由於 Promise 的 then() 具有 chain() 特性,實務上使用 Nested Promise 機會不大,大都可使用 Promise Chain 解決,若萬一使用 Nested Promise 時,該如何裡 Rejected Promise 呢 ?
Version
Ramda 0.27.1
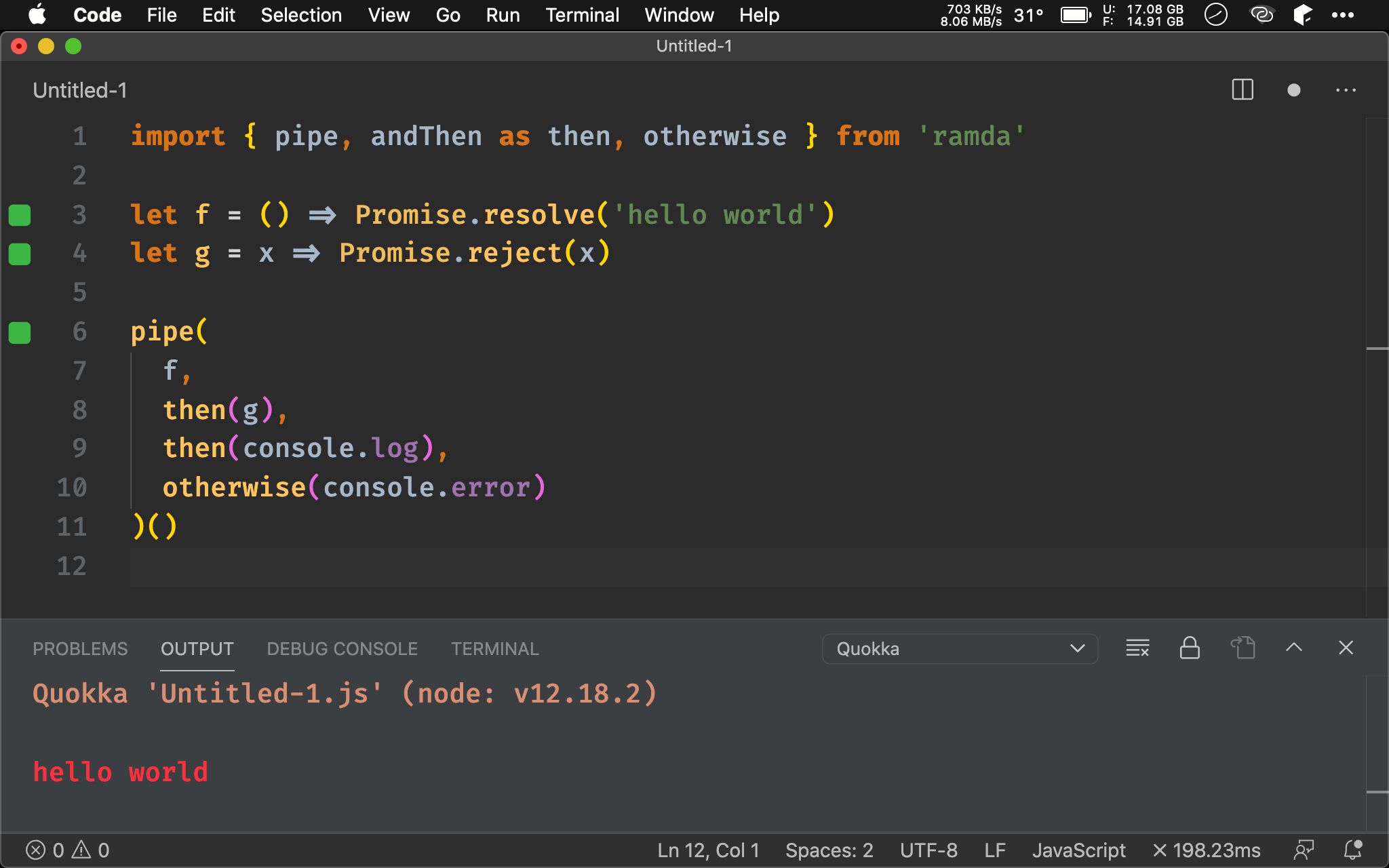
Promise Chain
import { pipe, andThen as then, otherwise } from 'ramda'
let f = () => Promise.resolve('hello world')
let g = x => Promise.reject(x)
pipe(
f,
then(g),
then(console.log),
otherwise(console.error)
)()
f() 回傳為 Fulfilled Promise,g() 根據傳入值回傳 Rejected Promise。
若要依序執行多個 asynchronous function,由於 Promise 的 then() 具有 chain() 特性,絕大部分應用都可使用單層 Promise Chain 完成,而不必使用 Nested Promise。
此時只要使用一個 otherwise() 就可處理 Rejected Promise。
Nested Promise
import { pipe, andThen as then, otherwise } from 'ramda'
let f = () => Promise.resolve('hello world')
let g = x => Promise.reject(x)
let h = pipe(
g,
then(console.log)
)
pipe(
f,
then(h),
otherwise(console.error)
)()
由於 Promise Chain 的值是一個 then() 一個 then() 往下傳,有時候在很後面的 then() 才會用到某一層 then() 的回傳值,此時 Nested Promise 會比 Promise Chain 方便。
第 6 行
let h = pipe(
g,
then(console.log)
)
使用 Nested Promise 時會再獨立抽出新 function,這時候會有疑問,這個新 function 是否要單獨處理 Rejected Promise,或者再將 Rejected Promise 拋出呢 ?
