實務上常遇到 API 回傳兩層 Array,其中 Object 僅包含 Flag,前端必須根據 Flag 值決定要新增的 Property,這種常見的需求該如何實現呢 ?
Version
macOS Mojave 10.14.6
VS Code 1.38.0
Quokka 1.0.240
Ramda 0.26.1
Array.prototype.map()
let data = [
[
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', isShipable: 1 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', isShipable: 0 },
],
[
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', isShipable: 1 }
]
];
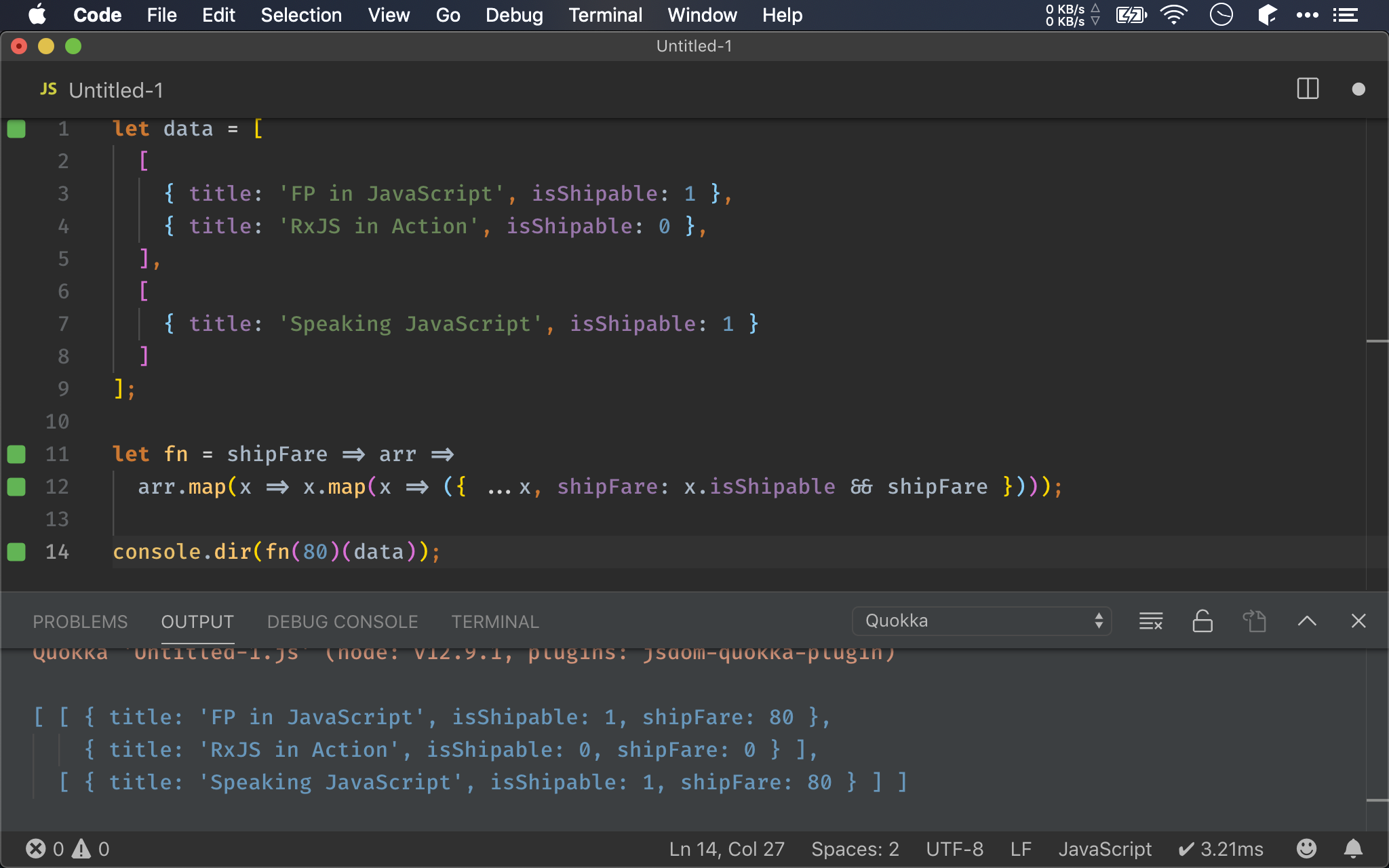
let fn = shipFare => arr =>
arr.map(x => x.map(x => ({ ...x, shipFare: x.isShipable && shipFare })));
console.dir(fn(80)(data));
一個很典型的需求,API 資料為兩層 array,其中只包含 isShipable property,表示是否可配送,至於運費則由 user 決定。
最後希望根據 isShipable property 結果動態新增 shipFare property,若為 1,則為 user 所指定的運費,若為 0,則運費亦為 0。
由於結果亦為兩層 array,因此不能使用 flatten()、unnets() 或 chain(),只能乖乖繼續使用兩層 map()。
