實務上 Validation 都會回傳 Either 避免後續 Function 繼續執行,可將多個回傳 Either 的 Function 組合成單一回傳 Either 的 Function。
Version
Sanctuary 3.1.0
Either
import { is, thunkify, isEmpty } from 'ramda'
import { pipe, map, chain, Right, Left, ifElse, complement, concat } from 'sanctuary'
let chkEmpty = ifElse
(isEmpty)
(thunkify (Left) ('is empty'))
(Right)
let chkString = ifElse
(complement (is (String)))
(thunkify (Left) ('is not String'))
(Right)
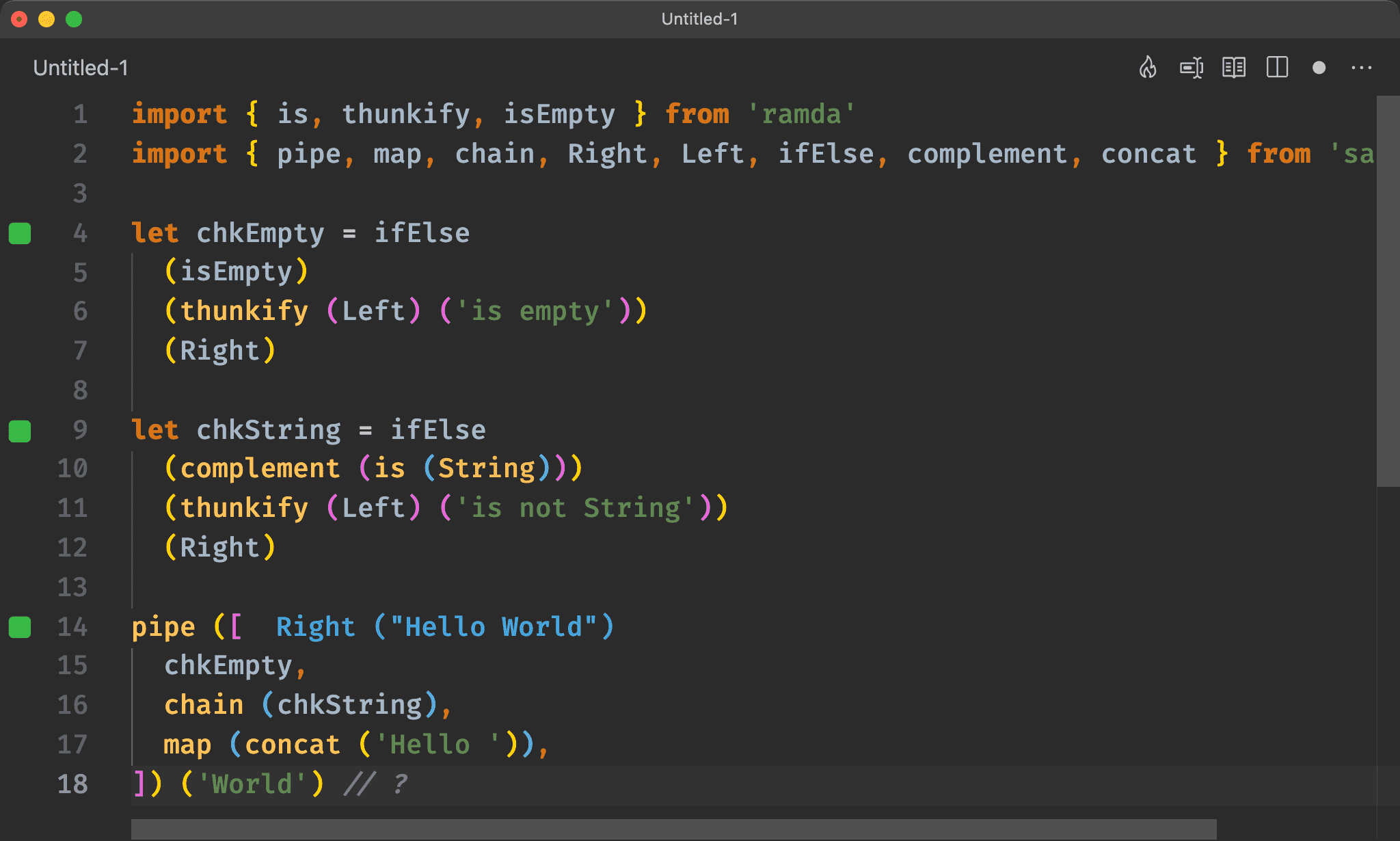
pipe ([
chkEmpty,
chain (chkString),
map (concat ('Hello ')),
]) ('World') // ?
