map() 是 FP 最常用的 Higher Order Function,事實上我們也可自行實作 map() 練習 FP 基本功。
Version
macOS Catalina 10.15.2
VS Code 1.41.1
Quokka 1.0.274
Ramda 0.26.1
Imperative
let data = [1, 2, 3]
let map = fn => arr => {
let result = []
for(let x of arr)
result.push(fn(x))
return result
}
map(x => x * 2)(data) // ?
map() 當然也可使用 imperative 實作。
reduce()
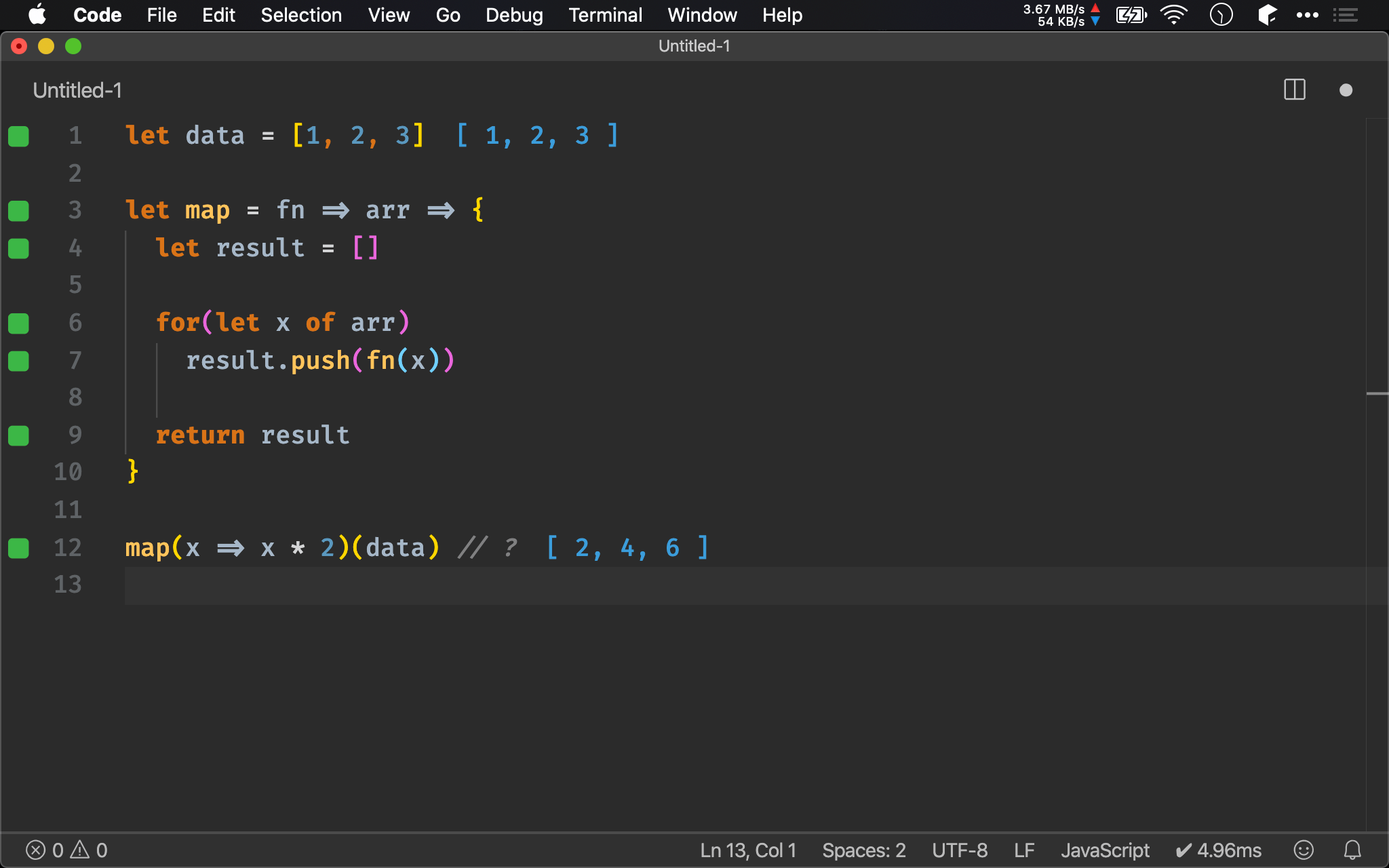
let data = [1, 2, 3]
let map = fn => arr => arr.reduce((a, x) => [...a, fn(x)], [])
map(x => x * 2)(data) // ?
