Promise 是 ECMAScript 2015 所提出的新型態,專門處理 Asynchronous,雖然也可 await 之後繼續以 Imperative 處理,但 Promise 本身具有 Functor 與 Monad 的一些特性,可搭配 Pure Function 繼續處理。
Version
Ramda 0.27.1
Functor
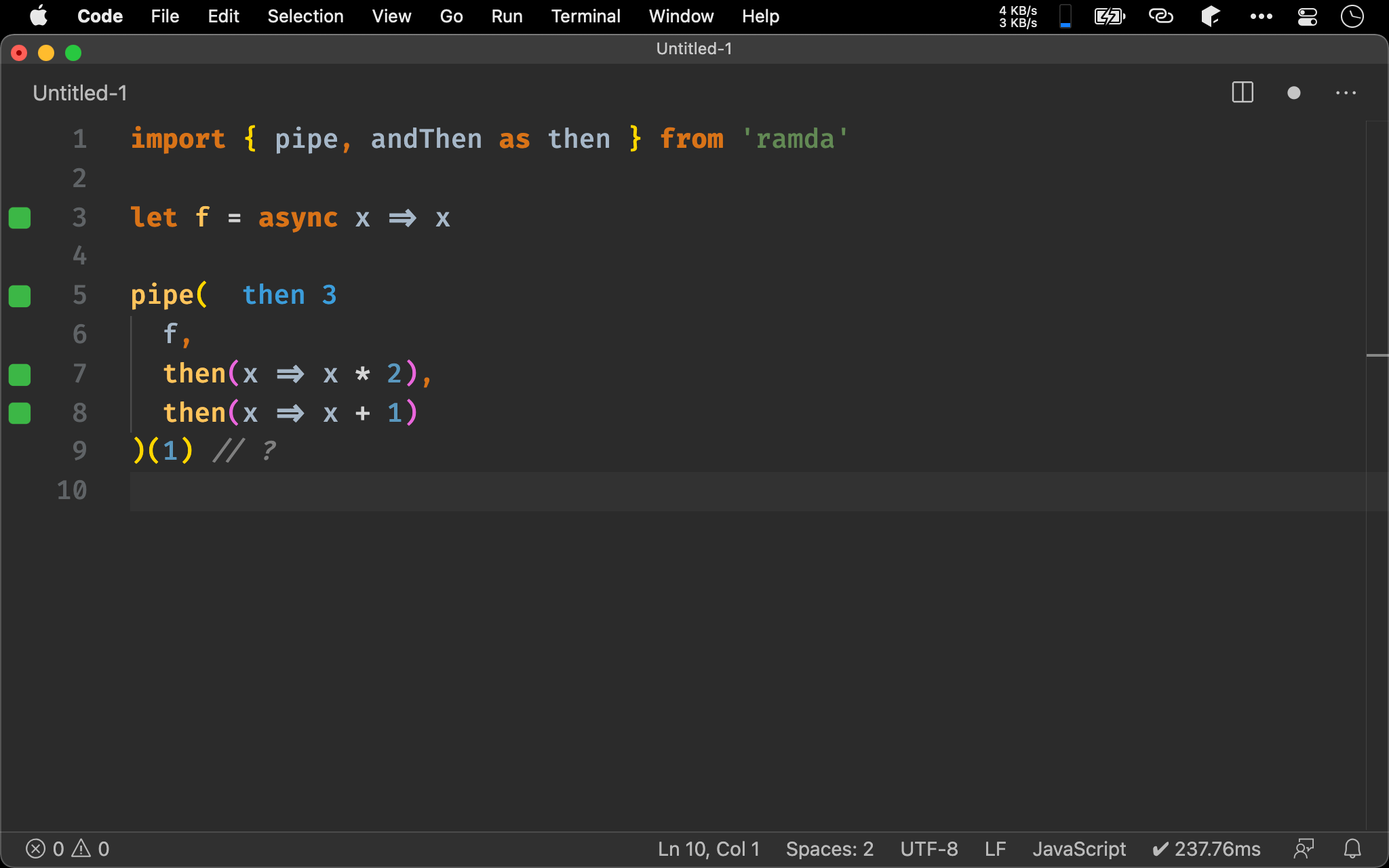
import { pipe, andThen as then } from 'ramda'
let f = async x => x
pipe(
f,
then(x => x * 2),
then(x => x + 1)
)(1) // ?
