若第一個 Function 結果為 Truthy Value 則回傳第一個 Function,否則回傳第二個 Function,在 FP 稱為 OR Combinator,可使用 Ramda 的 either() 實現。
Version
macOS Catalina 10.15.6
Ramda 0.27.1
Imperative
let f = n => {
if (n > 10 || !(n % 2)) return true
else return false
}
f(8) // ?
f(20) // ?
f(7) // ?
若要判斷 大於 10 且為 偶數,ECMAScript 可使用 if 一一判斷並搭配 ||。
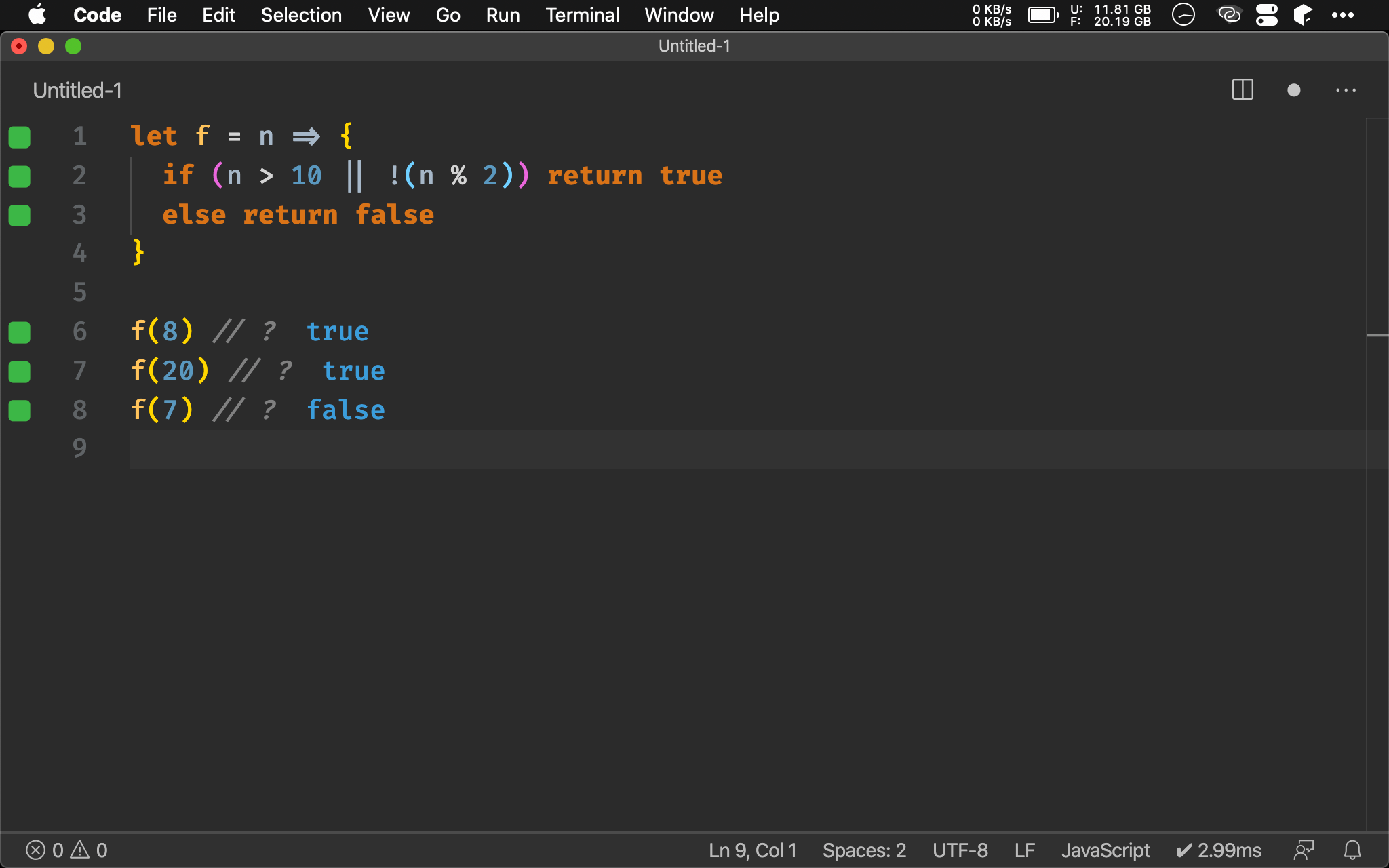
Extract Function
let isGt10 = n => n > 10
let isEven = n => !(n % 2)
let f = n => isGt10(n) || isEven(n)
f(8) // ?
f(20) // ?
f(7) // ?
也可將判斷 expression 抽成 isGt10() 與 isEven(),再搭配 || 判斷。
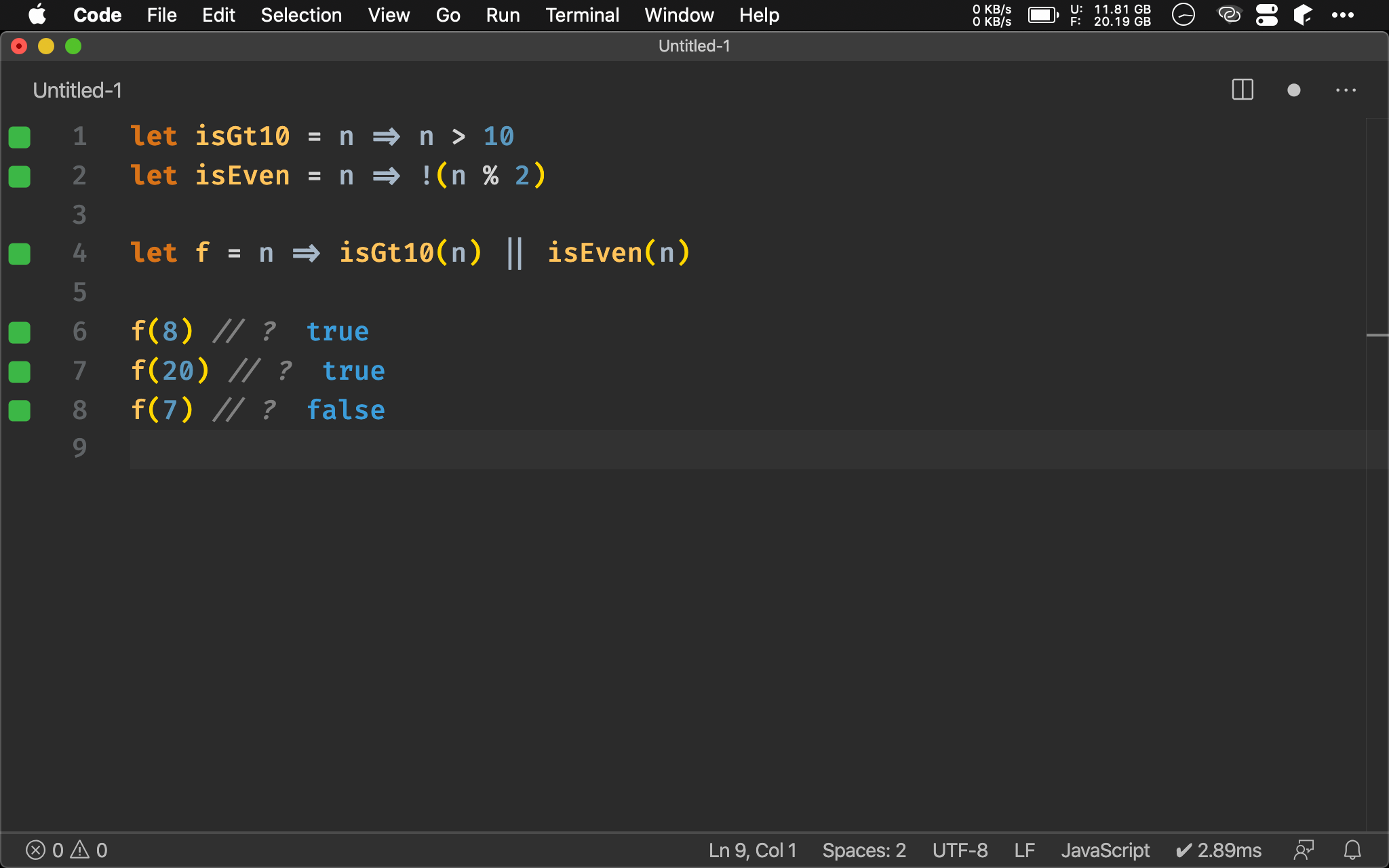
either()
let isGt10 = n => n > 10
let isEven = n => !(n % 2)
let either = f1 => f2 => n => f1(n) || f2(n)
let f = either(isGt10)(isEven)
f(8) // ?
