ECMAScript 2015 的最大亮點之一就是提出 Promise 這種 未來值 概念避免 Callback Hell,但很多人卻很依賴 async await 將 Promise 立即轉為一般值處理,事實上可使用 Pure Function 在 Promise 內處理,並直接以 pipe() 組合 Pure Function。
Version
Ramda 0.27.1
Async Await
let f = () => Promise.resolve([
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 200 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 100 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
])
let result = (async () => {
try {
let result = await f()
return result
.map(x => x.price)
.filter(x => x >= 200)
.reduce((a, x) => a += x, 0)
} catch (e) {
console.error(e)
}
})() // ?
f() 回傳並非普通 Array,而是包在 Promise 中的 Array,很多人拿到 Promise 的第一件事情就是 await 成一般值處理,最後再加上 async() 轉成 Promise。
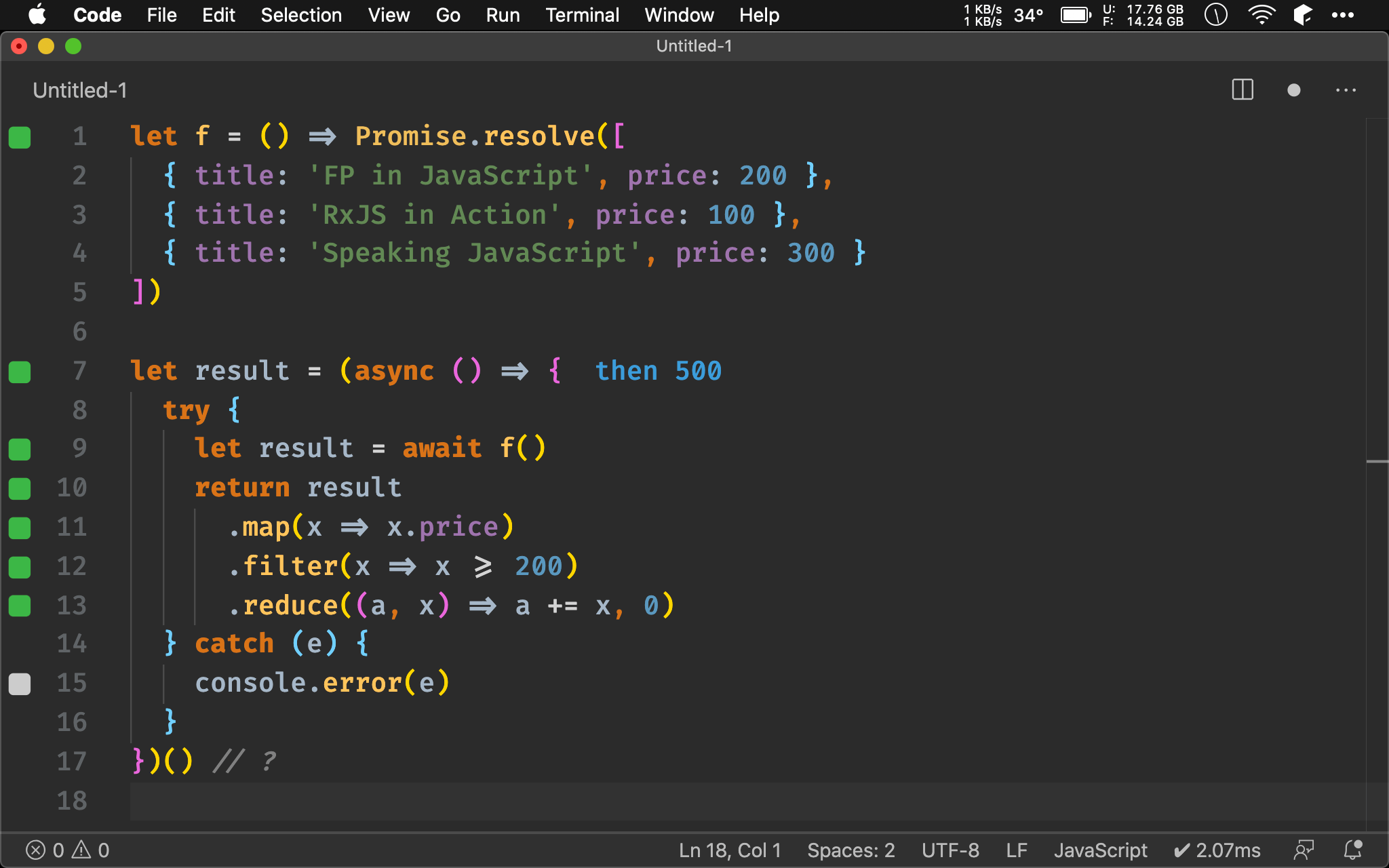
Method Chaining
let f = () => Promise.resolve([
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 200 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 100 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
])
f()
.then(x => x.map(x => x.price))
.then(x => x.filter(x => x >= 200))
.then(x => x.reduce((a, x) => a += x, 0))
.catch(console.error) // ?
