Ramda 之 curry() 也是非常實用的 Function,他能將普通 Function 轉成 Curried Function,這在 FP 語言算是標準配備,但一直到目前為止,ECMAScript 都還沒有正式支援,而 Curried Function 對於寫出 Point-free Style 有很大貢獻。
Version
macOS Mojave 10.14.5
VS Code 1.36.1
Quokka 1.0.240
Ramda 0.26.1
Imperative
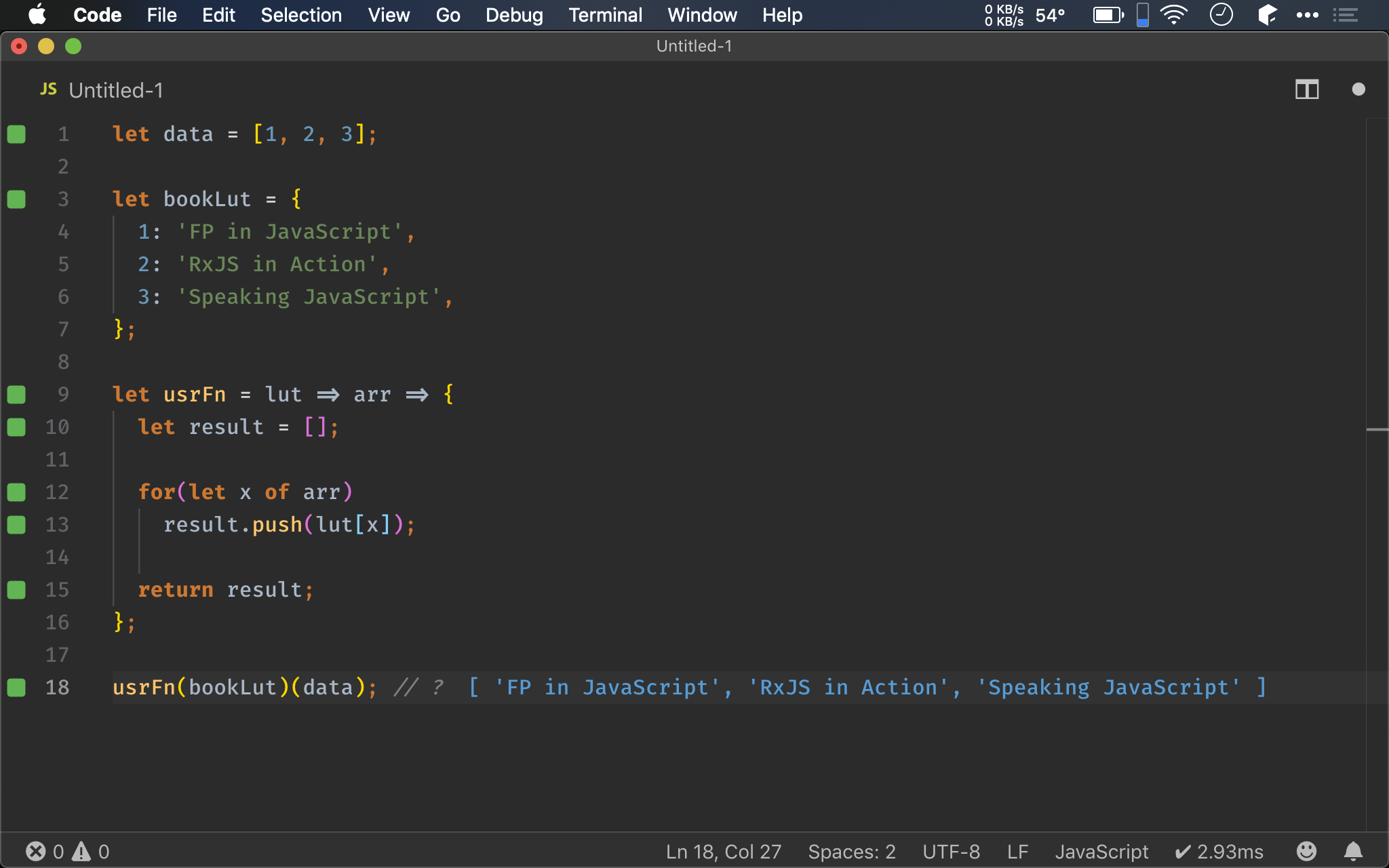
let data = [1, 2, 3];
let bookLut = {
1: 'FP in JavaScript',
2: 'RxJS in Action',
3: 'Speaking JavaScript',
};
let usrFn = lut => arr => {
let result = [];
for(let x of arr)
result.push(lut[x]);
return result;
};
usrFn(bookLut)(data); // ?