f(20) // ?
f(7) // ?
可自行以 || 實作 either() 回傳適當 function。
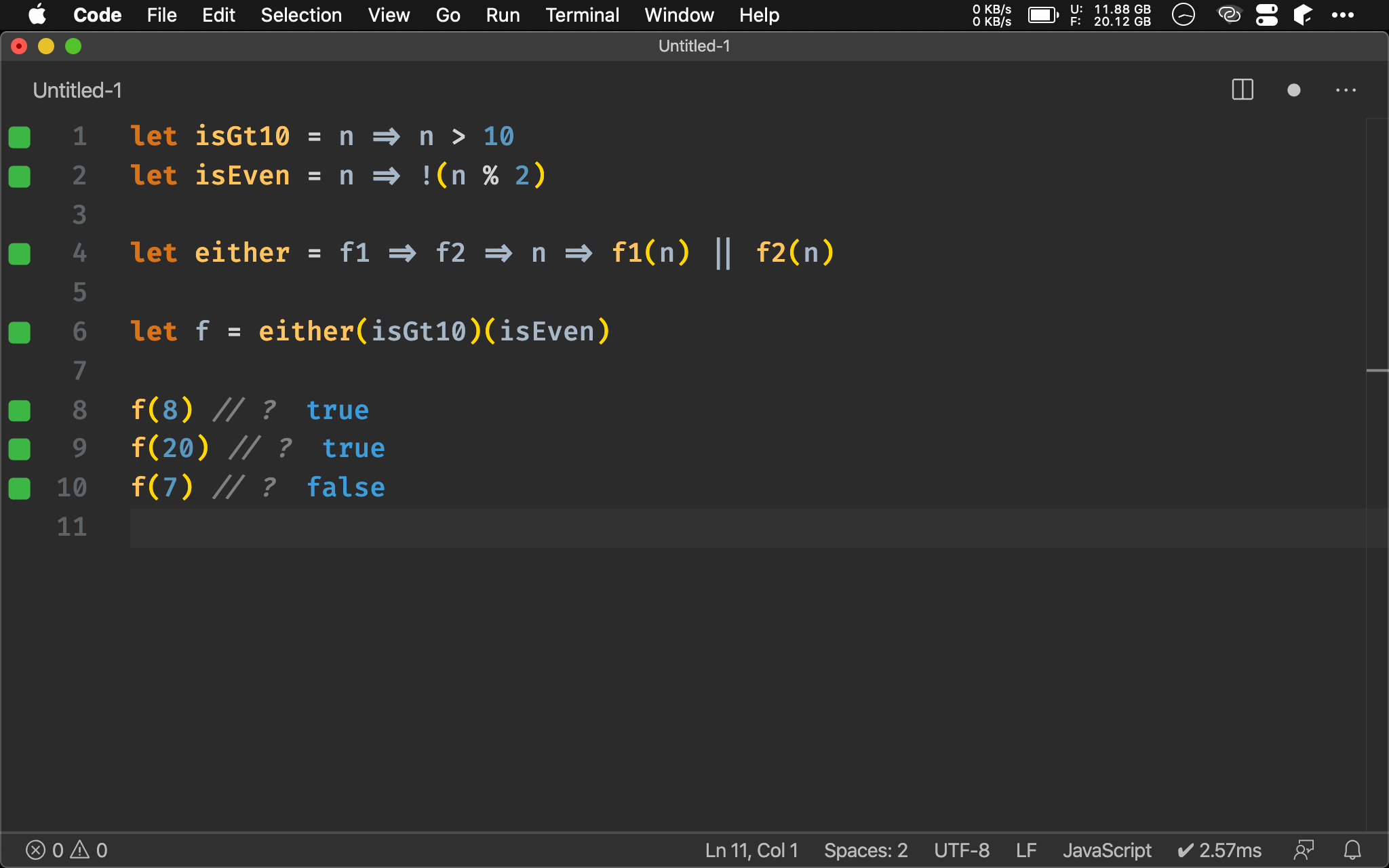
Ramda
import { either, gt, flip } from 'ramda'
import { isEven } from 'wink-fp'
let isGt10 = flip(gt)(10)
let f = either(isGt10)(isEven)
f(8) // ?
f(20) // ?
f(7) // ?