既然最後還是 Promise,為什麼要急著使用 await 取得 Promise 內部資料,最後又用 async 轉成 Promise 呢 ?
其實可用 then() 取得 Promise 內部 Array,直接在 then() 內使用 pure function,也就是所有處理都在 Promise 內完成。
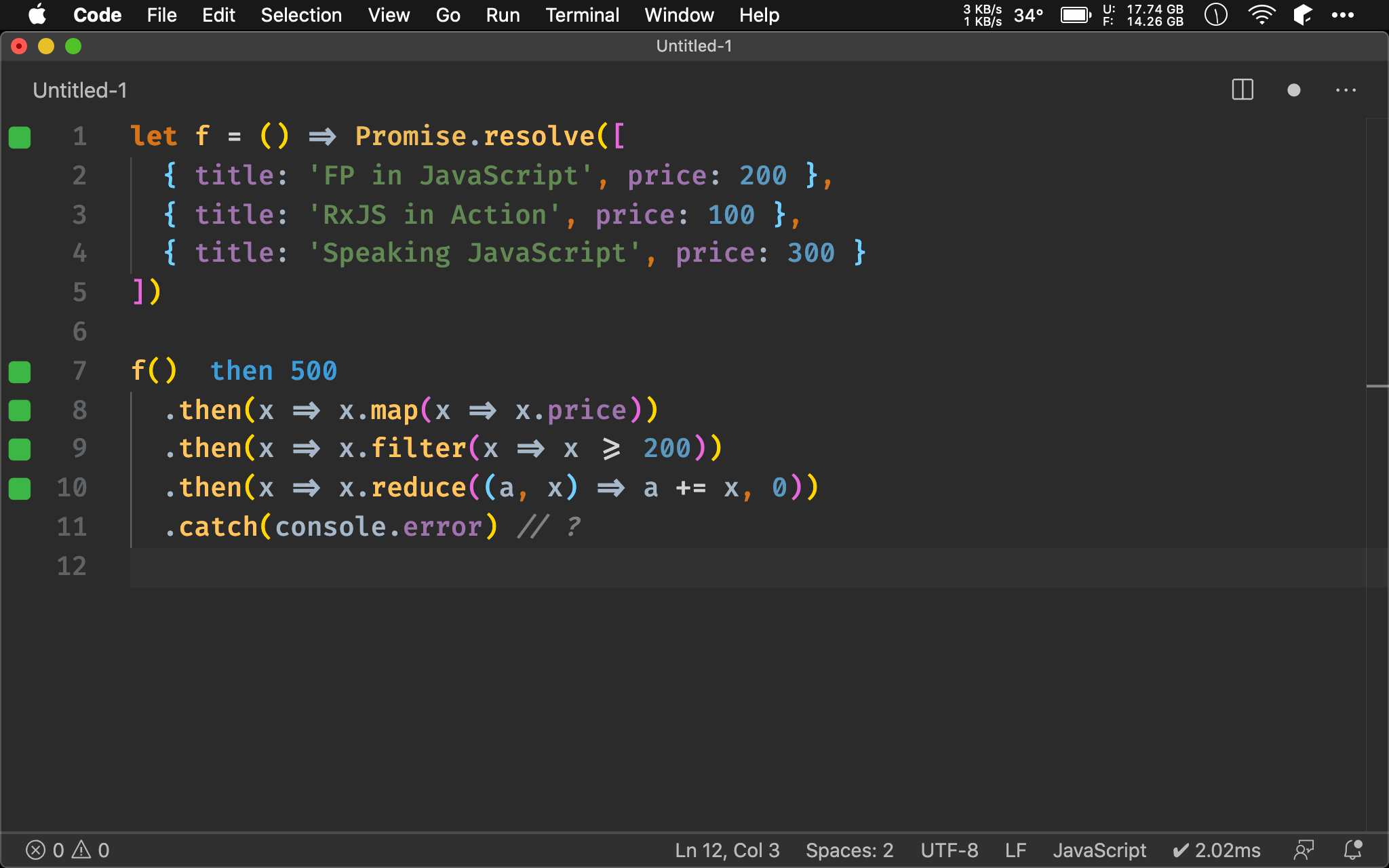
Function Pipeline
import { pipe, andThen as then, otherwise, map, filter, reduce } from 'ramda'
import { resolve } from 'wink-fp'
let f = () => resolve([
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 200 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 100 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
])
pipe(
f,
then(map(x => x.price)),
then(filter(x => x >= 200)),
then(reduce((a, x) => a += x, 0)),
otherwise(console.error)
)() // ?