一個實務上常見的需求,由 API 所得到的資料只有 代碼,而我們需要根據 代碼 轉成 對應資料 顯示。
至於 代碼 與 顯示文字 的對照表,會存在 object 內。
Imperative 會使用 for loop,若在 object 比對到,則 push() 到新的 result array,最後回傳 result array。
Array.prototype.map()
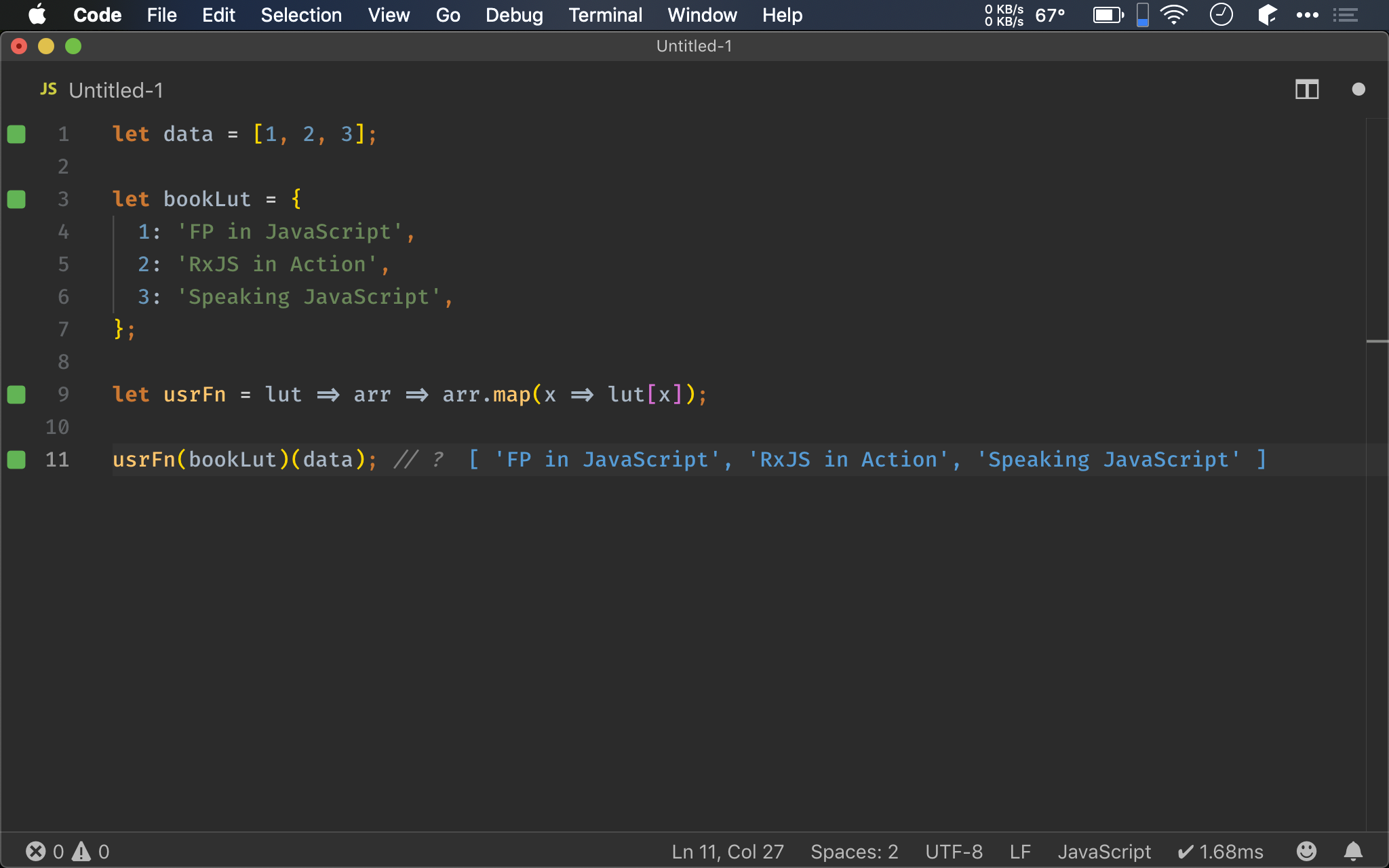
let data = [1, 2, 3];
let bookLut = {
1: 'FP in JavaScript',
2: 'RxJS in Action',
3: 'Speaking JavaScript',
};
let usrFn = lut => arr => arr.map(x => lut[x]);
usrFn(bookLut)(data); // ?