Ramda
import { map } from 'ramda';
let data = [
[
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', isShipable: 1 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', isShipable: 0 },
],
[
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', isShipable: 1 }
]
];
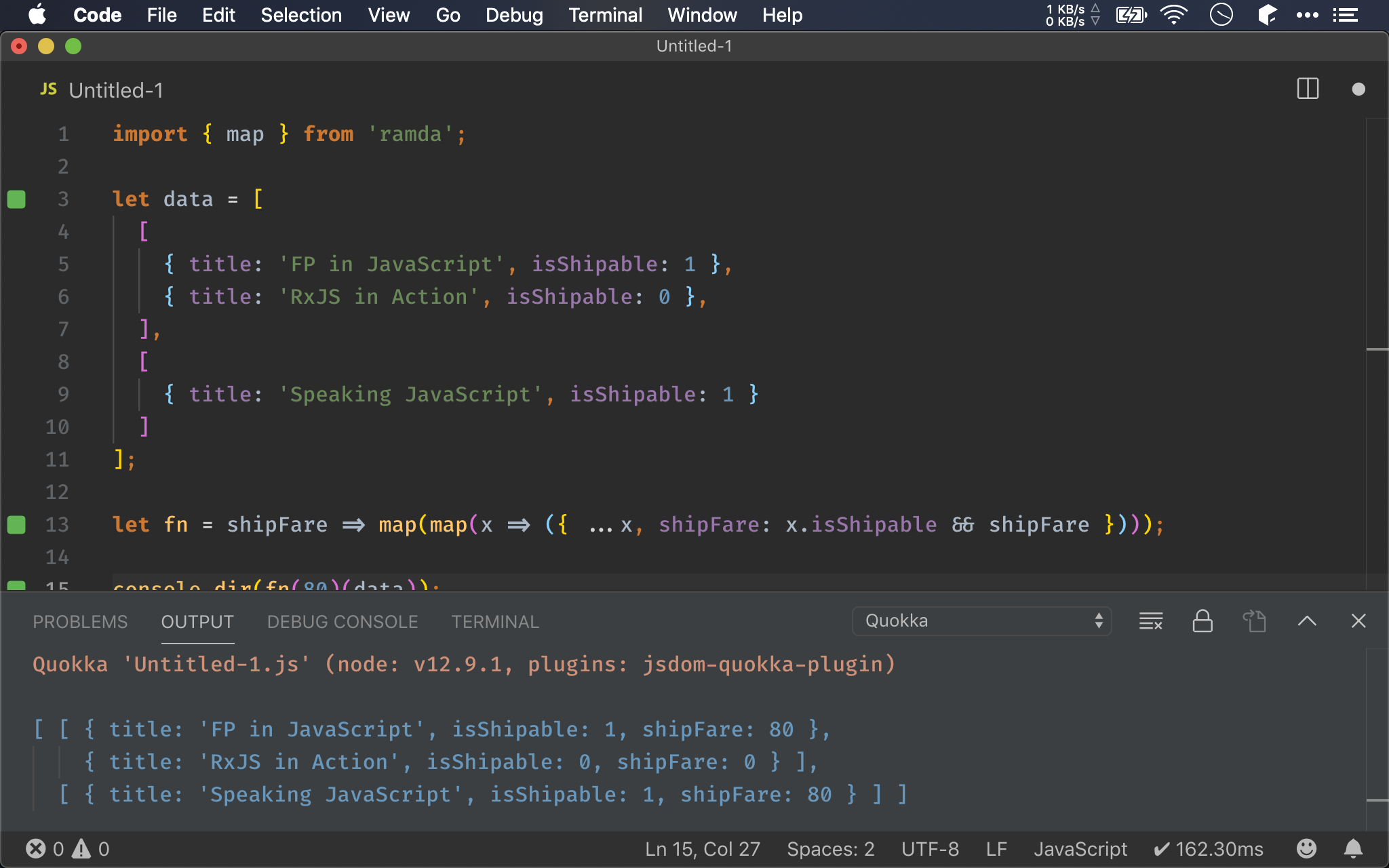
let fn = shipFare => map(map(x => ({ ...x, shipFare: x.isShipable && shipFare })));
console.dir(fn(80)(data));
Ramda 亦提供 map(),將 data 放在最後一個參數,因此改用 map() 後就將 data 給 point-free 了。
assoc()
import { map, chain, assoc, ifElse, prop, always } from 'ramda';
let data = [
[
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', isShipable: 1 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', isShipable: 0 },
],
[
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', isShipable: 1 }