Promise 具有 Functor 特性,因此可將 then() 當 map() 用。
Monad
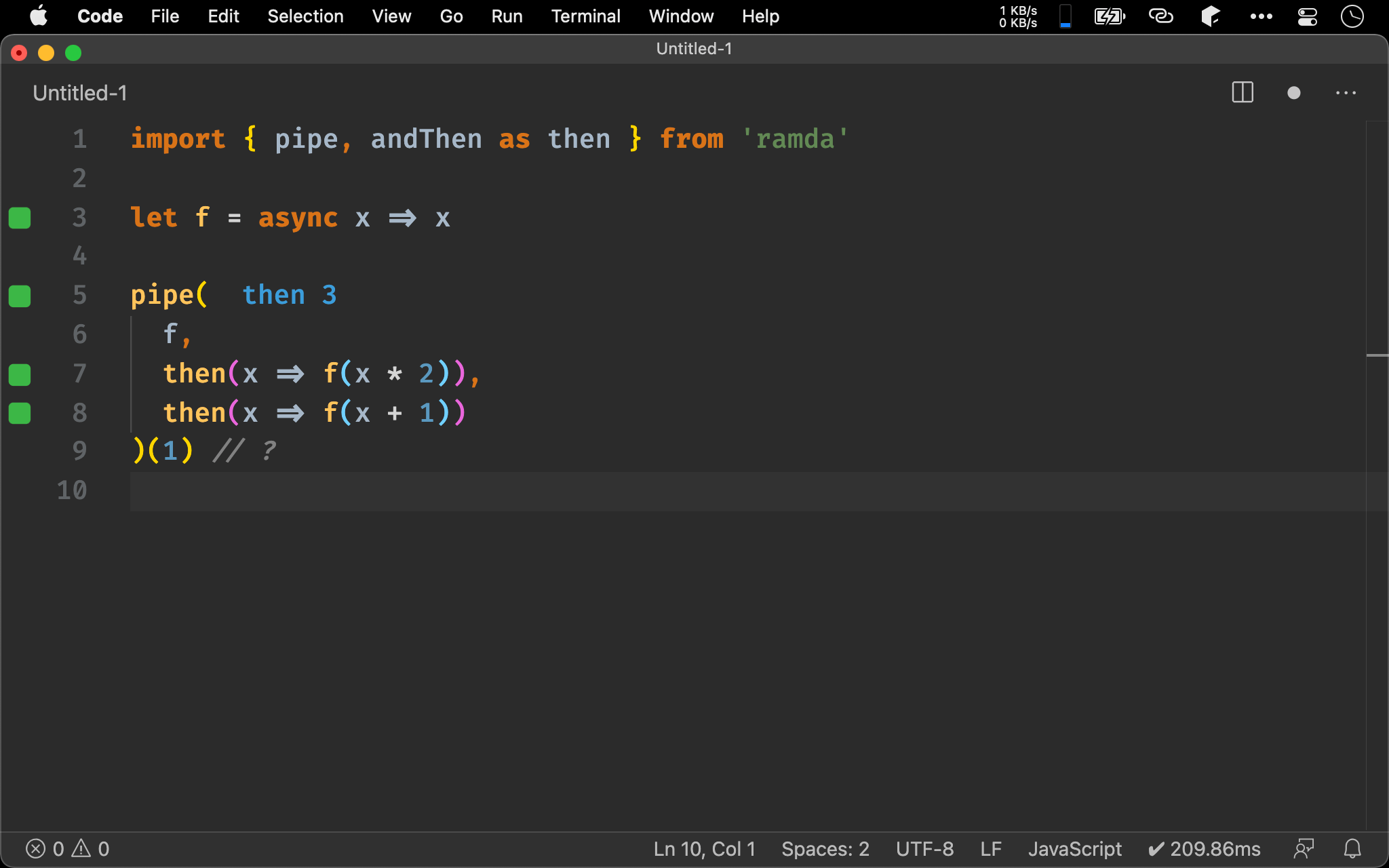
import { pipe, andThen as then } from 'ramda'
let f = async x => x
pipe(
f,
then(x => f(x * 2)),
then(x => f(x + 1))
)(1) // ?
