對於可有可無資料,後端 API 可能回傳 Object,其 Property 不一定存在,但對於前端而言,我們想要的是 Array 方便 HTML template 做 v-for,本文由實際 API 回傳資料所改寫,接近實務上應用。
Version
Ramda 0.27.1
Function Pipeline
import { pipe, keys, filter, has, map } from 'ramda'
let lut = {
price: 'General Price',
price1: 'Shipping Price',
price2: 'Duty-free price'
}
let data = {
title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
prices: [
{
price1: 120,
price2: 80
}
]
}
let pickAllPrice = obj => ({
...obj,
...obj.prices[0]
})
let objToArr = lut => obj => pipe(
keys,
filter(x => has(x, obj)),
map(x => ({ title: lut[x], price: obj[x]}))
)(lut)
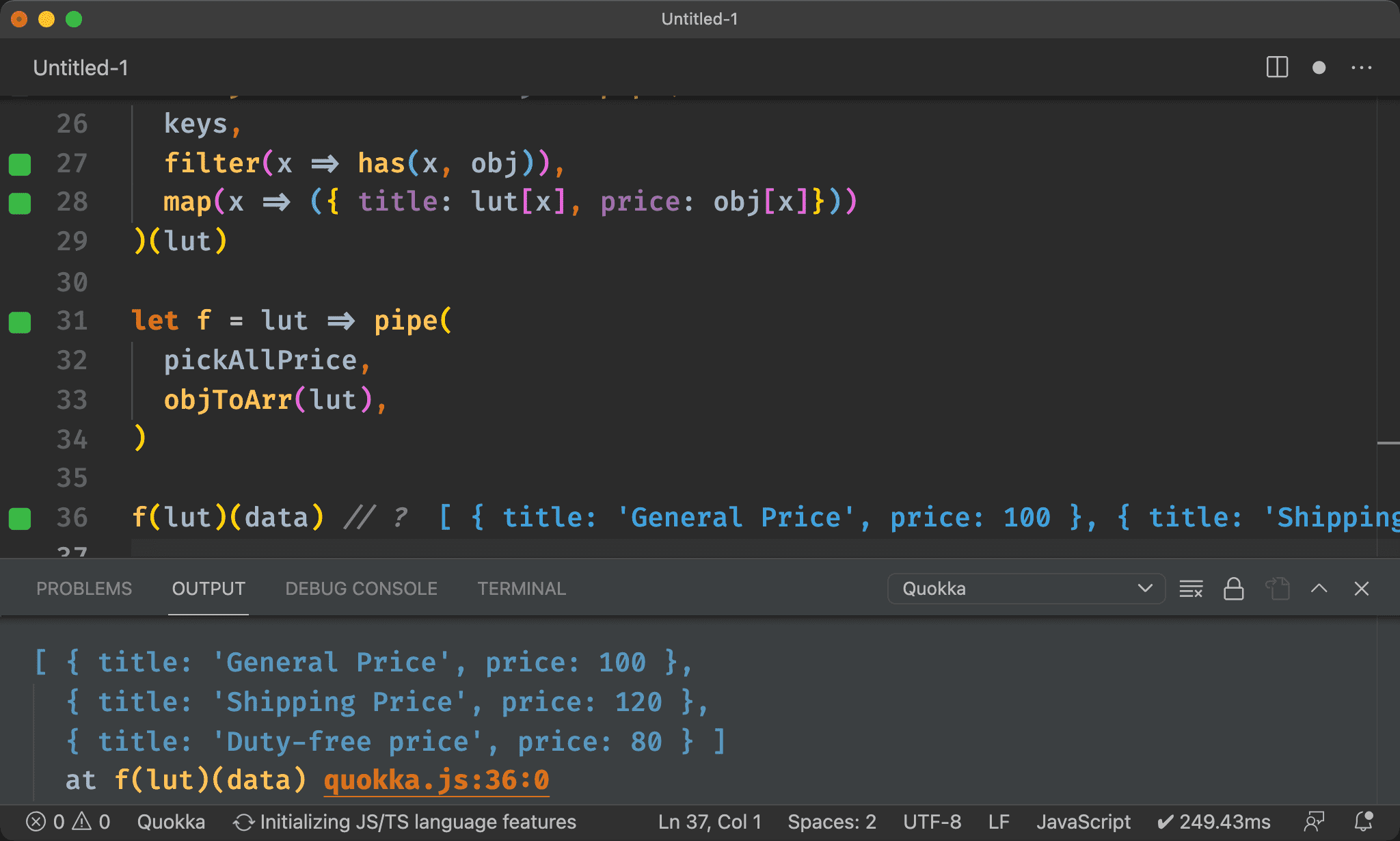
let f = lut => pipe(
pickAllPrice,
objToArr(lut),
)
f(lut)(data) // ?