Ramda 已提供 either() 可直接使用。
either()
(*… → Boolean) → (*… → Boolean) → *... → Boolean
若第一個 function 結果為 truthy value 則回傳第一個 function,否則回傳第二個 function
(*… → Boolean):傳入第一個 function
(*… → Boolean):傳入第二個 function
*...:傳入 data
Boolean:回傳任一 function 結果
Example
let data = [
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 100 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 200 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
]
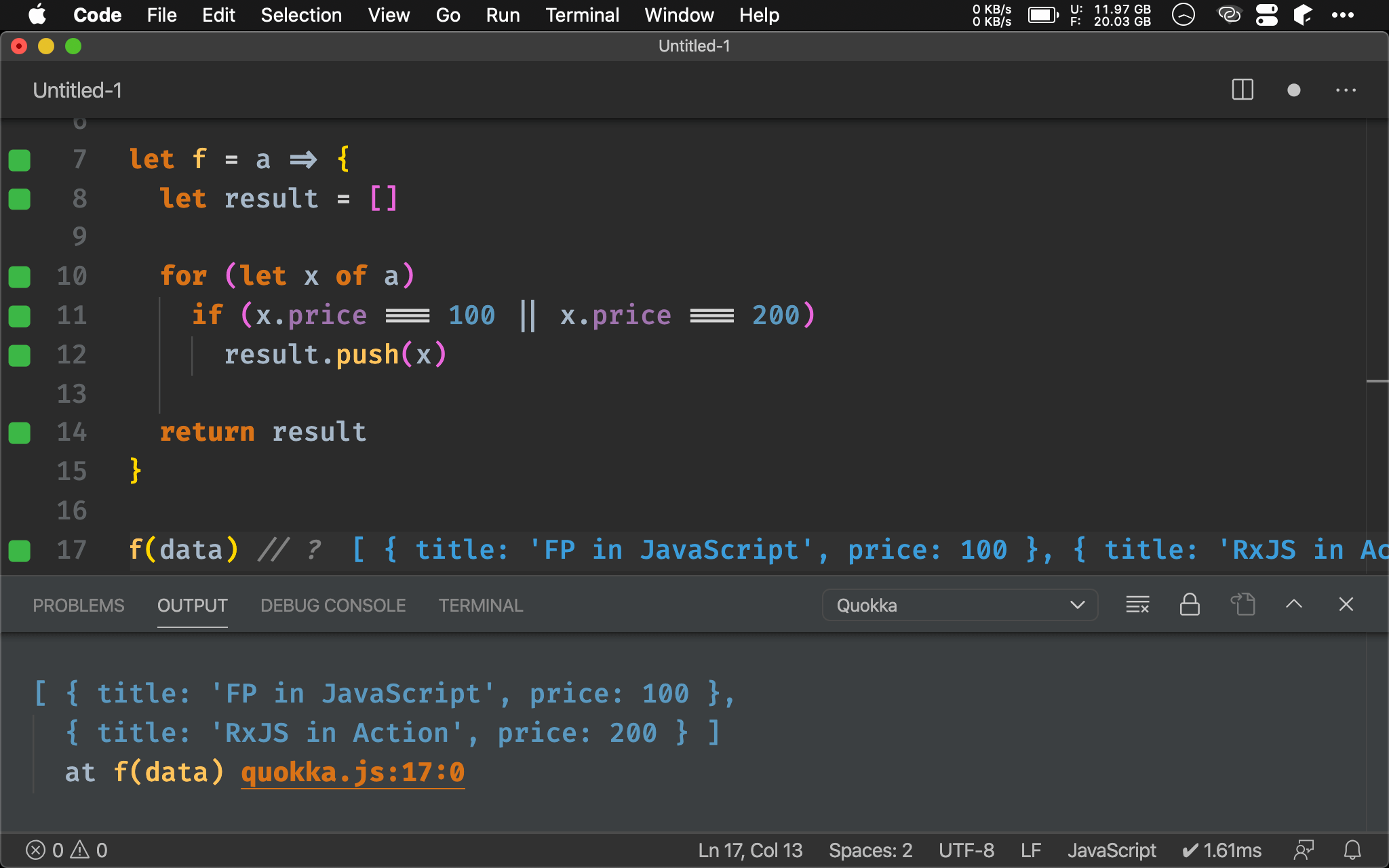
let f = a => {
let result = []
for (let x of a)
if (x.price === 100 || x.price === 200)
result.push(x)
return result
}
f(data) // ?
第 1 行
let data = [
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 100 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 200 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
]
只要是 price 為 100 或 200 都屬於合理價錢。
第 7 行
let f = a => {
let result = []
for (let x of a)
if (x.price === 100 || x.price === 200)
result.push(x)
return result
}
Imperative 會先建立 result empty array,使用 for loop 對 data 一筆一筆處理,然後使用 if 判斷 price 是否為 100 或 200,最後 push 進 resultarray 回傳。
Array.prototype.filter()
let data = [
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 100 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 200 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
]
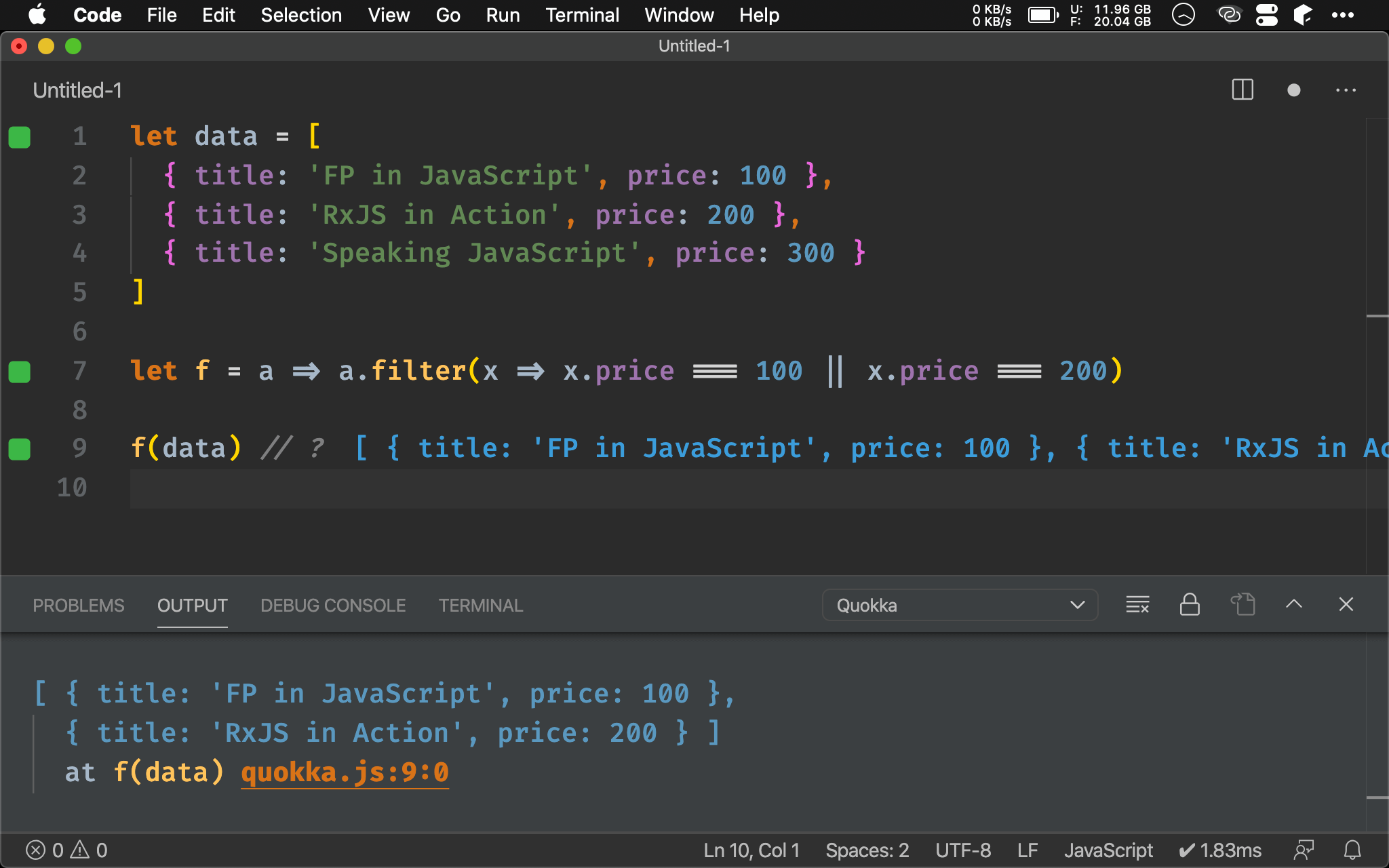
let f = a => a.filter(x => x.price === 100 || x.price === 200)
f(data) // ?