map() 最終為單一 array,故可用 reduce() 與 ES6 的 array spread 實現。
Recursion
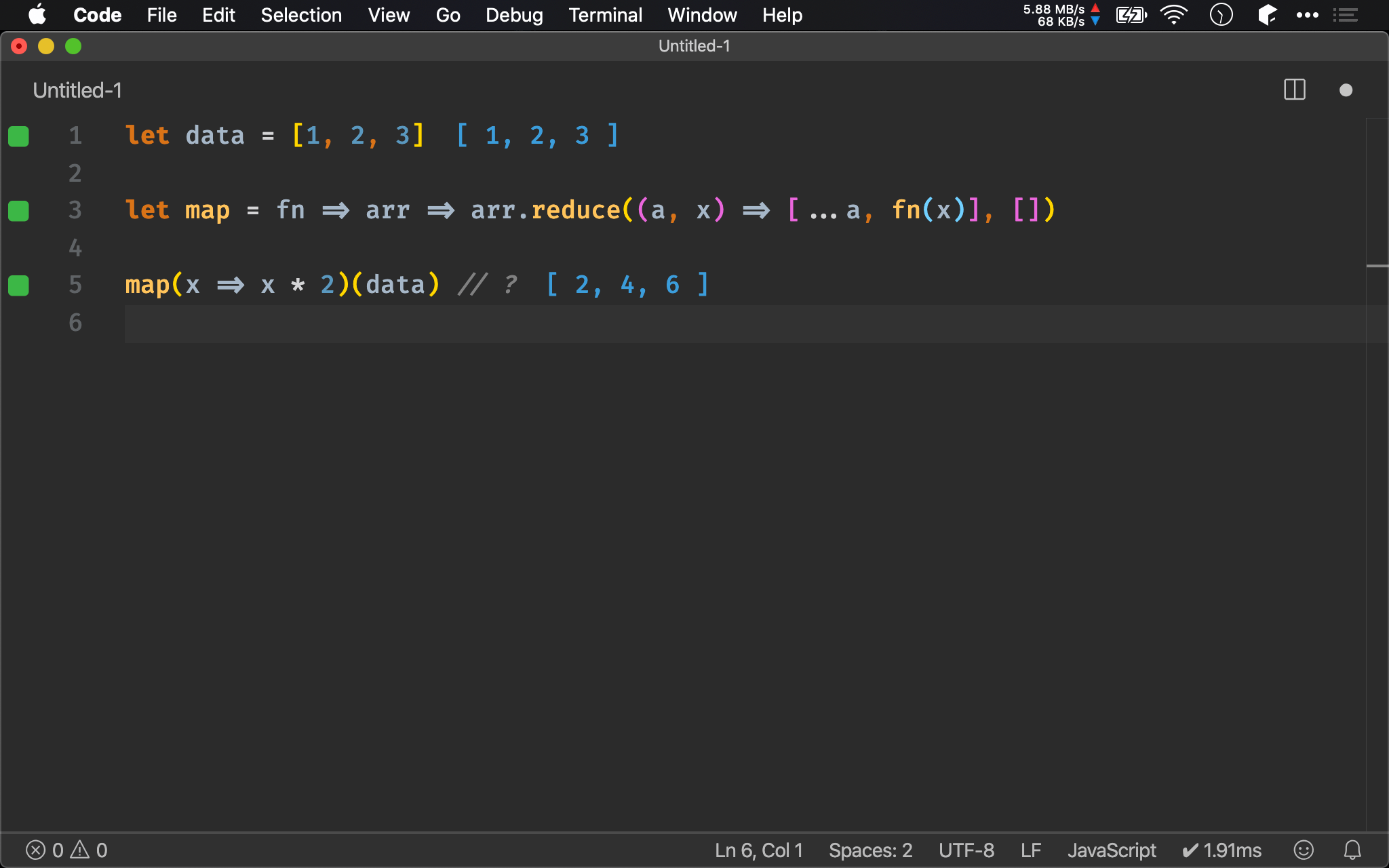
let data = [1, 2, 3]
let map = fn => ([h, ...t]) => h === undefined ? [] : [fn(h), ...map(fn)(t)]
map(x => x * 2)(data) // ?