第 4 行
let chkEmpty = ifElse
(isEmpty)
(thunkify (Left) ('is empty'))
(Right)
判斷是否為 empty,若為 Empty 則回傳 Left,否則回傳 Right:
isEmpty:判斷是否為 emptythunkify (Left) ('is empty'):empty 則回傳LeftRight:非 empty 則回傳Right
第 9 行
let chkString = ifElse
(complement (is (String)))
(thunkify (Left) ('is not String'))
(Right)
判斷是否為 String,若不是 String 則回傳 Left,否則回傳 Right:
complement(is (String)):判斷是否為 Stringthunkify (Left) ('is not String'):不是 String 則回傳LeftRight:String 則回傳Right
14 行
pipe ([
chkEmpty,
chain (chkString),
map (concat ('Hello ')),
]) ('World') // ?
使用 pipe 組合 IIFE:
chkEmpty:檢查輸入是否 empty 並回傳 Eitherchain (chkString):檢查是否為 String,也是回傳 Either 的 function,因此必須使用chain綁定map (concat ('Hello ')):若都通過檢查則回傳Hello World
Associativity
import { is, thunkify, isEmpty } from 'ramda'
import { pipe, map, chain, Right, Left, ifElse, complement, concat } from 'sanctuary'
let chkEmpty = ifElse