也可使用 ECMAScript 自帶的 filter(),只要在 predicate 判斷 price 為 100 或 200 即可。
Ramda
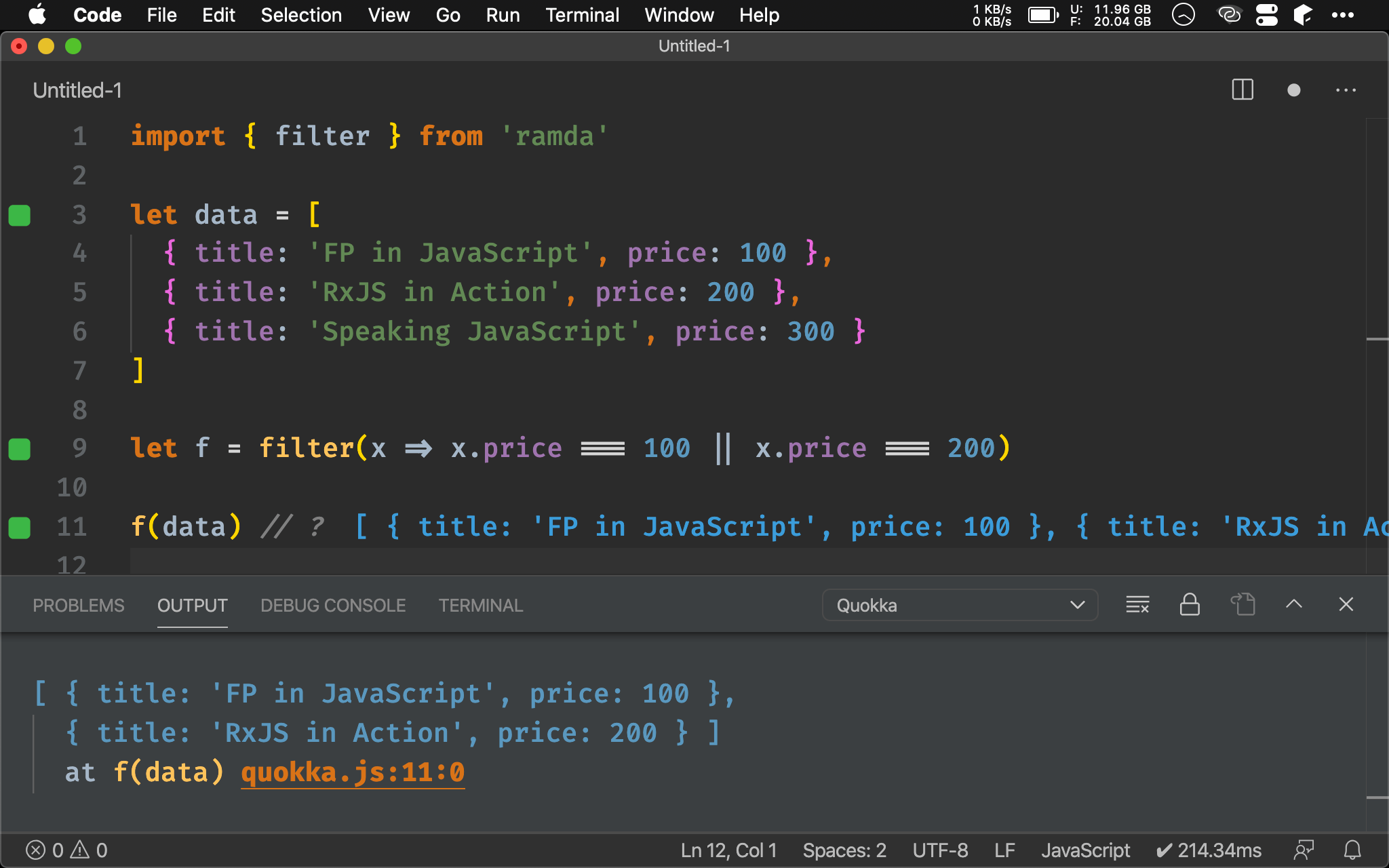
import { filter } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 100 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 200 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
]
let f = filter(x => x.price === 100 || x.price === 200)
f(data) // ?
也可使用 Ramda 的 filter() 使 f() 能 point-free。
Point-free
import { filter, either, propEq } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 100 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 200 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
]
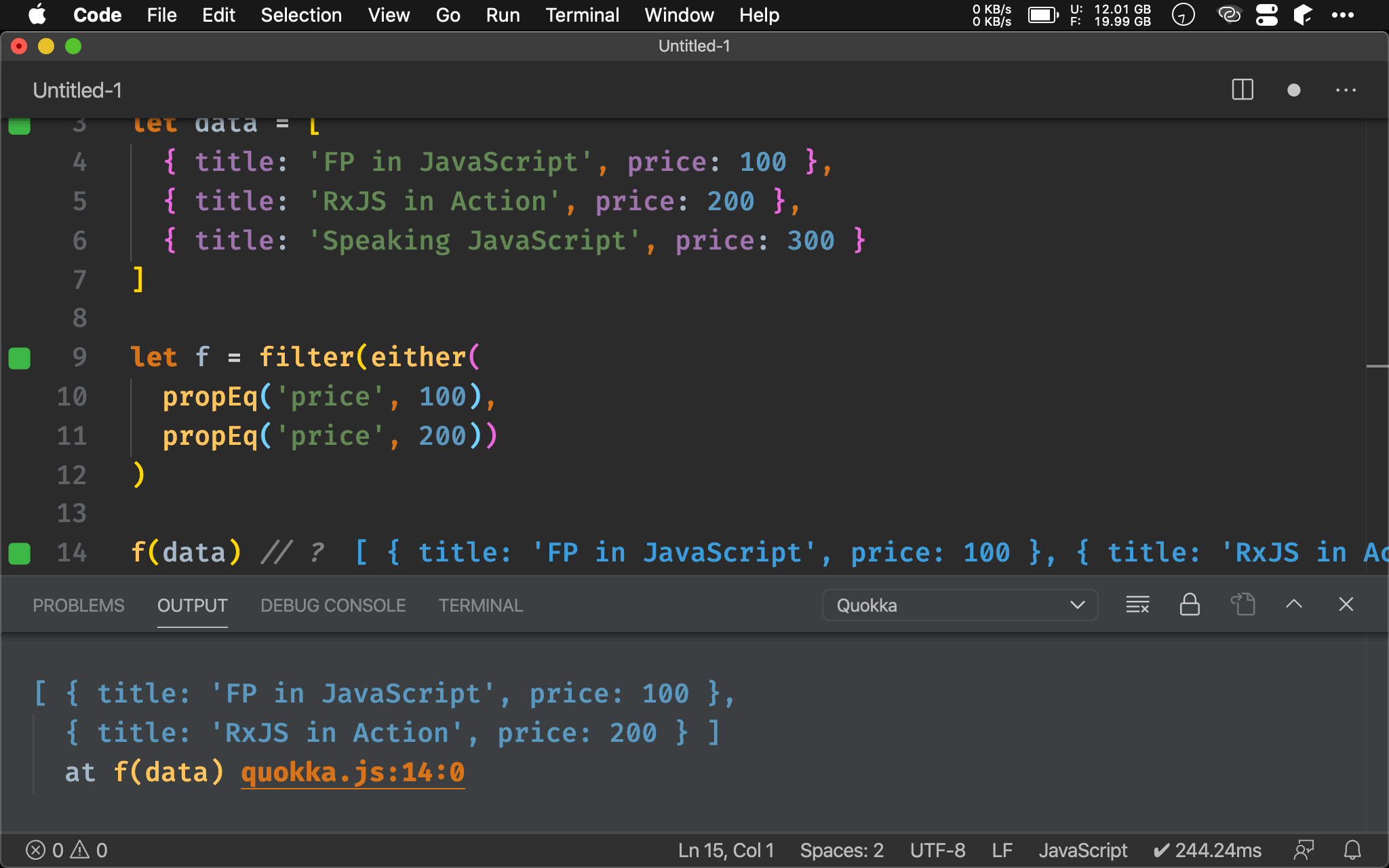
let f = filter(either(
propEq('price', 100),
propEq('price', 200))
)
f(data) // ?
