private key on the local machine and the public key on the remote server.
Version
Ubuntu 21.10
ssh-keygen
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "oomusou"
Generate SSH private key and public key.
-t rsa: specify RSA2 protocol to generate key-b 4096: specify4096bits to generate key-C: specify login name of Ubuntu
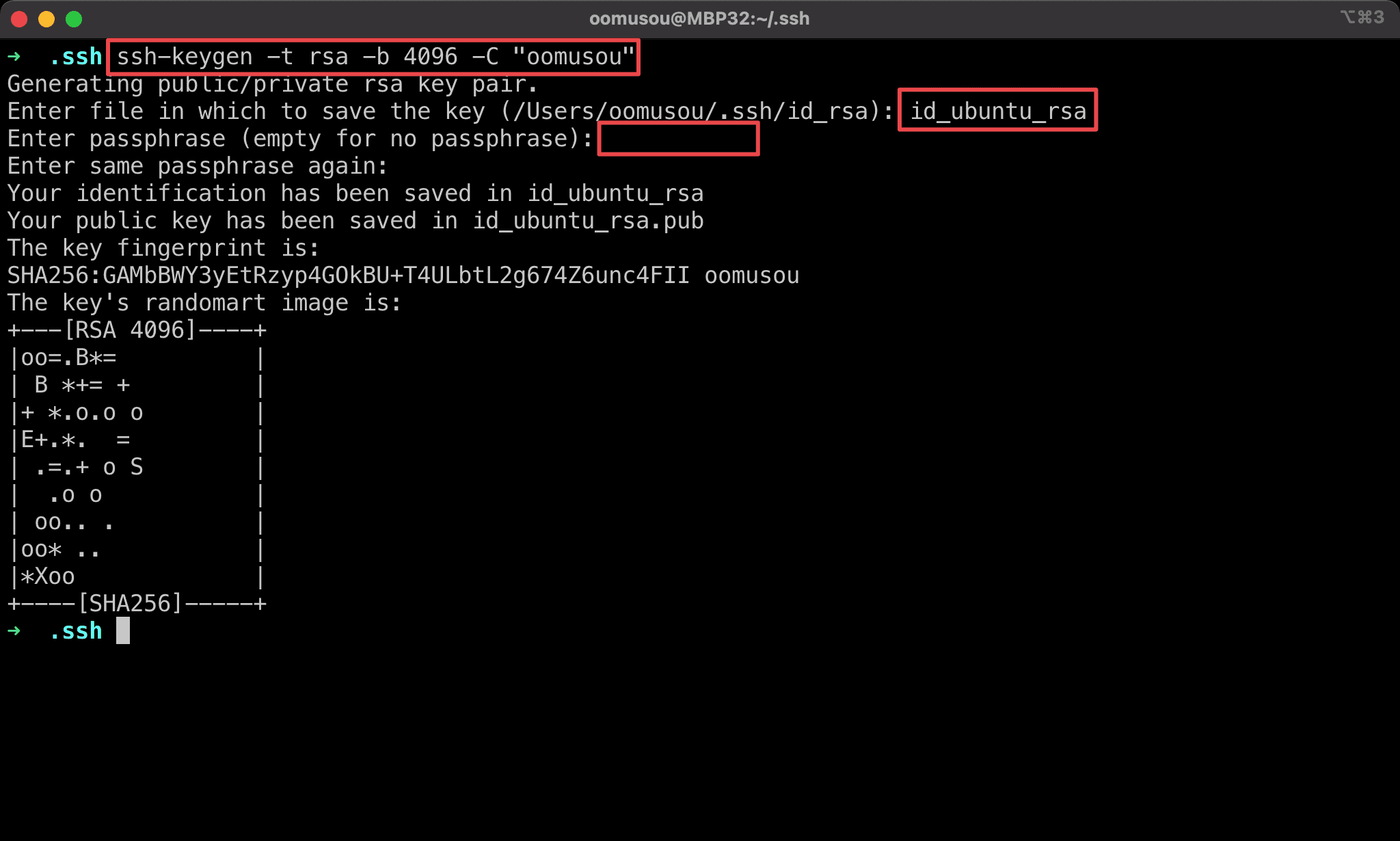
- if
id_rsaexists, enter another name for the new ssh key - Leave empty for passphrase
ssh-copy-id
$ ssh-copy-id -i ./id_rsa_ubuntu oomusou@ubuntu-test
Copy public key to Ubuntu.