也可使用 resursion 以 no side effect 方式實現 map()。
map()
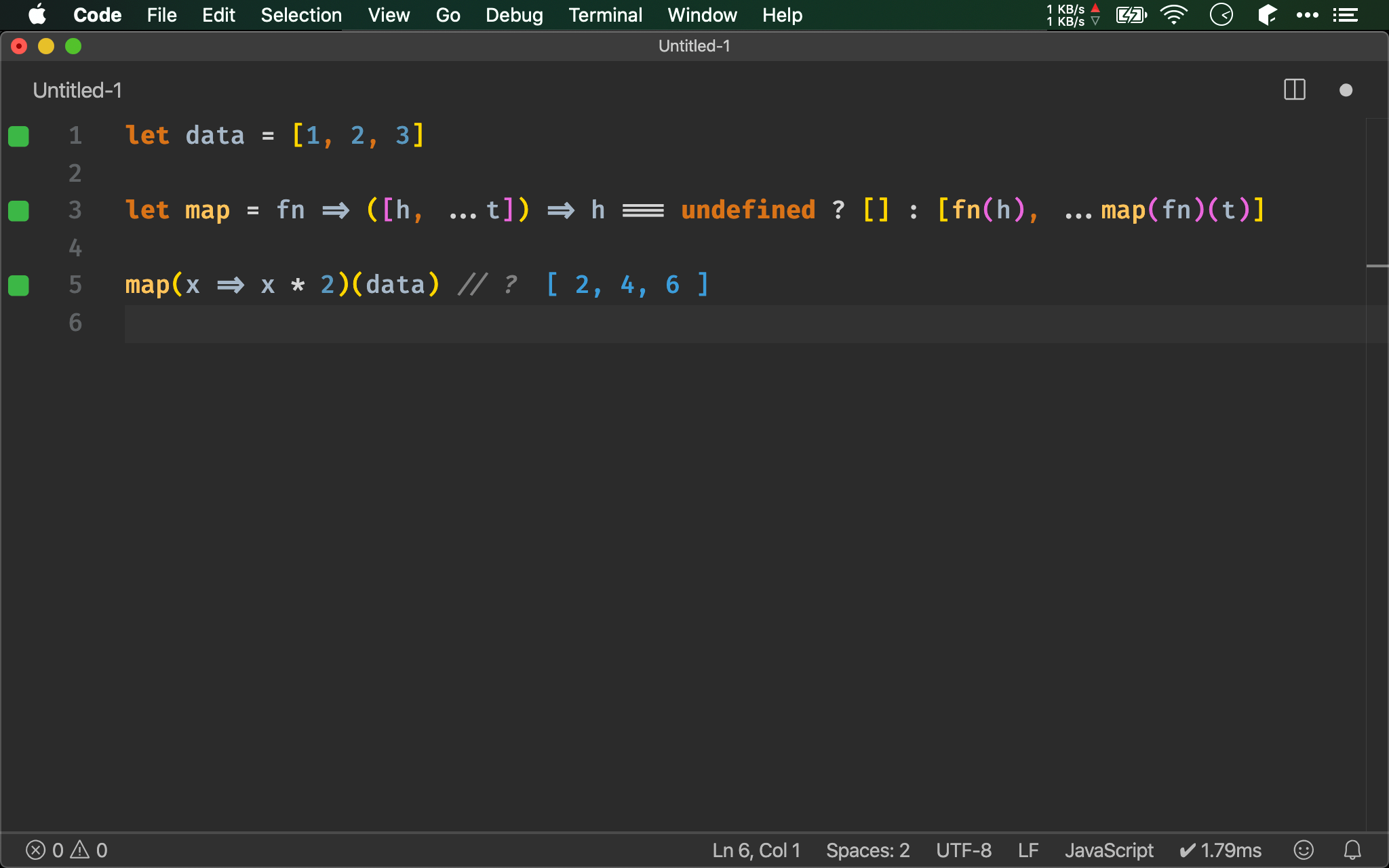
let data = [1, 2, 3]
let map = fn => arr => arr.map(fn)
map(x => x * 2)(data) // ?