]
];
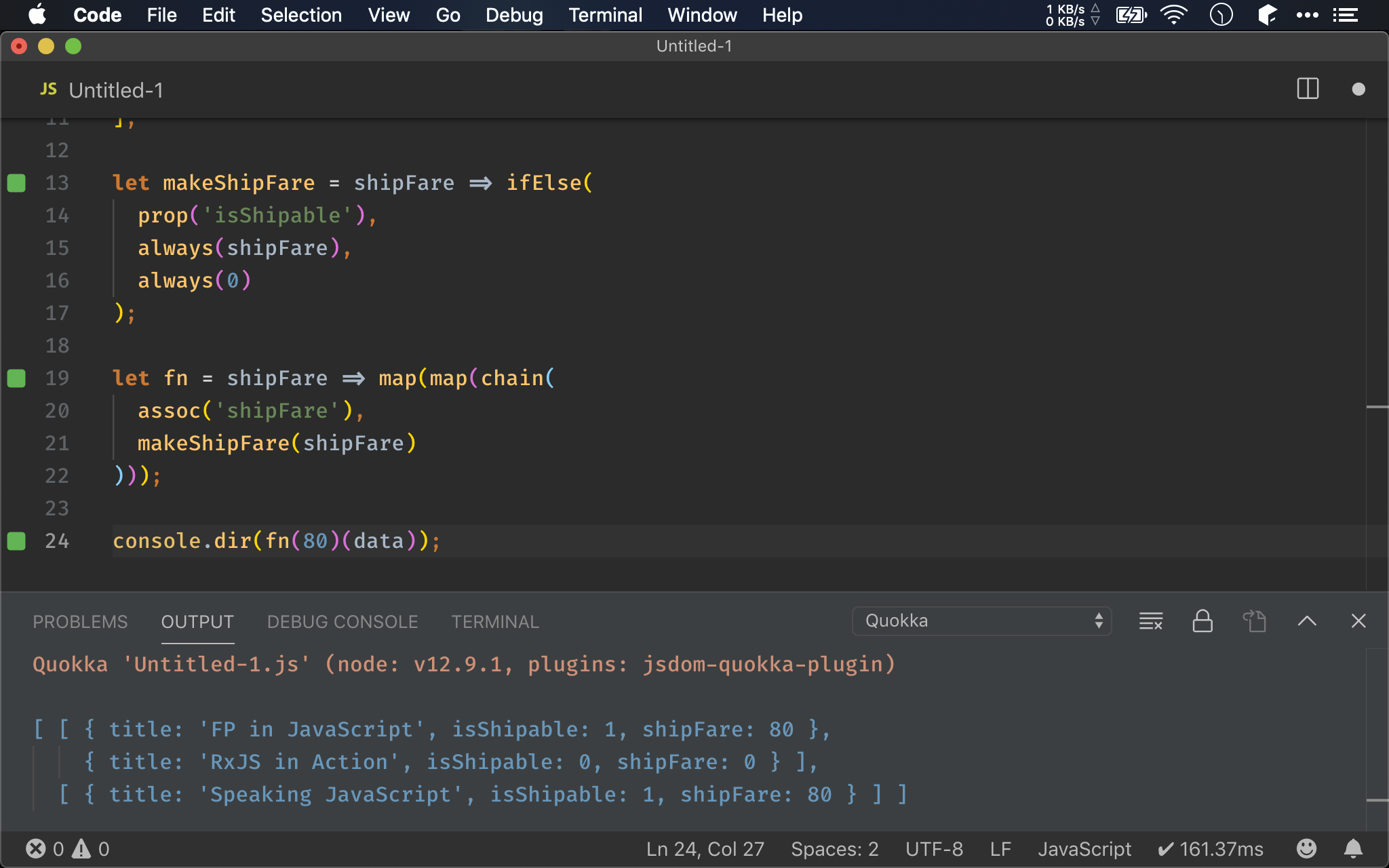
let makeShipFare = shipFare => ifElse(
prop('isShipable'),
always(shipFare),
always(0)
);
let fn = shipFare => map(map(chain(
assoc('shipFare'),
makeShipFare(shipFare)
)));
console.dir(fn(80)(data));
除了原本的 fn() 外,還另外抽出 makeShipFare()。
19 行
let fn = shipFare => map(map(chain(
assoc('shipFare'),
makeShipFare(shipFare)
)));
map() 的 projection function 可進一步 point-free。
在 array 內新增 property ,且保留原有的 property,在 Ramda 有固定 pattern 可用,就是 chain(assoc())。
assoc()
String -> a -> {k: v} -> {k: v}
複製原本 object 的 property 外,還可新增 property
let makeShipFare = shipFare => ifElse(
prop('isShipable'),
always(shipFare),
always(0)
);
根據 isShipable 決定 shipFare 部分,則獨立拉出 makeShipFare()。
?: 可使用 Ramda 的 ifElse(),由於 prop() 最後一個參數為 Object,因此 makeShipFare() 對於 object 是 point-free。