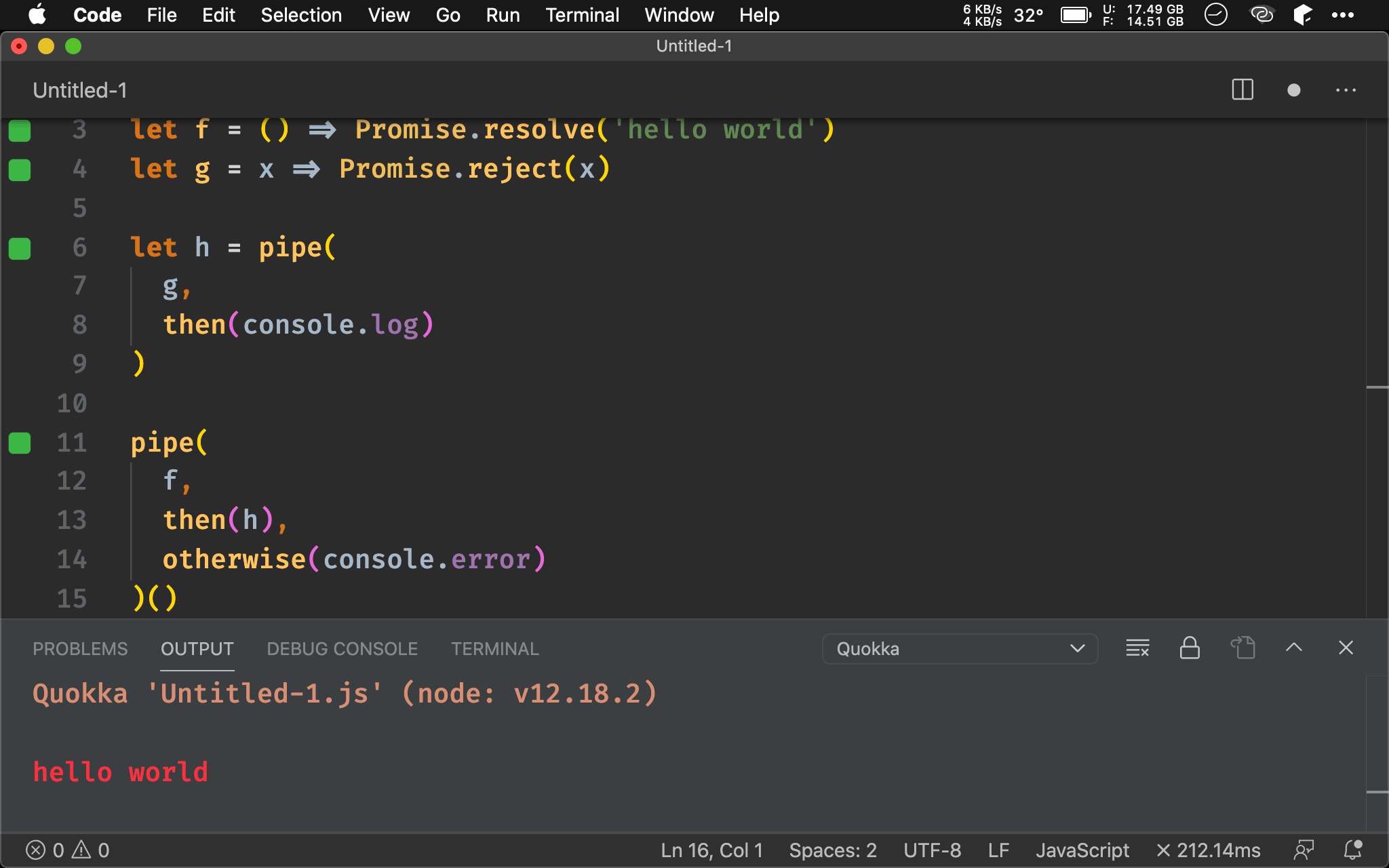
實際執行可發現,這類 Nested Promise 並不需要獨立處理 Rejected Promise 或者重新拋出 Rejected Promise,由於其產生的 Rejected Promise 也會由 then() 傳出,因此在最外層使用 otherwise() 統一處理即可。
Conclusion
- 由於
then()具有chain()特性,因此 Nested Promise 內不必特別處理 Rejected Promise,只要統一在最外層使用otherwise()處理即可