以 FP 角度,我們必須提供兩個 predicate,但只要其中一個 predicate 成立即可,因此使用 Ramda 的 either() 將兩個使用 propEq() 產生的 predicate 組合成單一 predicate。
注意新 predicate 接受的 data 與原本 predicate 都相同,一樣是 object。
Example
let data = [
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 100 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 200 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
]
let f = n => a => {
let result = a.find(x => x.title === n)
if (result === undefined)
result = { price: 0 }
return result.price
}
f('Speaking JavaScript')(data) // ?
f('RxJS')(data) // ?
either() 另外一個應用是搭配會回傳 undefined 的 function,如 find(),當找不到資料時提供預設值。
Imperative 會使用 if 判斷是否回傳 undefined,這雖然可行,但會終止 pipeline 而改用 variable。
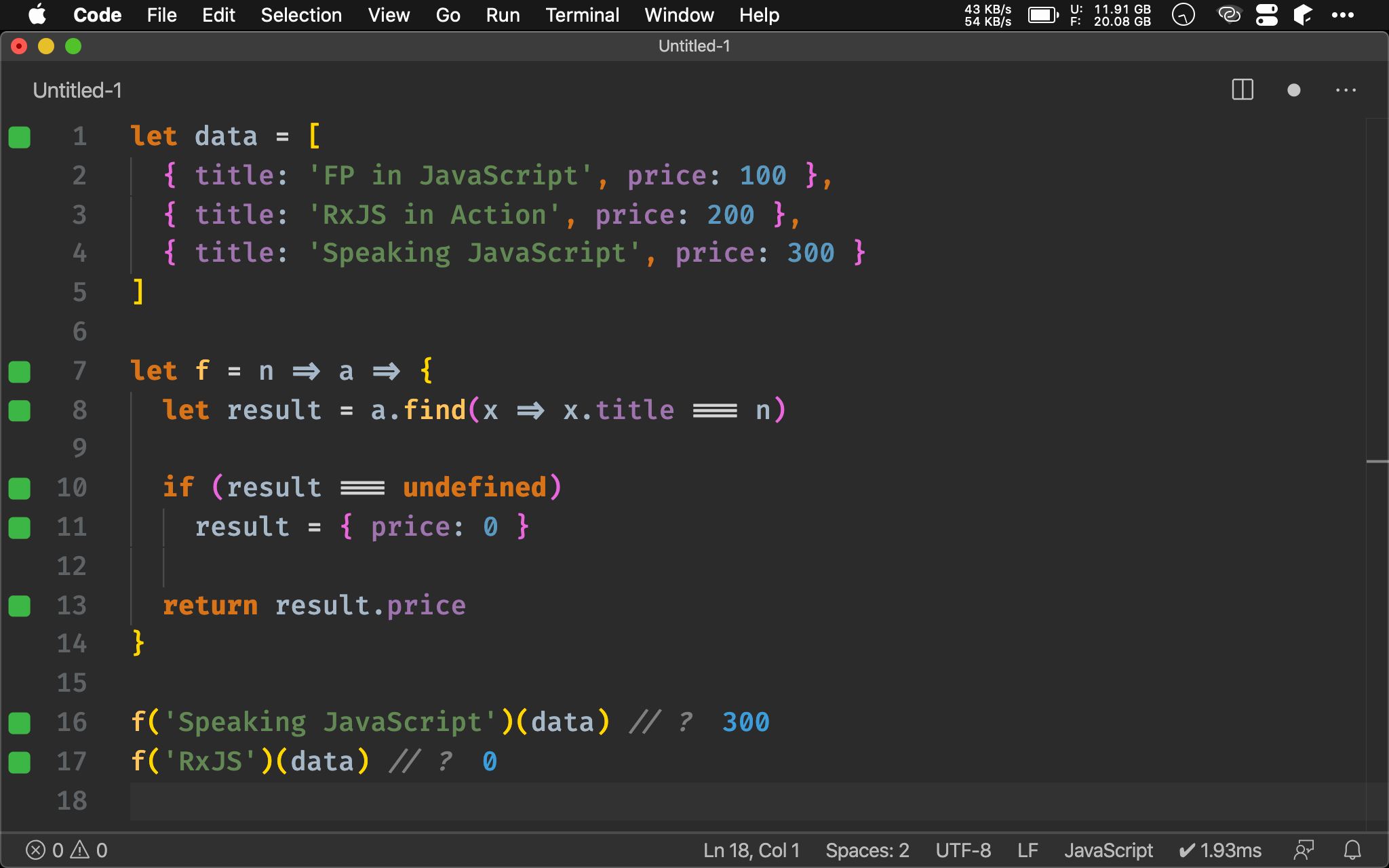
Ramda
import { find, either, pipe, prop, identity, always } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 100 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 200 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
]
let f = n => pipe(
find(x => x.title === n),
either(identity, () => ({ price: 0 })),
prop('price'),
)
f('Speaking JavaScript')(data) // ?
f('RxJS')(data) // ?