第 9 行
let data = {
title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
prices: [
{
price1: 120,
price2: 80
}
]
};
實際 data 為 Object 不是 Array,注意其 price 並不規則,主要 price 在第一層,其餘在 prices 下。
第 3 行
let lut = {
price: 'General Price',
price1: 'Shipping Price',
price2: 'Duty-free price'
}
至於 price、price1 與 price2 所對應的意義則定義在 lut Object。
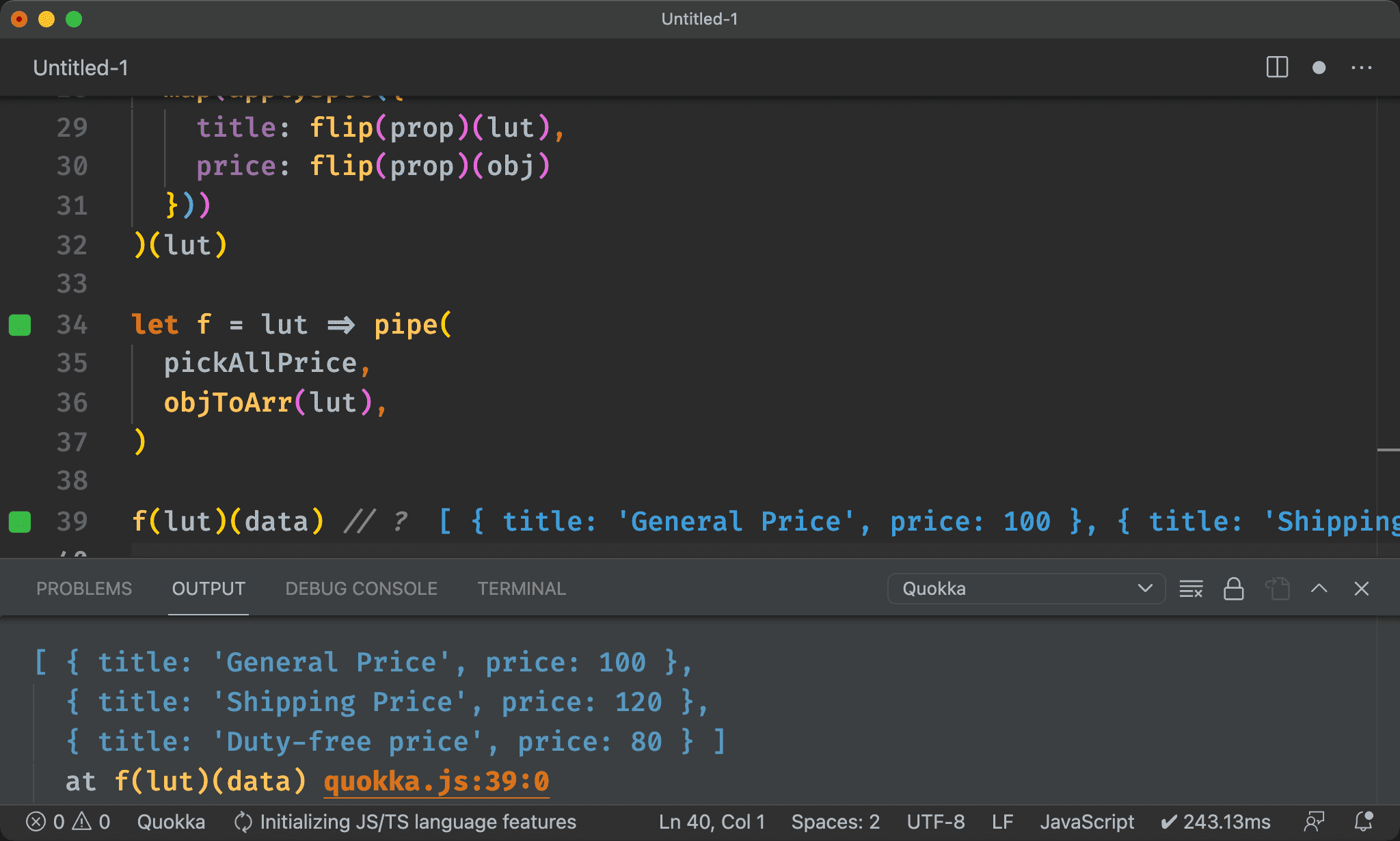
[ { title: 'General Price', price: 100 },
{ title: 'Shipping Price', price: 120 },
{ title: 'Duty-free price', price: 80 } ]
我們希望結果為 Object Array,且根據 lut 顯示對應的 title 與 price。
以 FP 角度思考:
- 先將不規則
price全部整理到 Object 第一層 property - 再將 Object 轉成我們要的 Array 格式
20 行
let pickAllPrice = obj => ({
...obj,
...obj.prices[0]
})
pickAllPrice() 將所有 prices 下的 property 全部整理到 Object 第一層。
25 行
let objToArr = lut => obj => pipe(
keys,
filter(x => has(x, obj)),
map(x => ({ title: lut[x], price: obj[x]}))
)(lut)
要將 Object 轉成 Array,使用 keys() 是關鍵。
但 prices 下的 property 個數並不確定,可能只有 price1 而沒有 price2,因此搭配 filter() 與 has(),只過濾出 prices 下實際有的 property。
最後使用 map() 整理出我們要的 Object Array。
31 行
let f = lut => pipe(
pickAllPrice,
objToArr(lut),
)
將問題各個擊破後,最後使用 pipe() 將所有 function 串起來。
Point-free
import { pipe, keys, filter, flip, has, map, applySpec, prop } from 'ramda'
let lut = {
price: 'General Price',
price1: 'Shipping Price',
price2: 'Duty-free price'
}
let data = {
title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
prices: [
{
price1: 120,
price2: 80
}
]
}
let pickAllPrice = obj => ({
...obj,
...obj.prices[0]
})
let objToArr = lut => obj => pipe(
keys,
filter(flip(has)(obj)),
map(applySpec({
title: flip(prop)(lut),
price: flip(prop)(obj)
}))
)(lut)
let f = lut => pipe(
pickAllPrice,
objToArr(lut),
)
f(lut)(data) // ?
27 行
filter(flip(has)(obj)),
別忘了 has() 的 currying 特性,可以 has() 直接產生 filter() 所需的 callback。
28 行
map(applySpec({
title: flip(prop)(lut),
price: flip(prop)(obj)
}))
map() 的 callback 也能再使用 applySpec() 使其 Point-free。
Conclusion
- FP 善於將問題最小化切割,然後各自擊破,最後再以 Function Pipeline 加以整合,而不是如 Imperative 一開始就思考如何整體解決問題
- Point-free 可視自身能力與程式碼可讀性取捨,不需強求