ifElse() 要求三個 argument 都是 function,因此要使用 always() 將 value 轉成 function。
Point-free
import { map, chain, assoc, ifElse, prop, always, pipe, __ } from 'ramda';
let data = [
[
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', isShipable: 1 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', isShipable: 0 },
],
[
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', isShipable: 1 }
]
];
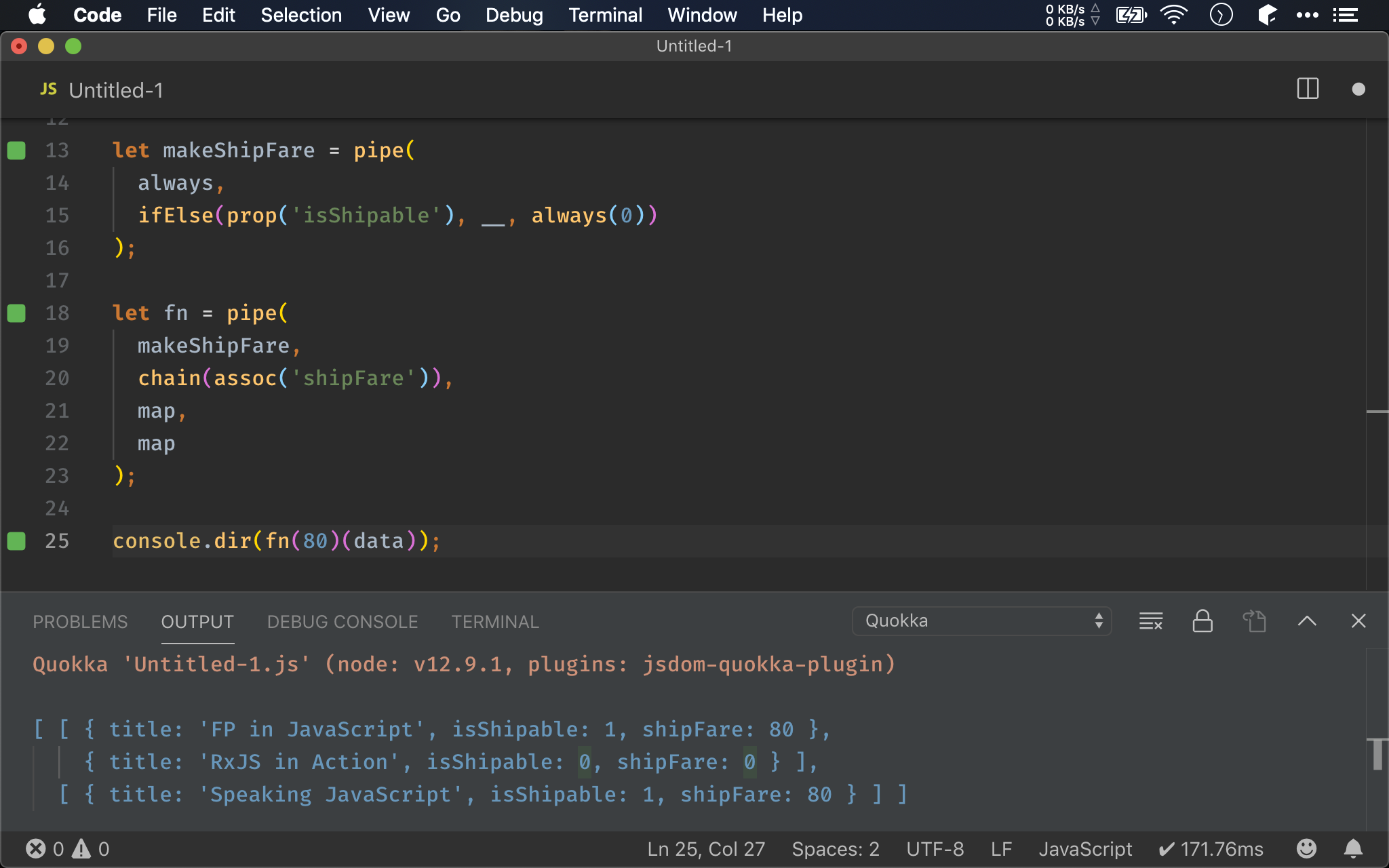
let makeShipFare = pipe(
always,
ifElse(prop('isShipable'), __, always(0))
);
let fn = pipe(
makeShipFare,
chain(assoc('shipFare')),
map,
map
);
console.dir(fn(80)(data));
目前 makeShipFare() 與 getBooks() 唯一的遺憾是仍帶有 shipFare 參數,還能進一步 point-free 嗎 ?
13 行
let makeShipFare = pipe(
always,
ifElse(prop('isShipable'), __, always(0))