Promise 也具有 Monad 特性,也可將 then() 當 chain() 用,儘管回傳 Promise,但最後也會 flatten() 成一層 Promise。
Composition Law
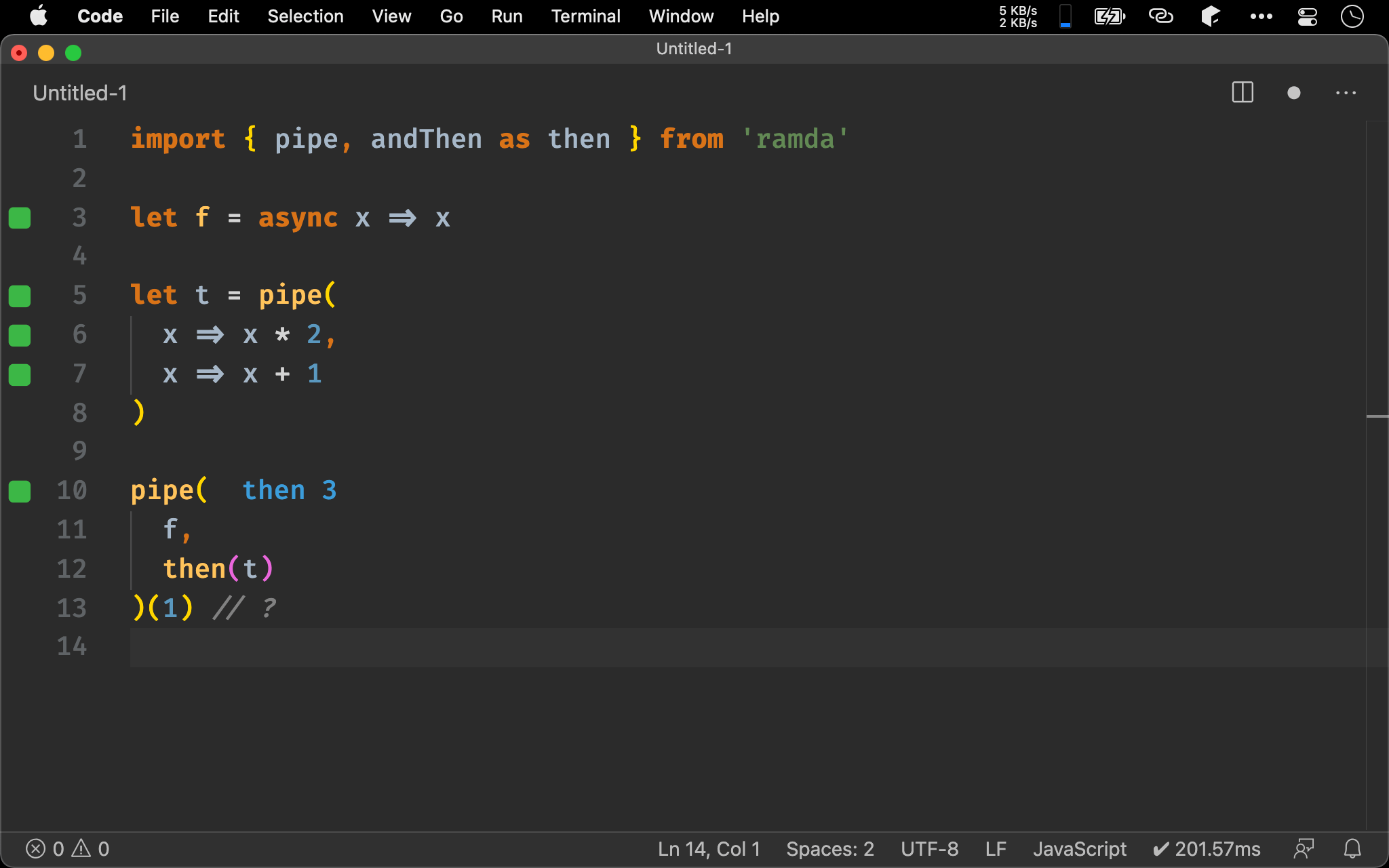
import { pipe, andThen as then } from 'ramda'
let f = async x => x
let t = pipe(
x => x * 2,
x => x + 1
)
pipe(
f,
then(t)
)(1) // ?
除了多次 then() 以外,Promise 也支援 composition law,可將 pure function 先組合起來,一次傳給 then() 執行。
Conclusion
- Promise 的
then()兼具map()與chain()特性,使得 Promise 看起來很像 Functor 又很像 Monad,但卻又不是 Functor 或 Promise - Promise 支援 composition law,因此可將
then()的 pure function 先組合起來,再一次傳給then()
Reference
Joel Thoms, Functional JavaScript - Functors, Monads, and Promises