(isEmpty)
(thunkify (Left) ('is empty'))
(Right)
let chkString = ifElse
(complement (is (String)))
(thunkify (Left) ('is not String'))
(Right)
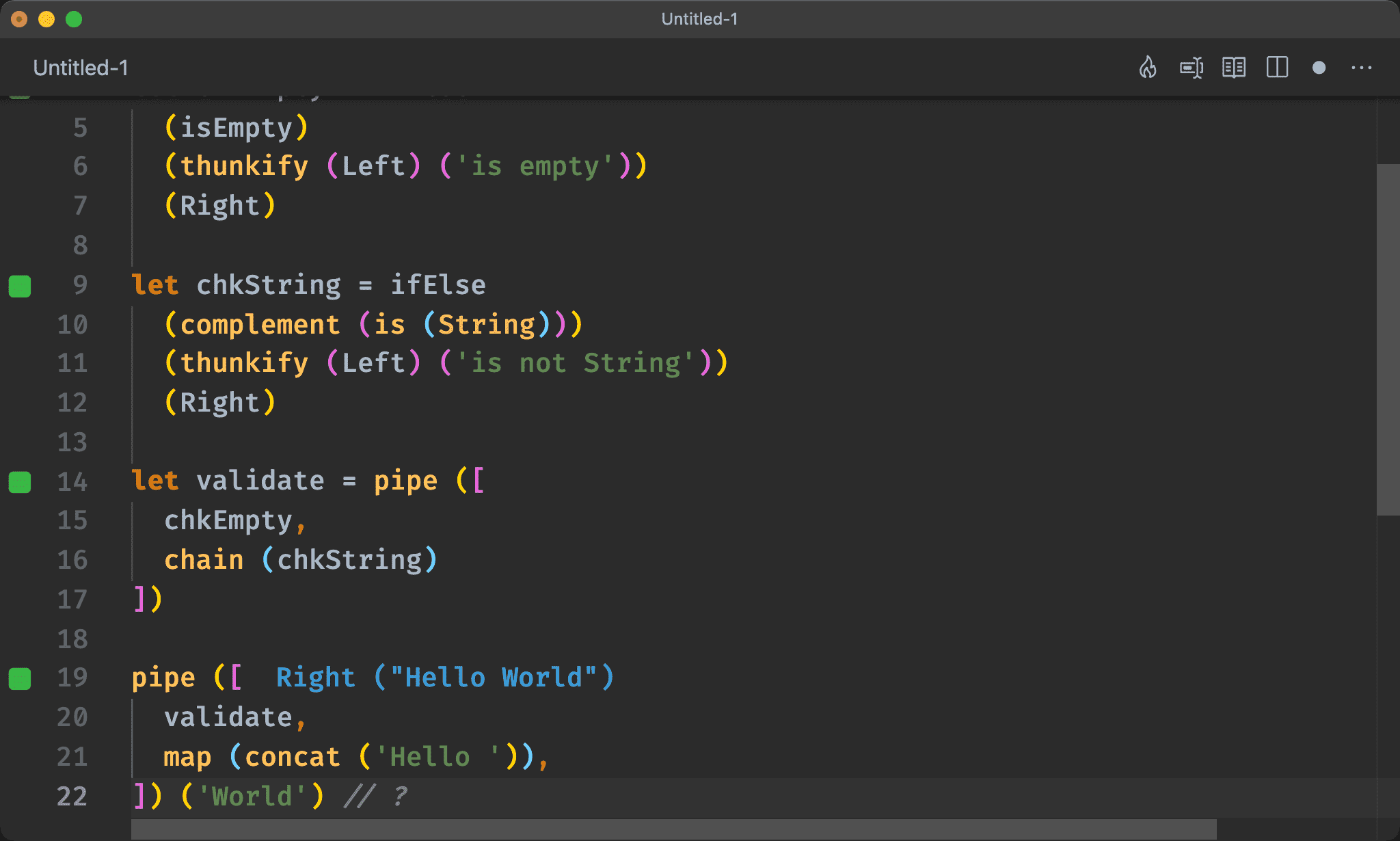
let validate = pipe ([
chkEmpty,
chain (chkString)
])
pipe ([
validate,
map (concat ('Hello ')),
]) ('World') // ?
14 行
let validate = pipe ([
chkEmpty,
chain (chkString)
])
Associativity 為 function 基本特性,因此可將 chkEmpty 與 chain (chkString) 先使用 pipe 組合起來。
19 行
pipe ([
validate,
map (concat ('Hello ')),
]) ('World') // ?
如此在 pipe 內只要呼叫一次 validate 即可。
Monad’s Associativity
import { is, thunkify, isEmpty } from 'ramda'
import { pipe, map, chain, Right, Left, ifElse, complement, concat } from 'sanctuary'
let chkEmpty = ifElse
(isEmpty)
(thunkify (Left) ('is empty'))
(Right)
let chkString = ifElse
(complement (is (String)))
(thunkify (Left) ('is not String'))
(Right)