Array.prototype 有自帶 map(),所以我們也可以直接使用,再透過 bookLut[x] 加以對照轉換。
這種寫法已經比 imperative 精簡很多,但仍有兩個問題:
- 由於內建的
map()不是 curried function,因此usrFn()仍然要提供arrargument,無法如 point-free style 那樣精簡 map()的 map function 為一次性 function,無法重複使用
map()
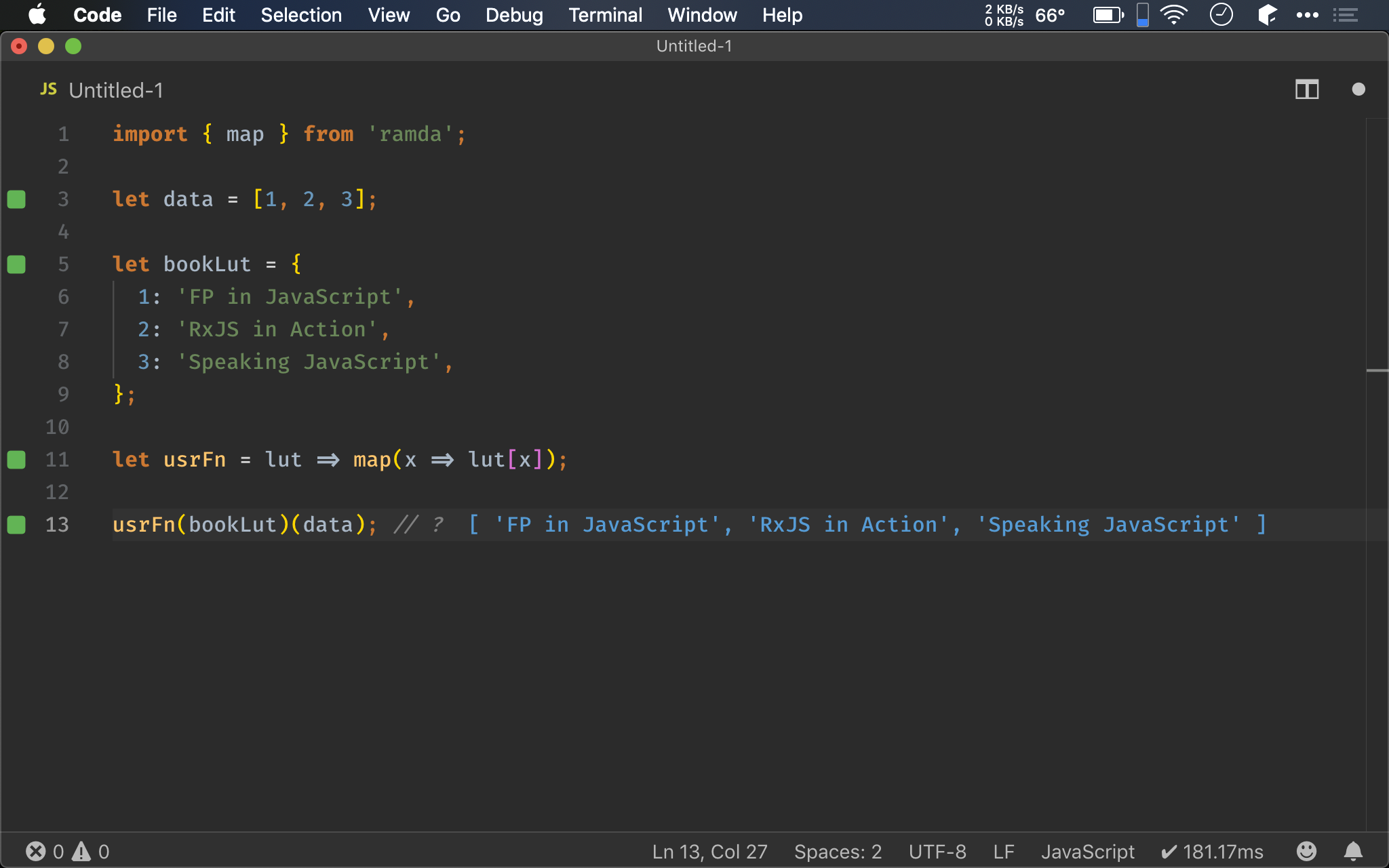
import { map } from 'ramda';
let data = [1, 2, 3];
let bookLut = {
1: 'FP in JavaScript',
2: 'RxJS in Action',
3: 'Speaking JavaScript',
};
let usrFn = lut => map(x => lut[x]);
usrFn(bookLut)(data); // ?