Array.prototype 已經內建 map(),可直接使用。
Ramda
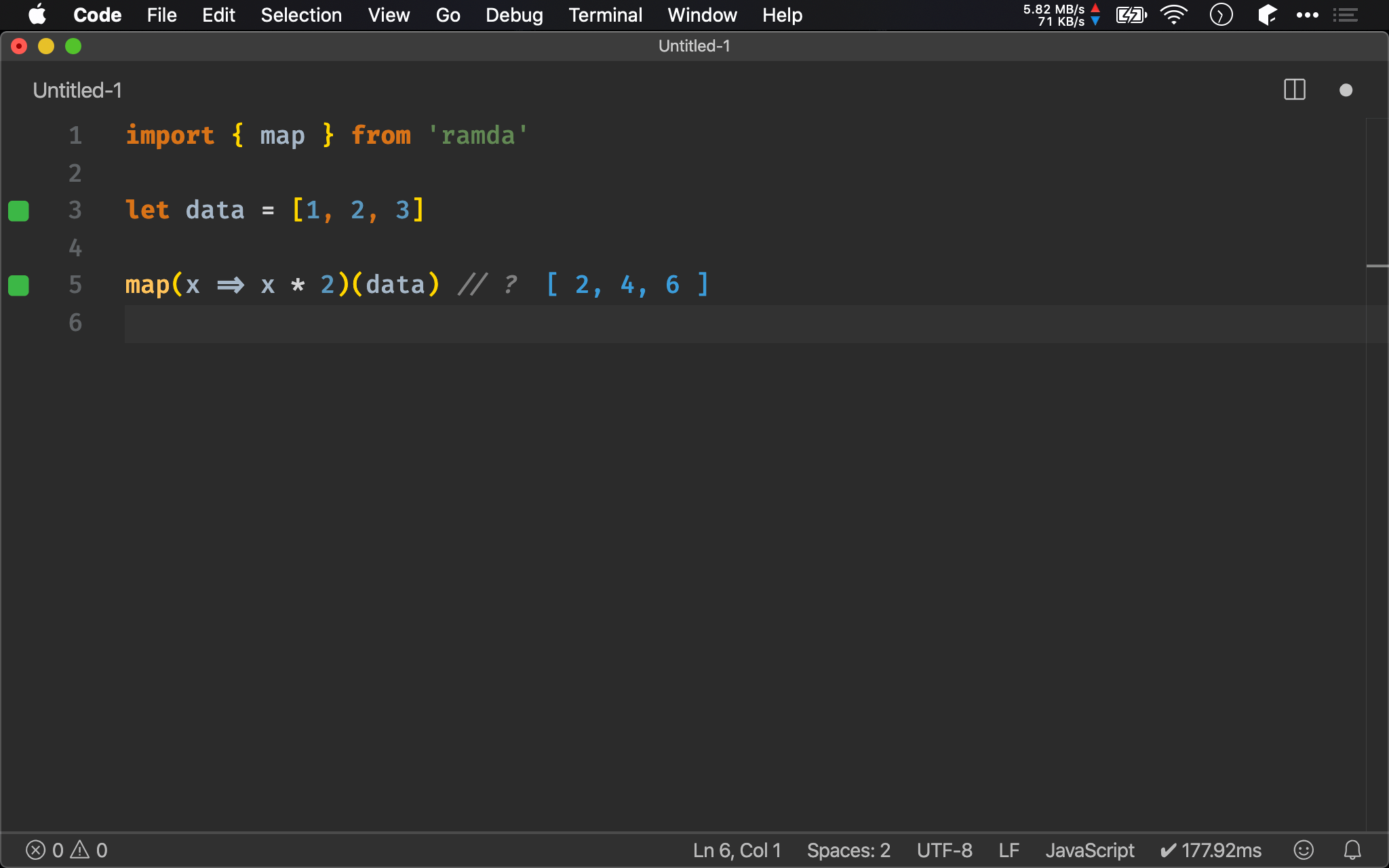
import { map } from 'ramda'
let data = [1, 2, 3]
map(x => x * 2)(data) // ?