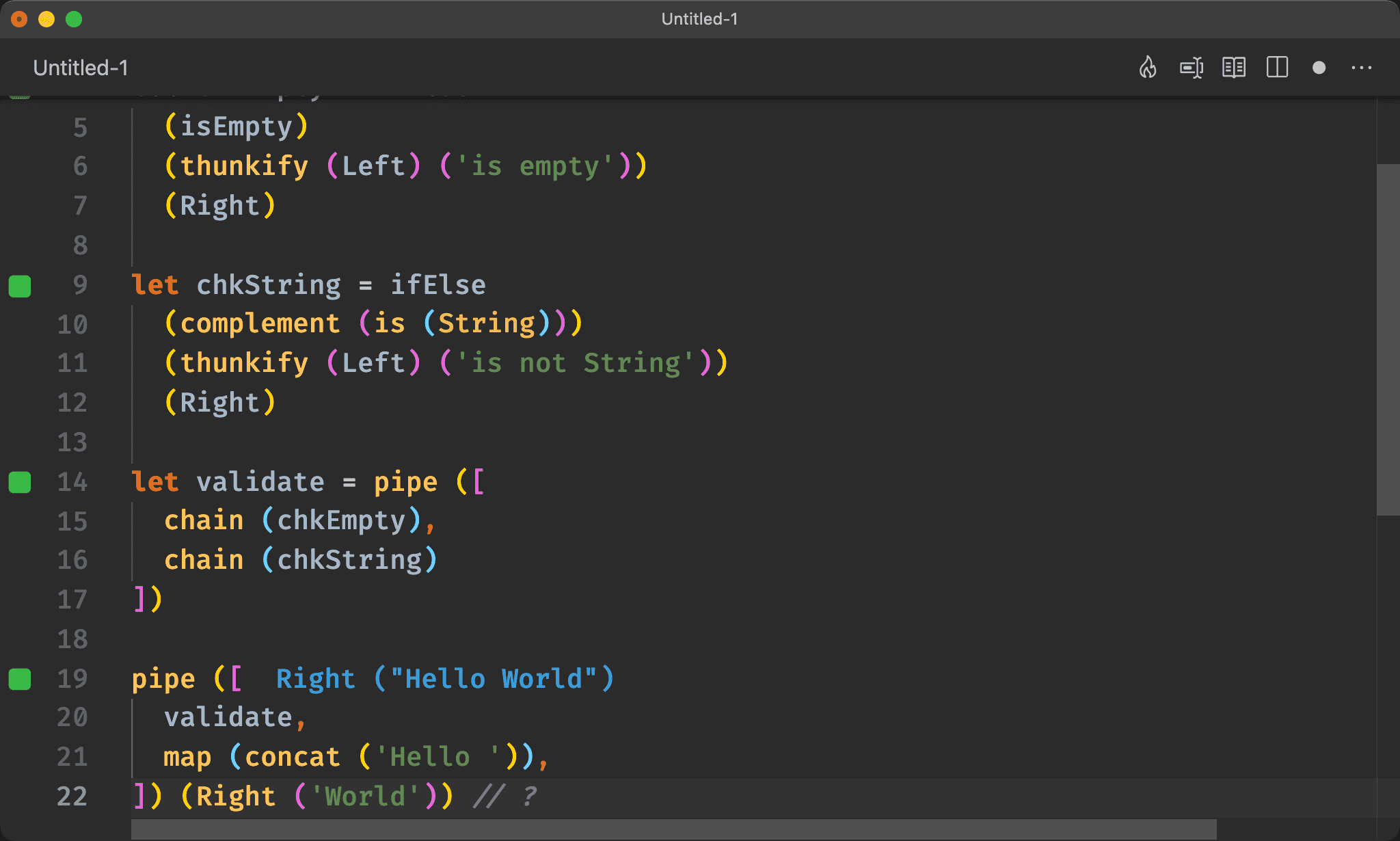
let validate = pipe ([
chain (chkEmpty),
chain (chkString)
])
pipe ([
validate,
map (concat ('Hello ')),
]) (Right ('World')) // ?
19 行
pipe ([
validate,
map (concat ('Hello ')),
]) (Right ('World')) // ?
Monad 有自己的 associativity:
(m >>= f) >>= g === m >>= (\x -> f x >>= g)
Monad 先使用chain依次與回傳 Monad 的 function 綁定,相當於 value 先經過 function 運算,最後再包進 Monad
Either 也是 Monad,因此適用 Monad 的 associativity。
但必須先將 world 包進 Either。
14 行
let validate = pipe ([
chain (chkEmpty),
chain (chkString)
])
使用 pipe 將所有經過 chain 處理過的 function 都組合。
可發現都是組合成
validate,但藉由 Monad 自己的 associativity 有了不同的組合方式
Conclusion
- 雖然可在 Function Piepline 中多次使用
chain將 Either 與回傳 Either 的 function 綁定,但可將多個回傳 Either 的 function 組合成單一 function - 可使用 function 最基本的 associativity 組合 function,由於 Either 也是 Monad,因此也可使用 Monad 獨特的 associativity 組合 function,唯 data 必須先包進 Either