Ramda 亦提供 map(),與 Array.prototype 的 map() 不同在於:他是個 curried function,最後一個參數為 data,因此 usrFn() 可使用 point-free 寫法,如此將省下一個 argument,程式碼更精簡。
map()
(a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]
將 a array 轉換成 b array,且筆數不變
(a -> b) : map() 要轉換的 function
[a]:data 為 array
[b]:回傳為新的 array
由於最後一個參數為 data,使得 map() 可使用 Point-free。
import { map } from 'ramda';
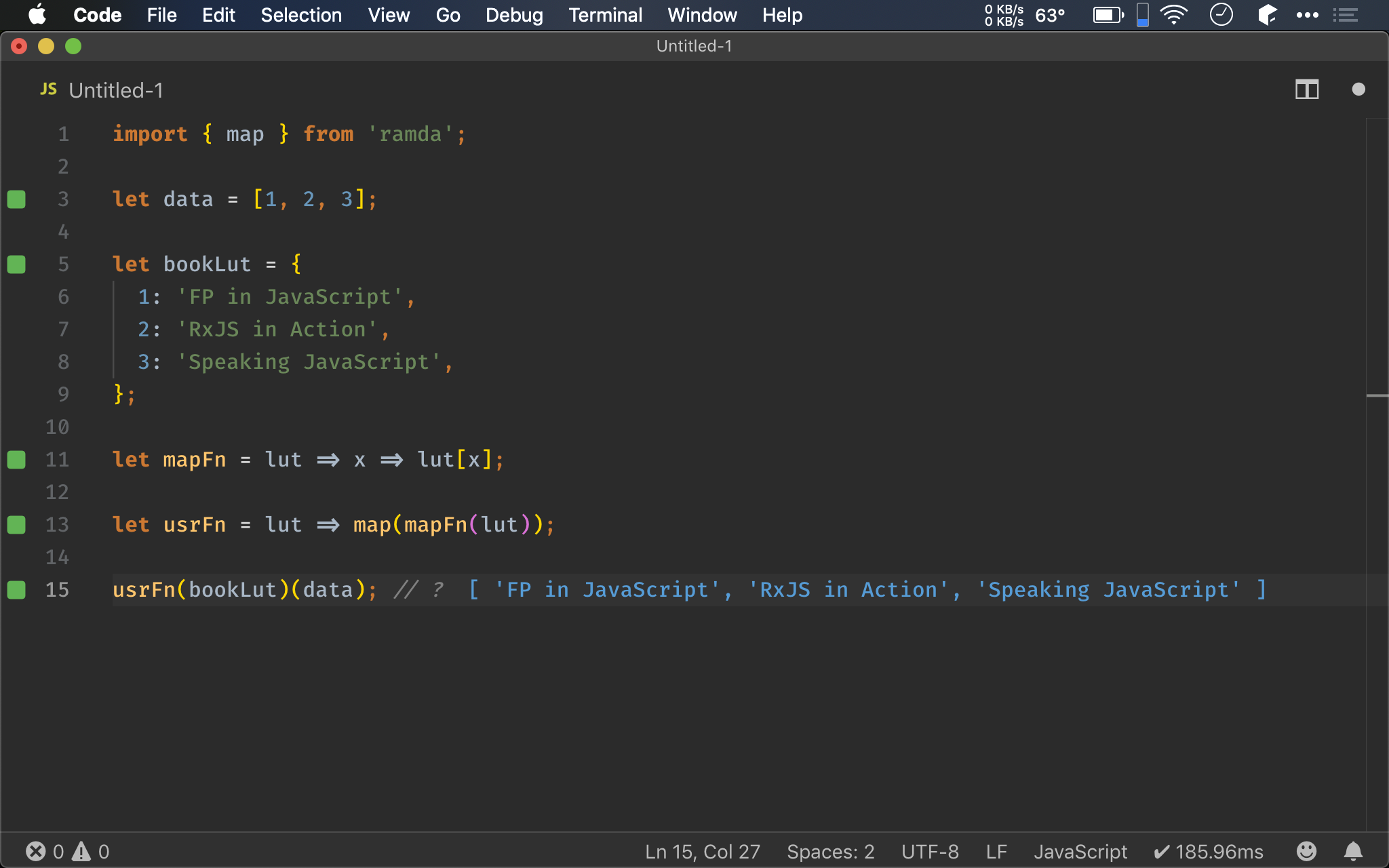
let data = [1, 2, 3];
let bookLut = {
1: 'FP in JavaScript',
2: 'RxJS in Action',
3: 'Speaking JavaScript',
};
let mapFn = lut => x => lut[x];
let usrFn = lut => map(mapFn(lut));
usrFn(bookLut)(data); // ?