);
為了讓 makeShipFare() 能 point-free,將原本 always(shipFare) 拆成 always() 與 __,讓 pipe() 先接 always(),則將 shipFare 給 point-free。
思維可想成
always()缺一個參數,因此makeShipFare()要傳入shipFare,然後再傳給ifElse()的__,最後產生新的 function
18 行
let fn = pipe(
makeShipFare,
chain(assoc('shipFare')),
map,
map
);
從原本的雙層 map(),我們發現其本質是先執行 makeShipFare(),然後再執行 chain(assoc('shipFare')),最後再執行兩個 map(),將這個流程以 pipe() 組合,由於 makeShipFare 原本就缺最後一個參數,因此就順理成章將 shipFare 給 point-free 了。
從內層往外層拆是 point-free 起手式,最後再以
pipe()串起來
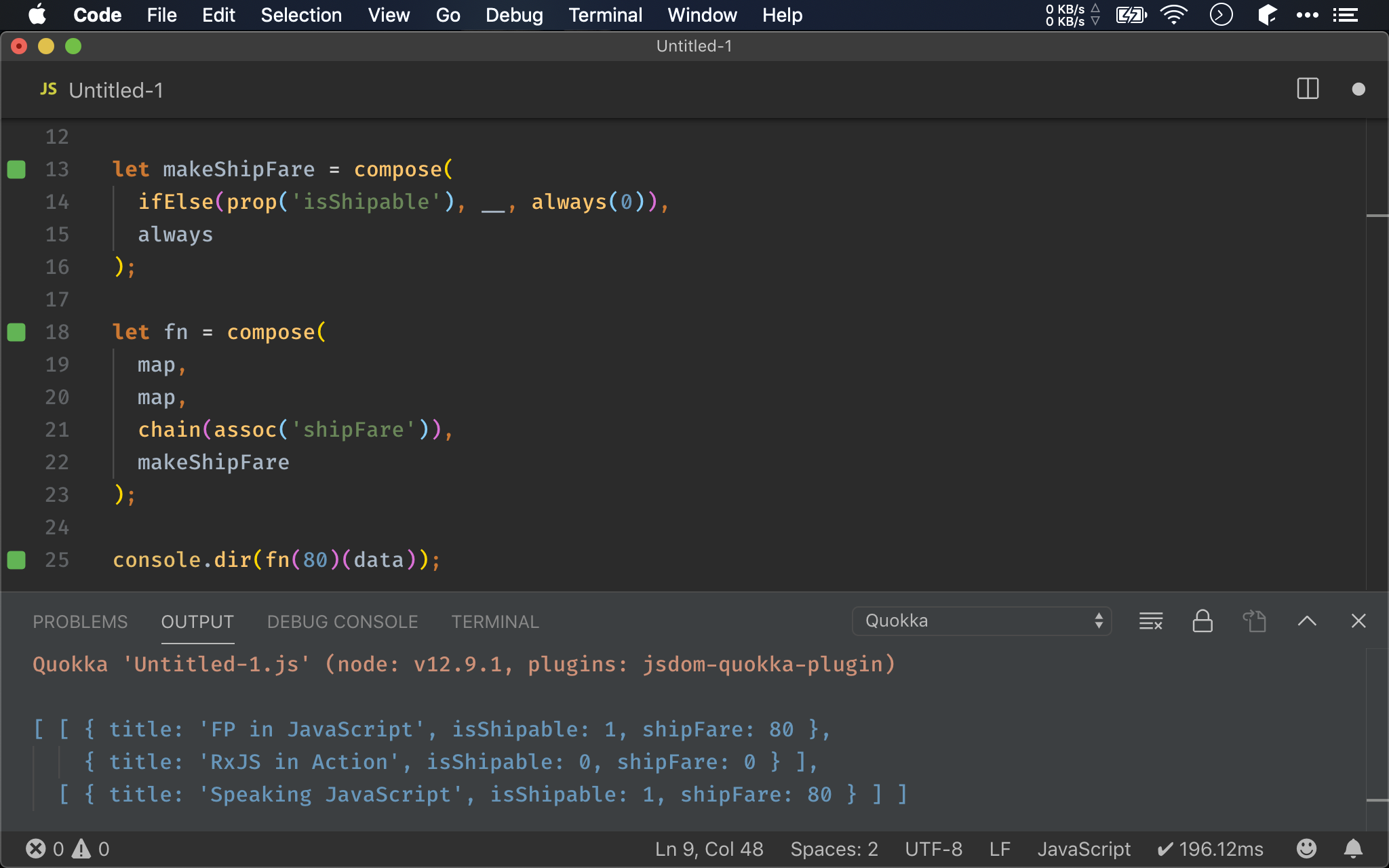
compose()
import { map, chain, assoc, ifElse, prop, always, compose, __ } from 'ramda';
let data = [
[
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', isShipable: 1 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', isShipable: 0 },
],
[
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', isShipable: 1 }
]
];
let makeShipFare = compose(
ifElse(prop('isShipable'), __, always(0)),
always
);
let fn = compose(
map,
map,
chain(assoc('shipFare')),
makeShipFare
);
console.dir(fn(80)(data));
從另外一個角度思考,既然之前都可以使用 pipe() 將所有 function 以 pipeline 執行,也就是這些 function 都能透過 compose() 組合出新 function。
Conclusion
- 兩層 array 都可以更簡單的方式處理,但若結果依然是兩層 array,那只能使用兩次
map() - 在 Point-free 時,只要能看清楚程式執行流程的本質,從內層往外層拆開,就能變成 point-free
chain()搭配assoc()為常見的 pattern,專門用來為 object 新增 property- 當發現一個 function 很難 point-free 時,很可能是該 function 有太多功能,掌握 FP 心法:
將問題最小化、然後各自擊破,先將 function 拆小,然後再各自 point-free - 既然所有 function 都能 point-free,則表示這些 function 能組合出新的 function
Reference
Ramda, map()
Ramda, chain()
Ramda, assoc()
Ramda, always()
Ramda, ifElse()
Ramda, prop()
Ramda, pipe()
Ramda, compose()