Ramda 亦提供 map(),與內建不同的是 data 放在最後一個 argument,方便 function composition。
map()
(a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]
將 array 重新 mapping 成另一個 array
(a -> b):傳入 map function 轉換
[a]:data 為 array
[b]:回傳另一個 array
Point-free
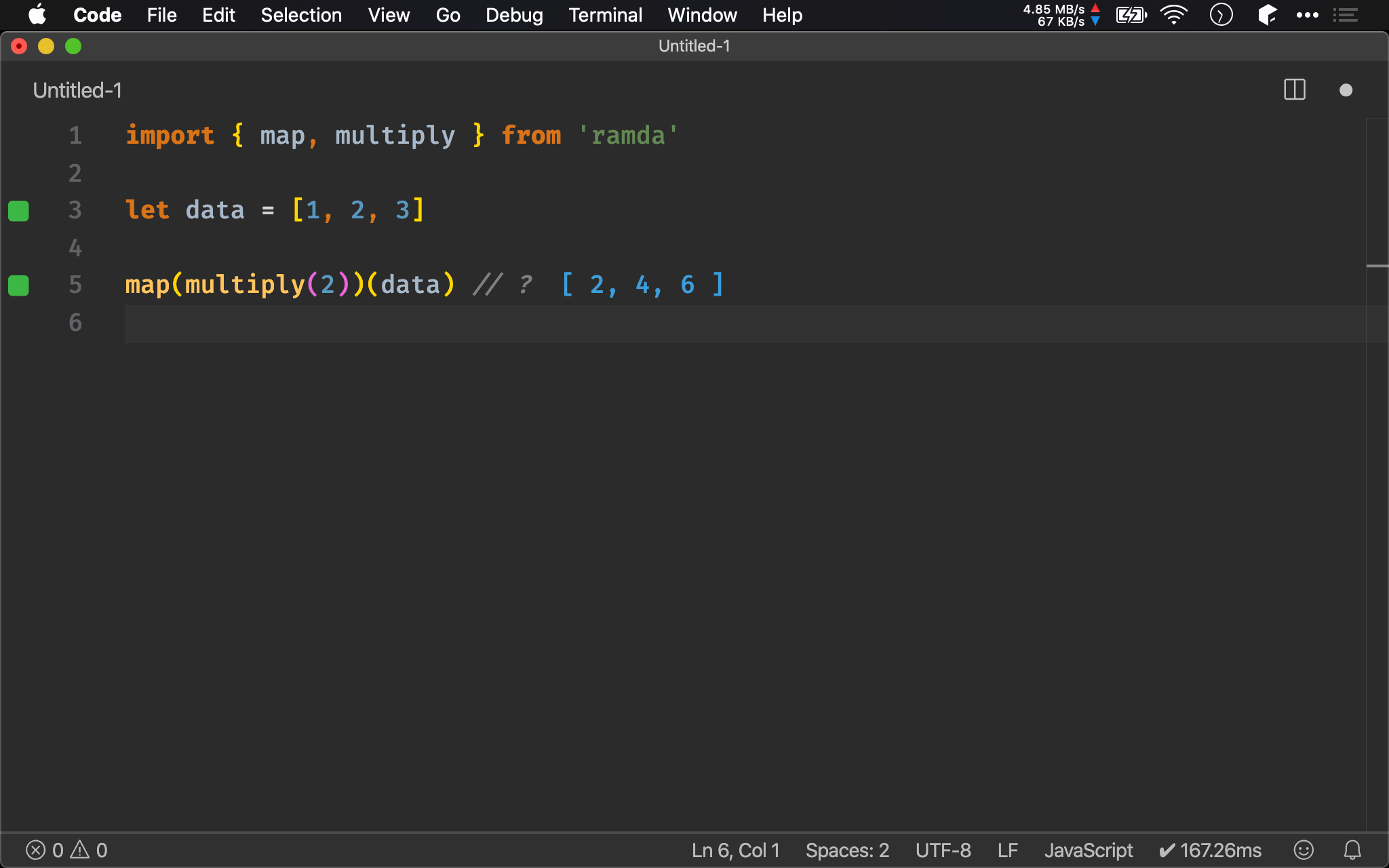
import { map, multiply } from 'ramda'
let data = [1, 2, 3]
map(multiply(2))(data) // ?