由於 find() 可能回傳 undefined,可使用 either() 判斷若為 falsy value 時提供 default value,如此可使 Function Pipeline 不中斷。
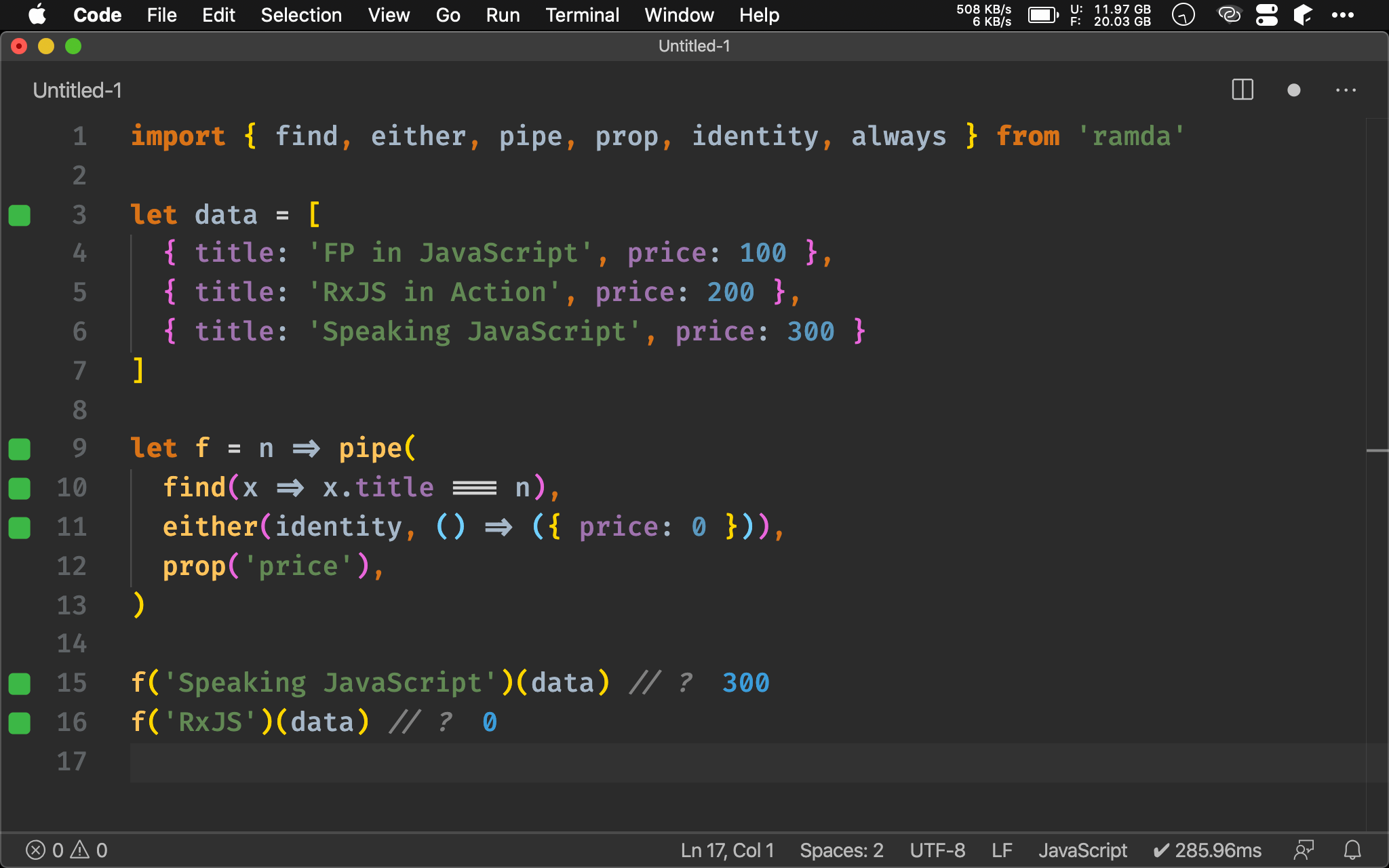
Point-free
import { find, either, pipe, prop, propEq, identity, always } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript', price: 100 },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action', price: 200 },
{ title: 'Speaking JavaScript', price: 300 }
]
let f = n => pipe(
find(propEq('title', n)),
either(identity, always({ price: 0 })),
prop('price'),
)
f('Speaking JavaScript')(data) // ?
f('RxJS')(data) // ?