若改用 Ramda 的 then() 與 otherwise(),則可將 Promise Chain 整合在 pipe() 當中以 Function Pipeline 完成。
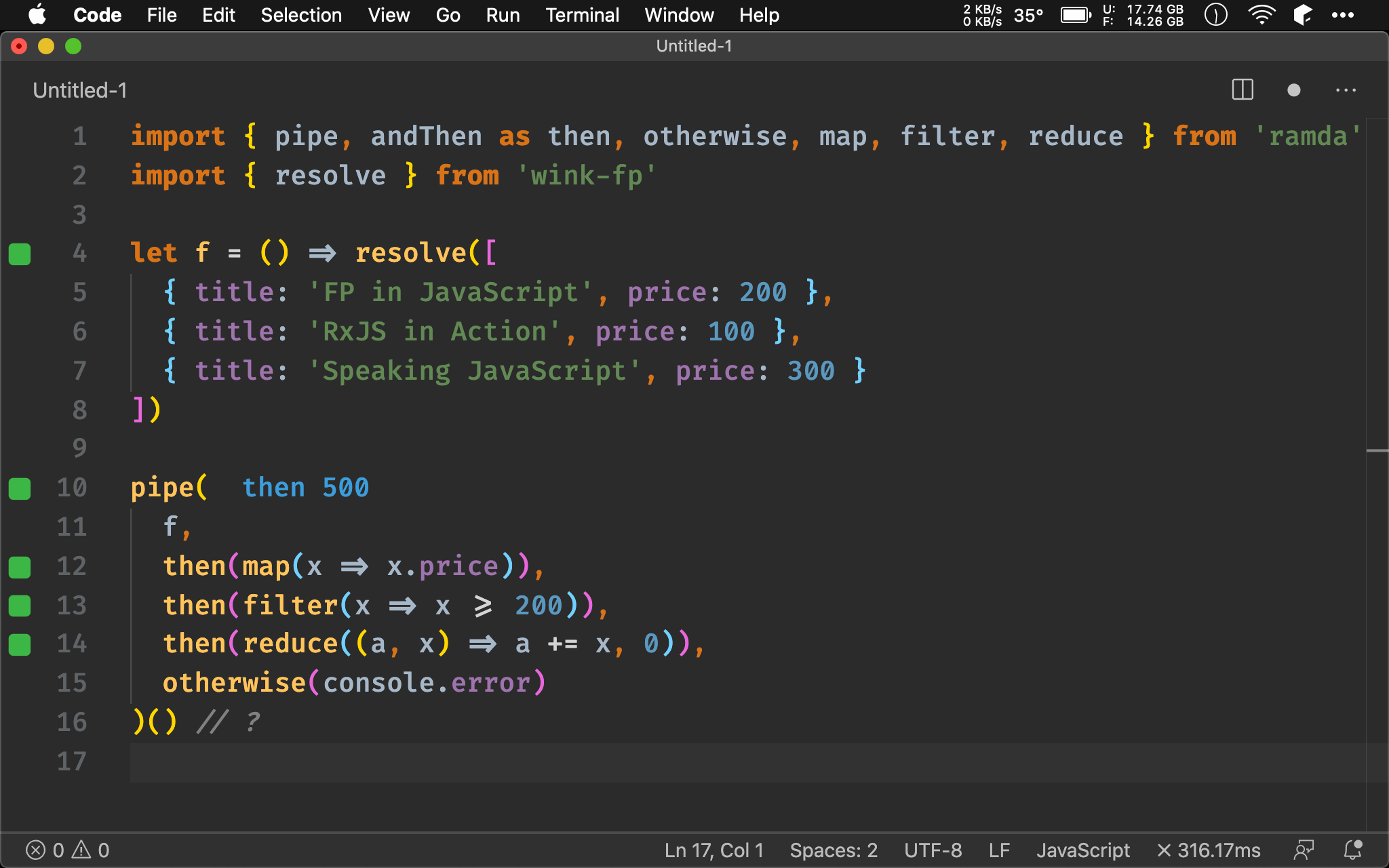
Composition Law
import { pipe, andThen as then, otherwise, map, filter, reduce } from 'ramda'
import { resolve } from 'wink-fp'
let f = () => resolve([
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 200 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 100 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
])
let t = pipe(
map(x => x.price),
filter(x => x >= 200),
reduce((a, x) => a += x, 0),
)
pipe(
f,
then(t),
otherwise(console.error)
)() // ?