map() 的 callback 亦可使用 multiply() 加以 point-free。
Function Composition
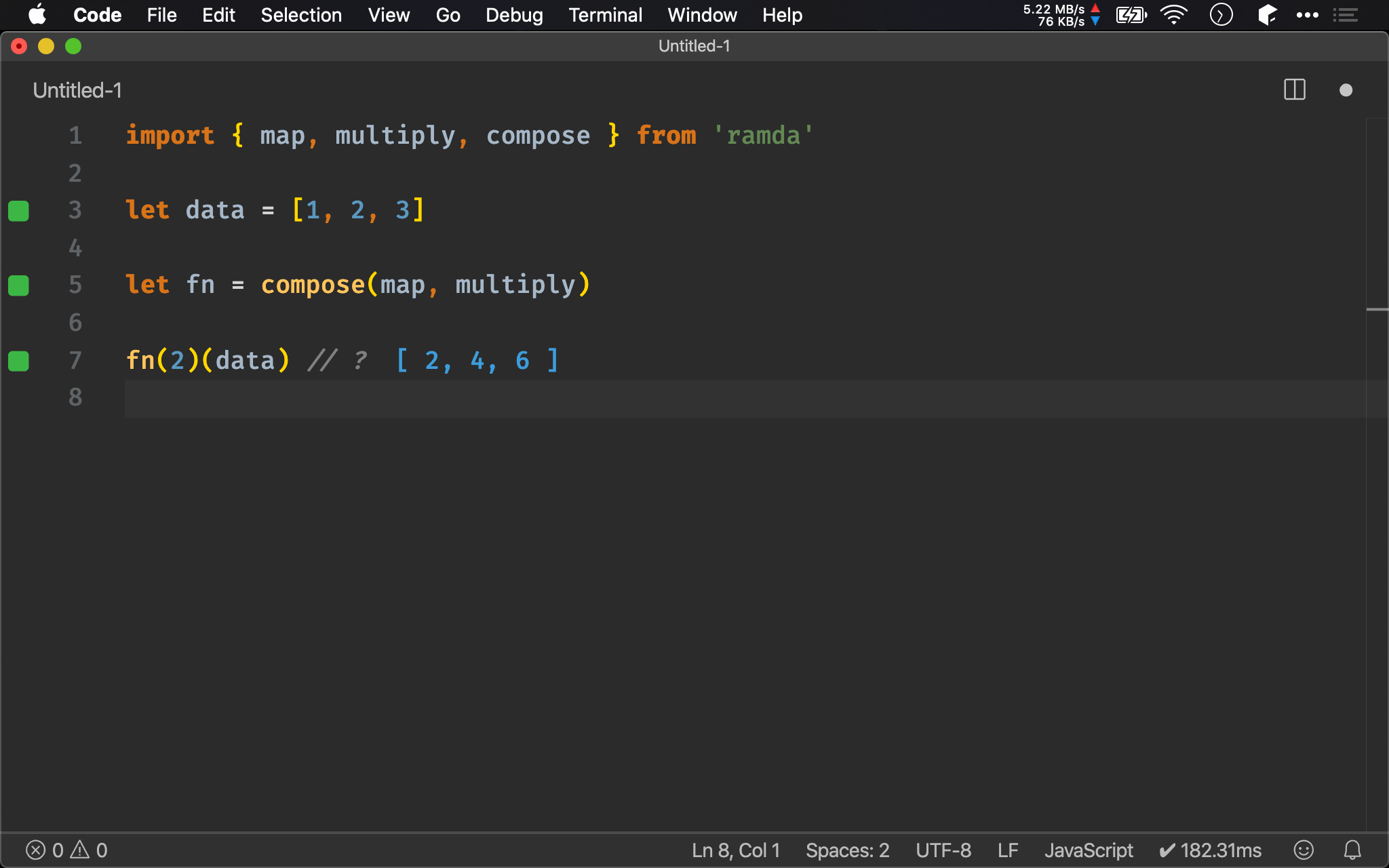
import { map, multiply, compose } from 'ramda'
let data = [1, 2, 3]
let fn = compose(map, multiply)
fn(2)(data) // ?
亦可使用 compose() 將 multiply() 與 map() 組合起來。
Conclusion
map()雖然用起來很直覺,也可使用 imperative 與reduce()實作,事實上 imperative 要重構時,與自行實作map()思考過程類似- 當 map function 也 point-free 後,就更能看出 function composition 雛形,可使用
compose()將map()與 callback 組合起來
Reference
MDN, Array.prototype.reduce()
MDN, Array.prototype.map()
Ramda, map()
Ramda, multiply()