可將 find() 與 either() 進一步 point-free。
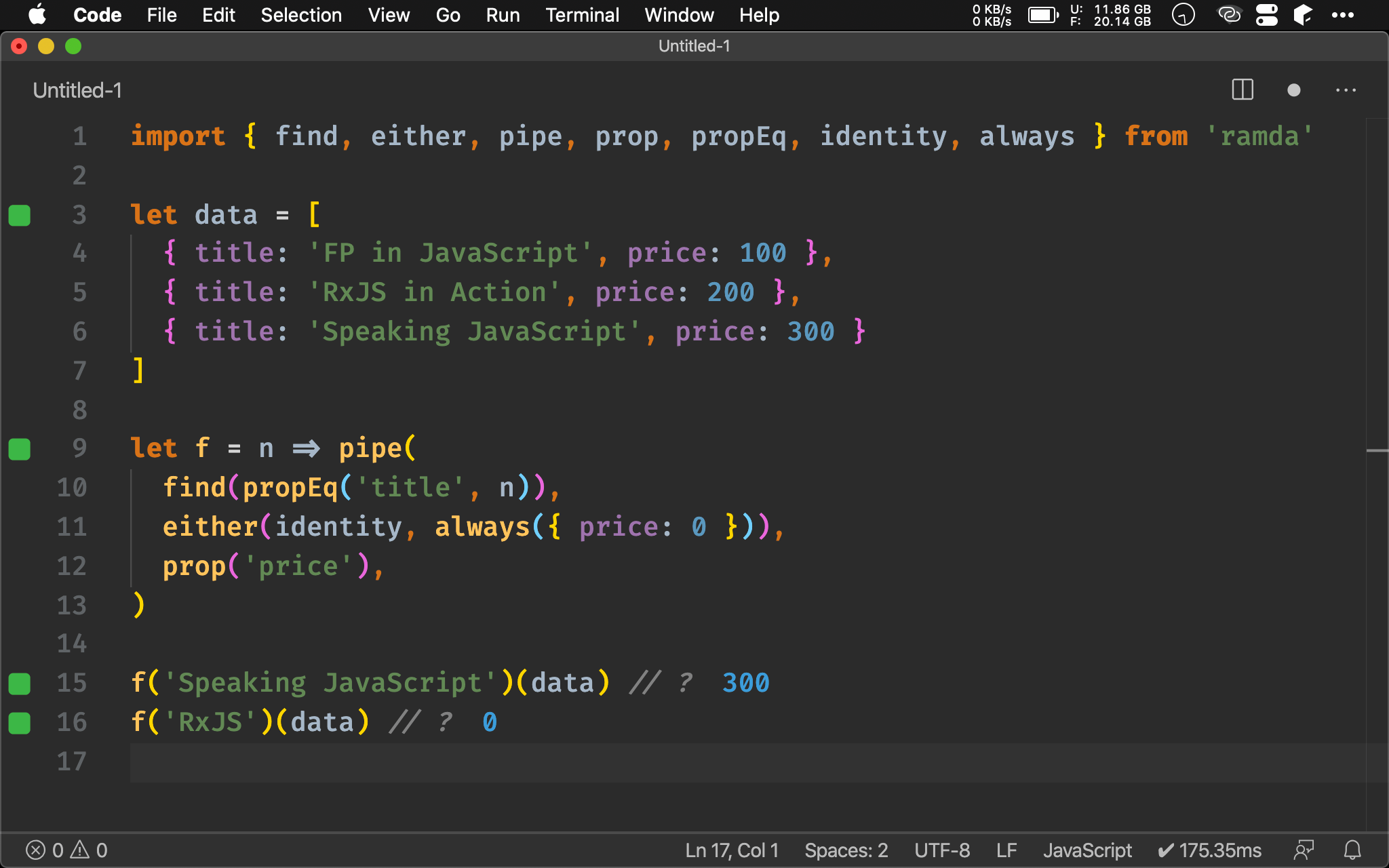
ADT
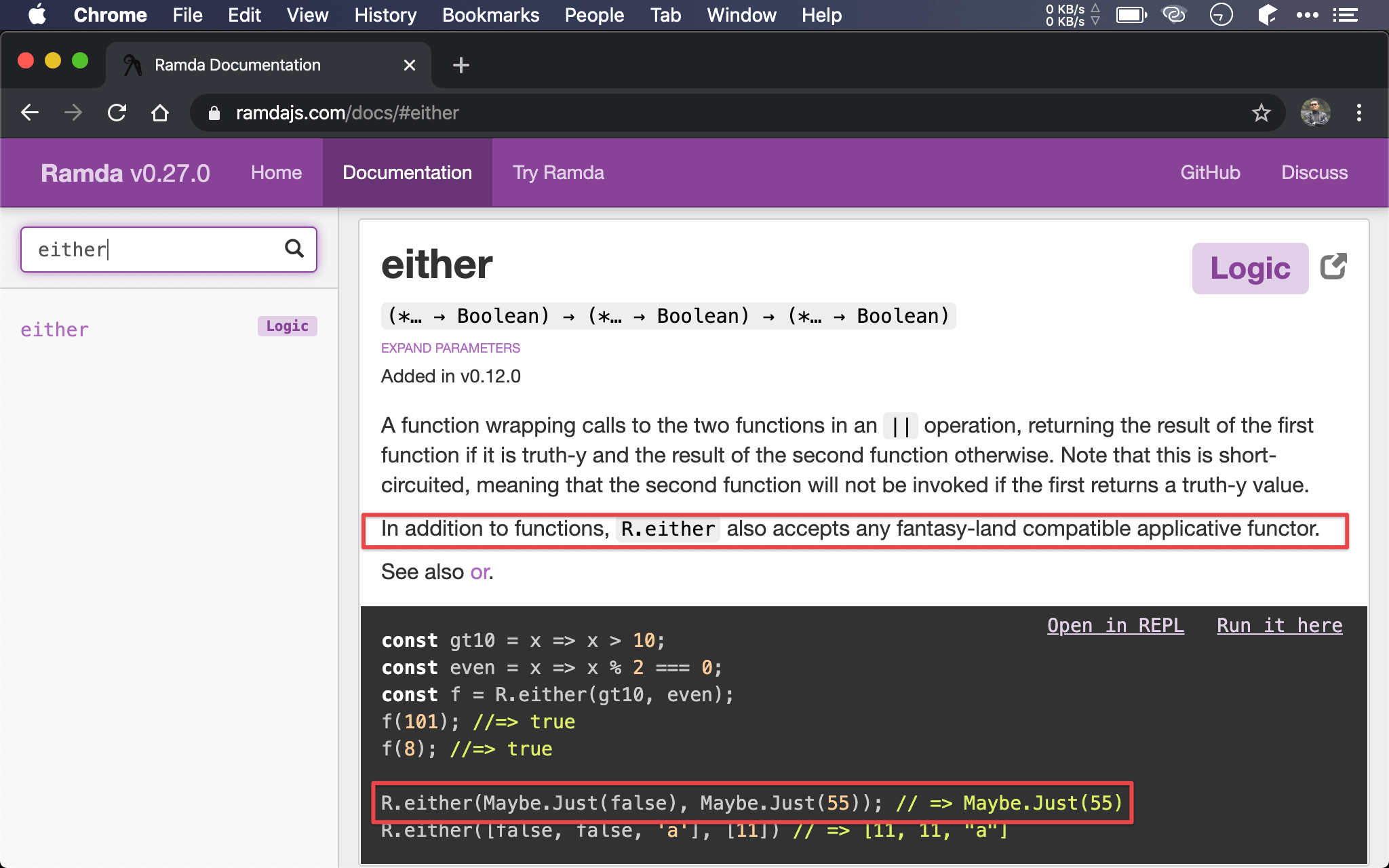
在 Ramda 文件中 either() 最後一行提到支援 Applicative Functor,且範例還用到 Maybe,這是什麼呢 ?
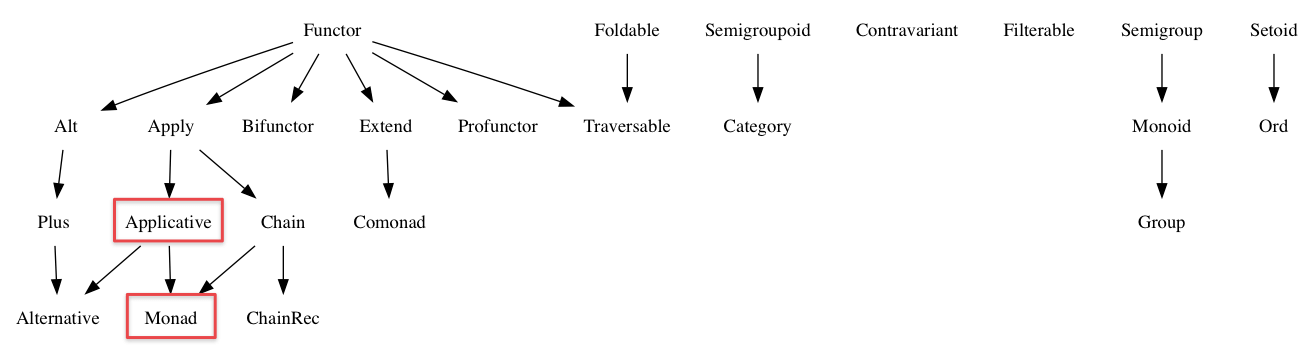
根據 fantasy-land 定義,Applicative 必須支援 Apply 與 Functor 所有特性,而 Monad 亦需支援 Applicative 所有特性,either() 既然支援 Applicative,這表示 either() 亦支援 Monad。
Maybe Monad
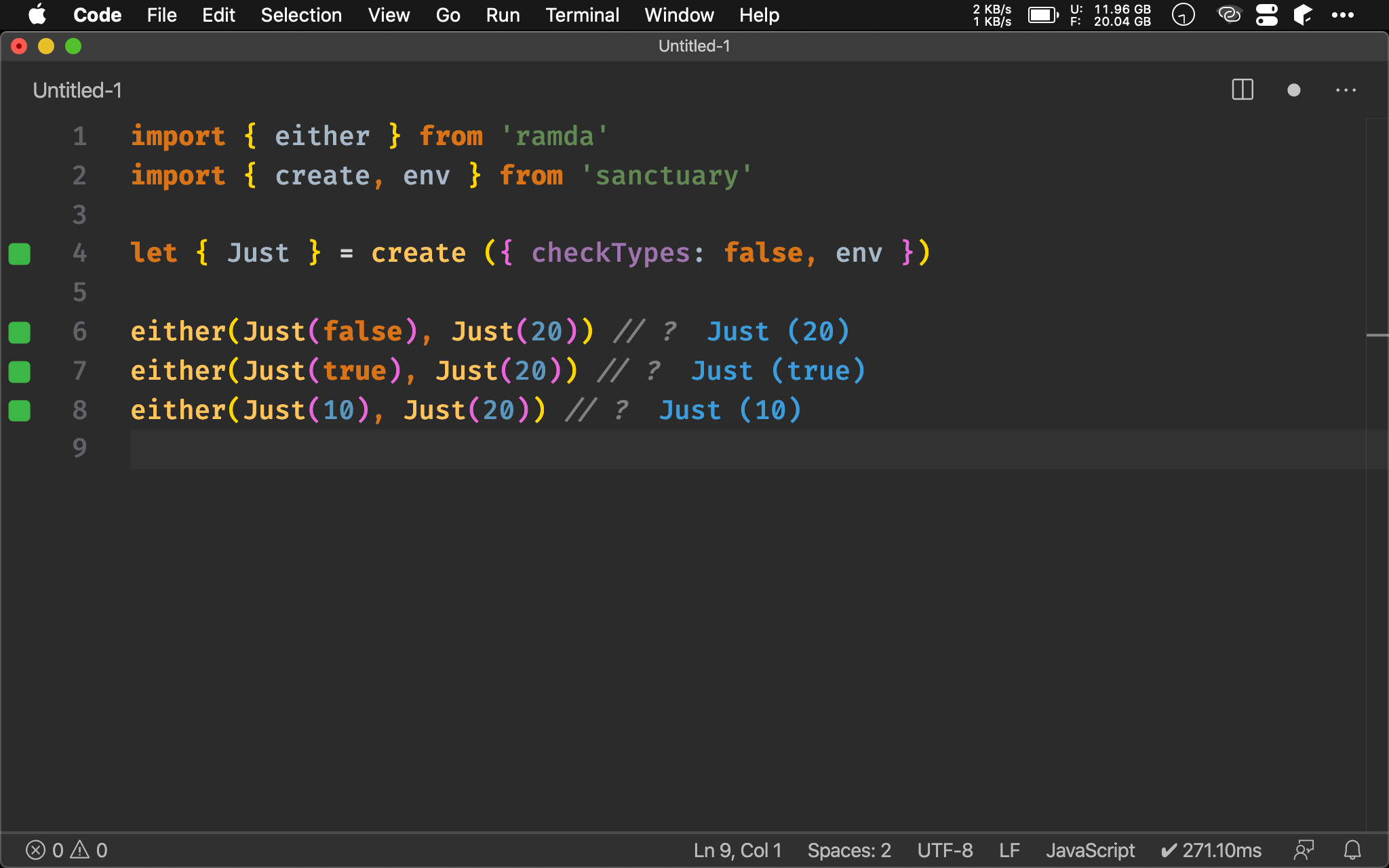
import { either } from 'ramda'
import { create, env } from 'sanctuary'
let { Just } = create ({ checkTypes: false, env })
either(Just(false), Just(20)) // ?