-i: specify the location of the SSH keyoomusou@ubuntu-test:username@server
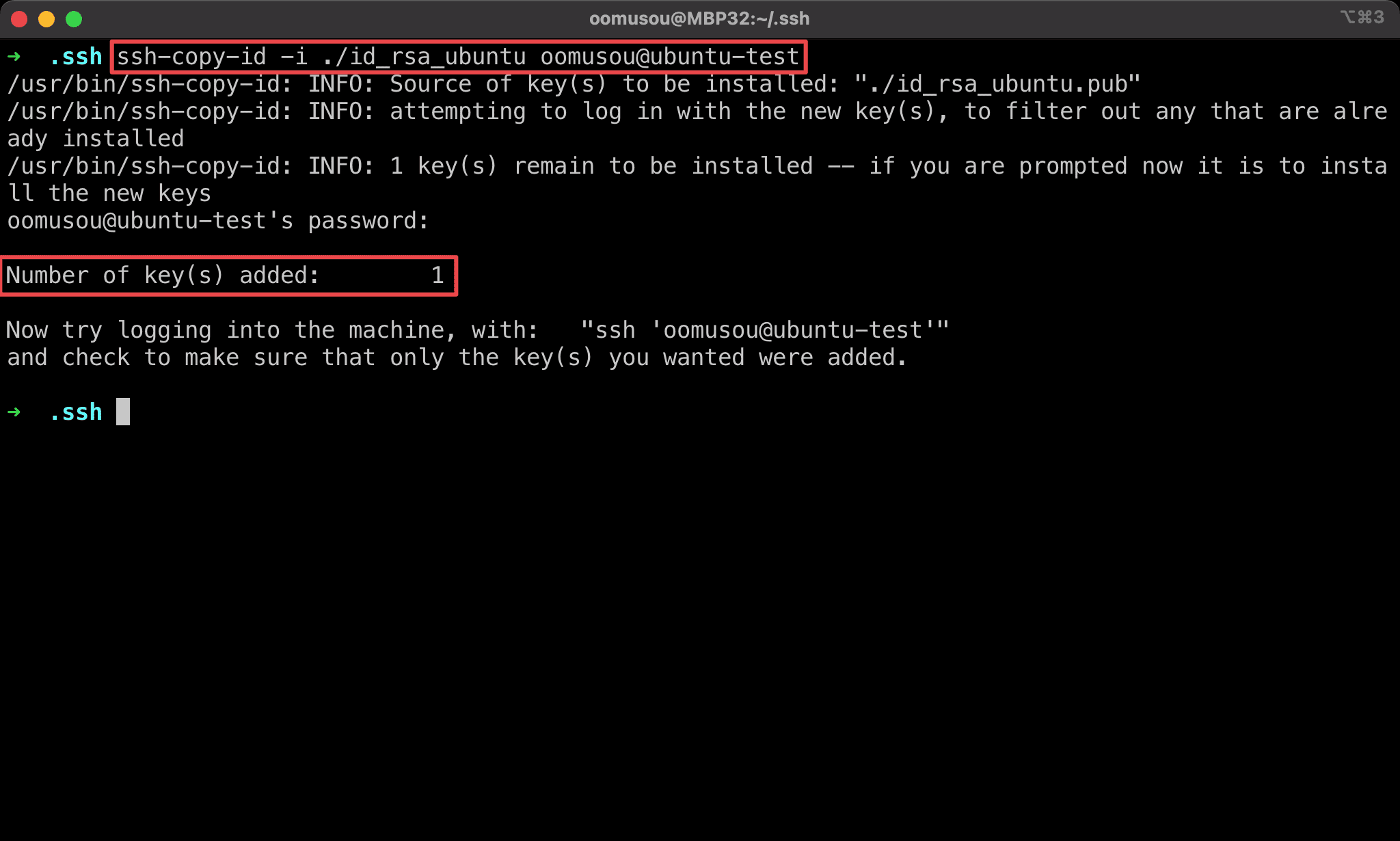
Number of key(s) added: 1 means ssh-copy-id copies the public key to the server successfully.
SSH Config
# GitHub
Host github.com
HostName github.com
User git
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
# Ubuntu
Host ubuntu
HostName ubuntu-test
User oomusou
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_ubuntu
We often have multiple SSH keys on the local machine; for example, we already have an SSH key for GitHub, but we want to add a different SSH key for Ubuntu.