不過之前寫法,map() 之後仍然是傳 arrow function,因此 重複使用 程度依然是 0。
我們試著將 arrow function 抽成 mapFn()。
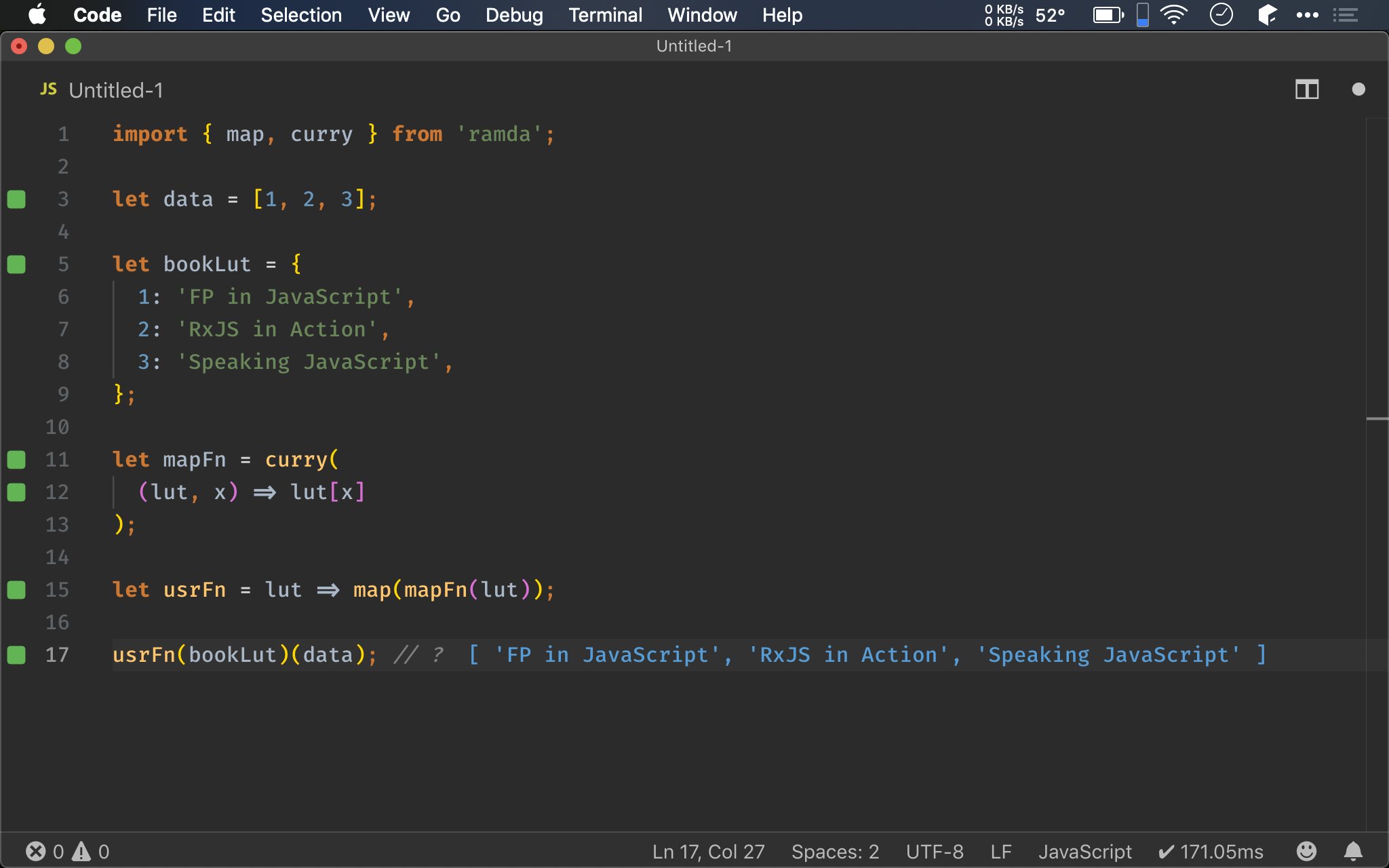
import { map, curry } from 'ramda';
let data = [1, 2, 3];
let bookLut = {
1: 'FP in JavaScript',
2: 'RxJS in Action',
3: 'Speaking JavaScript',
};
let mapFn = curry(
(lut, x) => lut[x]
);
let usrFn = lut => map(mapFn(lut));
usrFn(bookLut)(data); // ?
mapFn() 雖然能重複使用,也能使用 point-free 寫法,但有個致命傷:只是 curried function,也就是要使用 mapFn() 時,一定要 mapFn(bookLut)(1) 這種形式。
這種寫法配合 map() 時不是問題,但若要讓 mapFn() 單獨使用就不方便,也不符合一般使用 function 習慣。
比較好的方式是 mapFn() 提供兩種方式:可以 mapFn(bookLut, 1) 使用,亦可 mapFn(bookLut)(1) 使用,如此 mapFn() 實用程度就大大提高,既可以當成一般 function 使用,也可在 callback 做 point-free。
這時就要使用 Ramda 的 curry() function,能將一般 function 轉成 curried function,亦能維持一般 function 的 signature,成為兩用 function。
curry()
(* -> a) -> (* -> a)
將普通 function 轉成 curried function 與普通 function 兩用的 signature
Conclusion
curry()能將一般 function 轉換成 curried function,如此就不必為了 point-free 量身定做寫出 curried function- 由於
curry()過的 function 仍然可用一般 function 方式呼叫,既可當 callback,又可單獨使用,重複使用程度大大提升