either(Just(true), Just(20)) // ?
either(Just(10), Just(20)) // ?
either() 可直接比較 Just 內的值,若第一個 Just 內為 true 則直接回傳 Just,若為 false 則回傳第二個 Just。
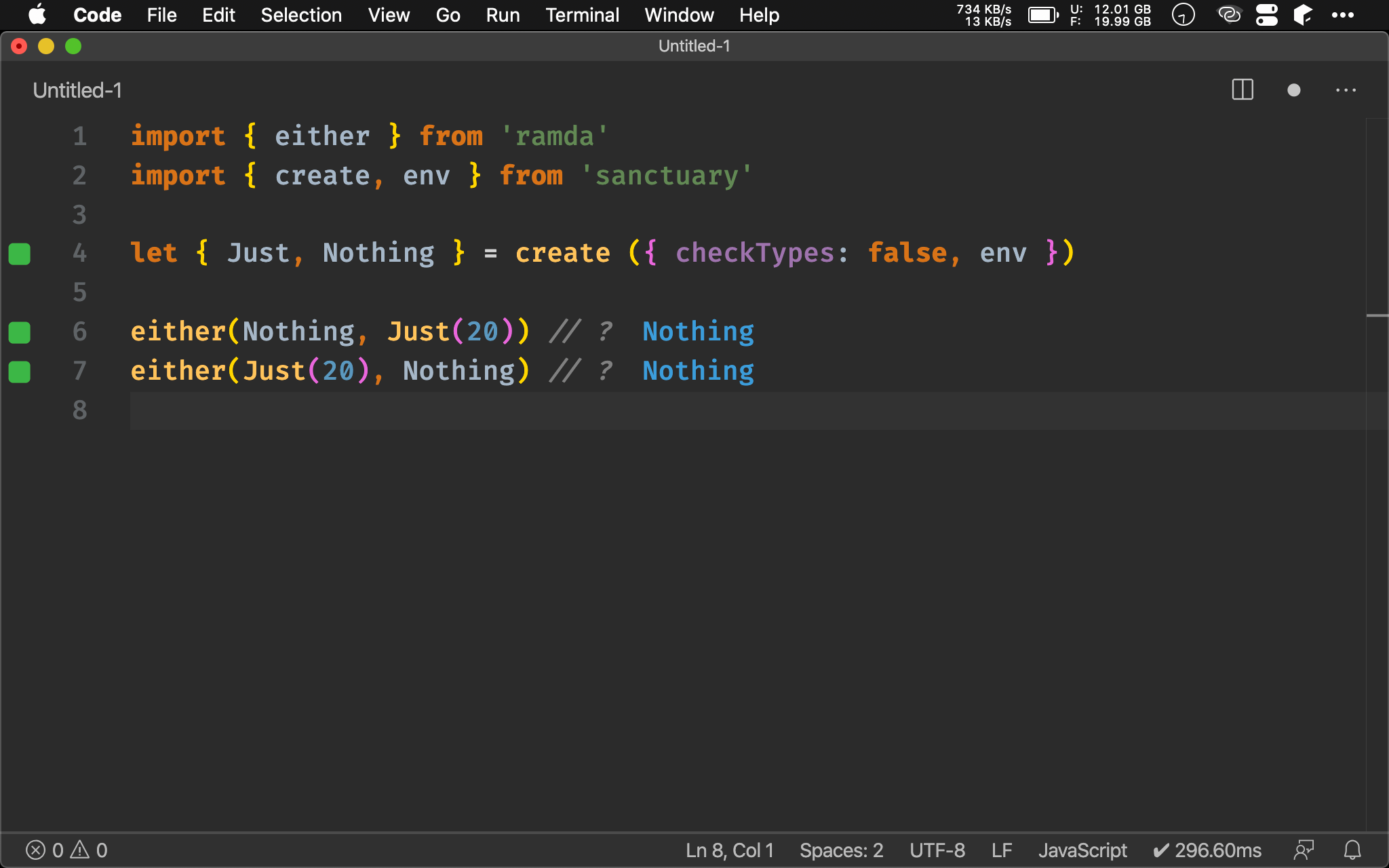
import { either } from 'ramda'
import { create, env } from 'sanctuary'
let { Just, Nothing } = create ({ checkTypes: false, env })
either(Nothing, Just(20)) // ?
either(Just(20), Nothing) // ?
若其中之一為 Nothing 則直接回傳 Nothing。
Conclusion
or()為||的 value 版本;而either()為||的 function 版本either()在 FP 也稱為 OR combinator- 若只有兩個 predicate,則
either()等效於anyPass() either()由於底層是||因此支援 truthy value 與 falsy value,不必如ifElse()一定要傳入 transfer functioneither()由於底層是||,因此支援 short-circuitited,也就是第二個 function 有可能不執行,因此可提高執行效率either()由於是傳入兩 function,因此實務上有兩種用法:一種是將兩個只會用到其一的 predicate 合併為一;另一種時搭配會回傳undefind的 function 使其能繼續 Function Pipelineeither()除了能用於 ECMAScript 原生型別外,還支援 Applicative Functor,可直接搭配 Maybe Monad 使用