We have to edit the config file in the .ssh directory to manage multiple SSH keys.
Line 7
# Ubuntu
Host ubuntu
HostName ubuntu-test
User oomusou
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_ubuntu
Add new section for Ubuntu :
Host: nickname for serverHostName: actual hostname for the serverUser: login user nameIdentityFile: the location of SSH private key file
ssh
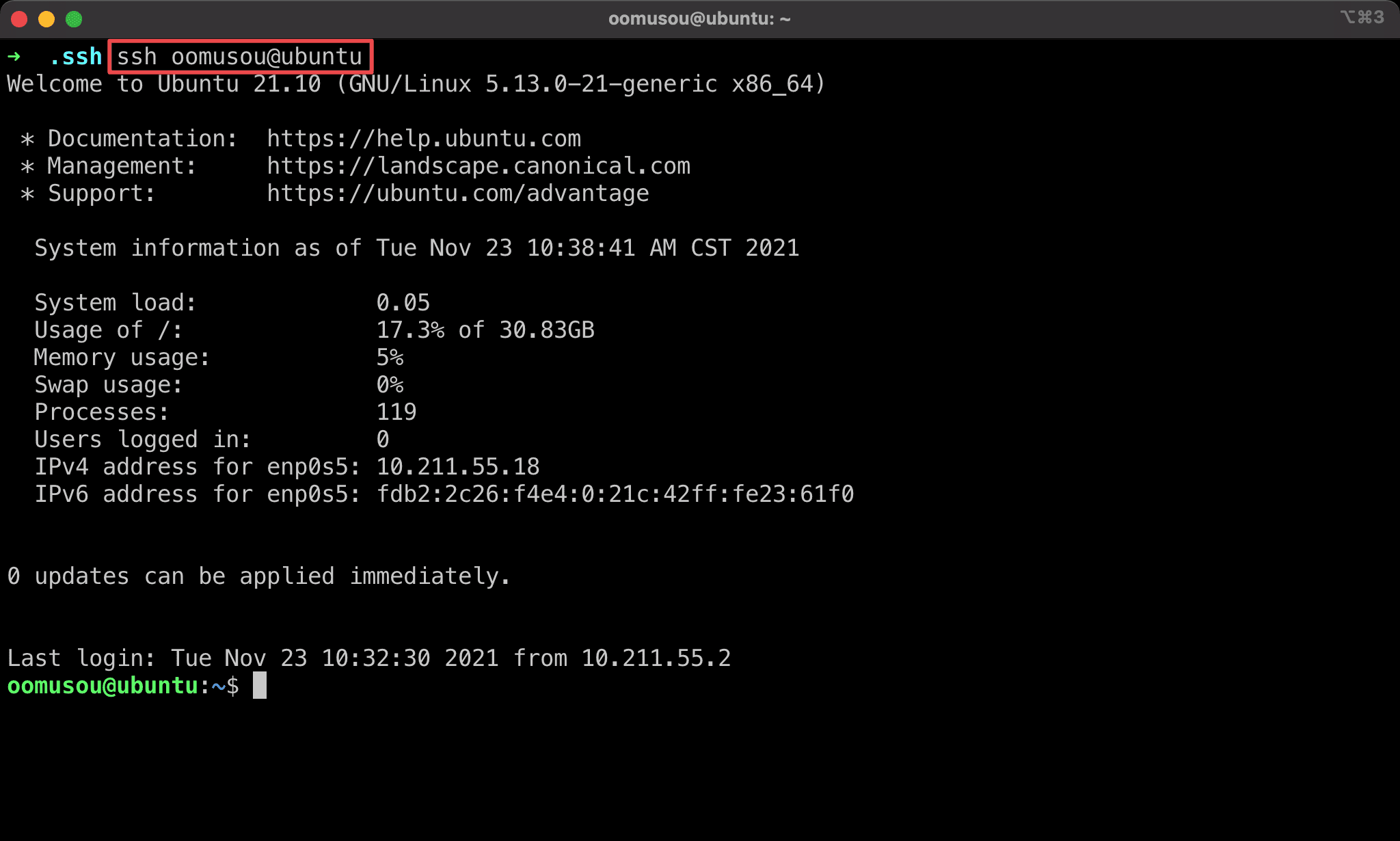
$ ssh oomusou@ubuntu
Use ssh to login to Ubuntu without any password.
Conclusion
- If we don’t have any other SSH key on the local machine, we don’t need to edit the
configfile in the.sshdirectory