Promise 是 Monad,也具有 Functor 特性,因此支援 composition law,其實可將 then() 的所有 pure function 先組合起來,最後一次傳給 then()。
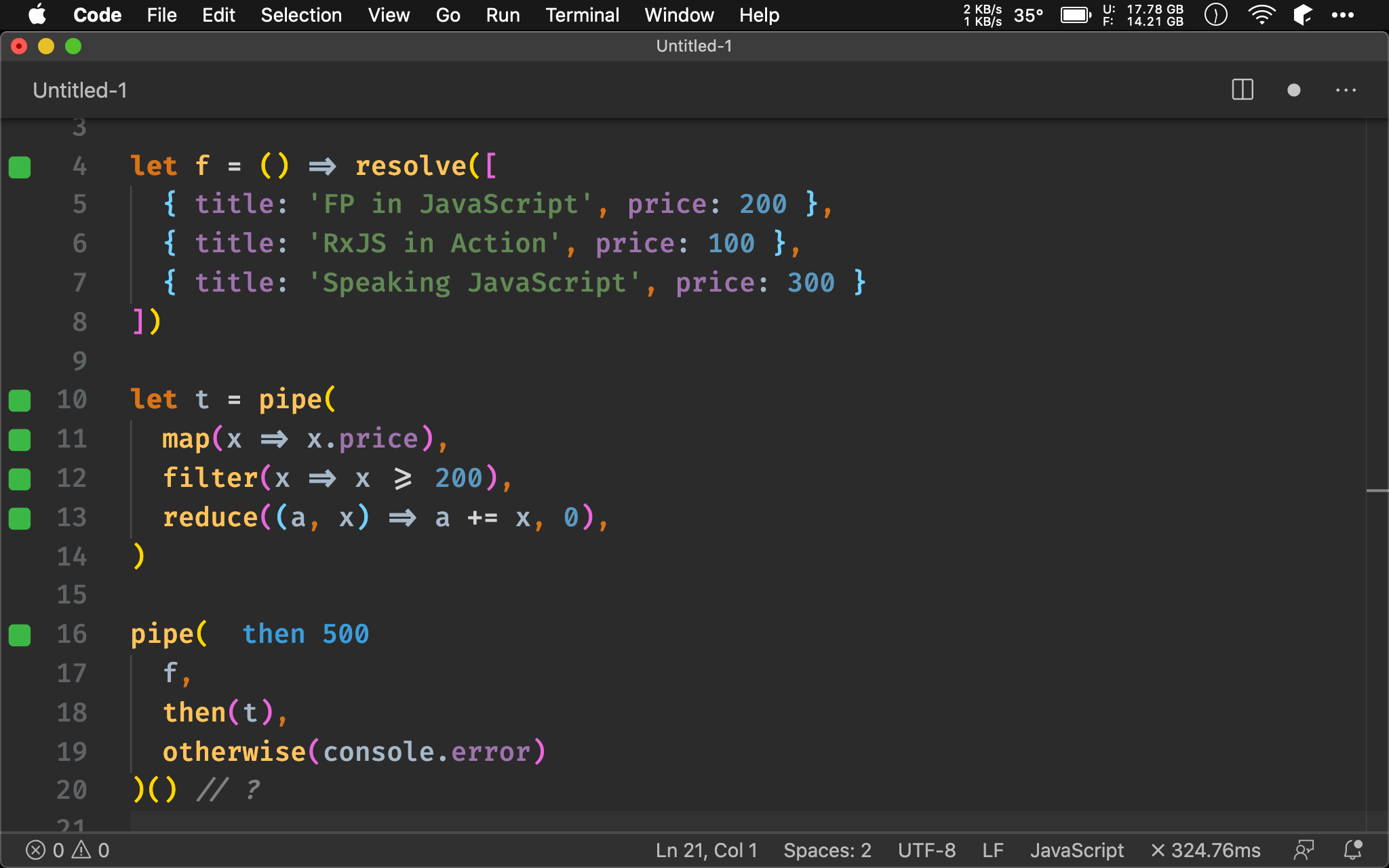
Point-free
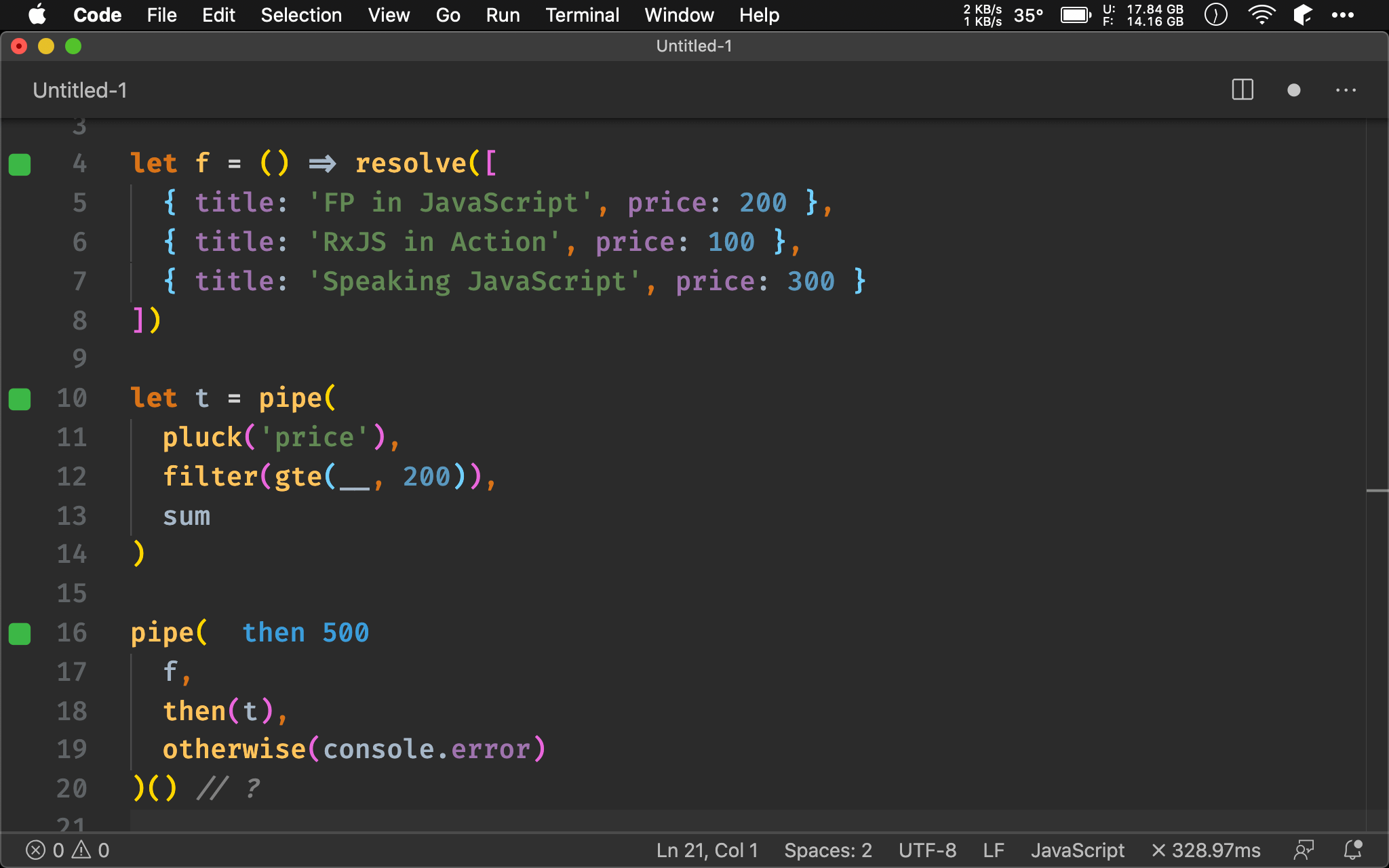
import { pipe, andThen as then, otherwise, pluck, filter, sum, gte, __ } from 'ramda'
import { resolve } from 'wink-fp'
let f = () => resolve([
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 200 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 100 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
])
let t = pipe(
pluck('price'),
filter(gte(__, 200)),
sum
)
pipe(
f,
then(t),
otherwise(console.error)
)() // ?
可進一步加以 Point-free。
Conclusion
- 拿到 Promise 後別先急著
await,透過 composition law 其實可讓你以原本 FP 組合 pure function 方式解結問題,最後再將 function 傳入then()即可 - Promise 只要使用
await之後,因為有了 variable 開第一槍,之後很容易以 Imperative 去處理,唯有直球對決避免使用await產生 variable,盡量以 pure function 解決問題,才能繼續使用 Function Pipeline 與 Point-free