chain() 屬於 Ramda 較進階 Function,威力強大。當 Data 為 Nested Array 時,其結果將攤平為一層 Array,俗稱 flatMap()。
Version
Ramda 0.27.1
ECMAScript
Array.prototype.map()
let data = [
{ title: 'Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja',
authors: ['John Resig', 'Bear Bibeault'] },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action',
authors: ['Paul P.Daniels', 'Luis Atencio'] }
]
let f = (k, a) => a.map(x => x[k])
f('authors', data) // ?
Data 為 Nested Array,想以一層 Array 列出所有 author。
若使用 map(),由於 data 是兩層 Array,最後結果也會維持兩層 Array,這顯然不是我們所要的。
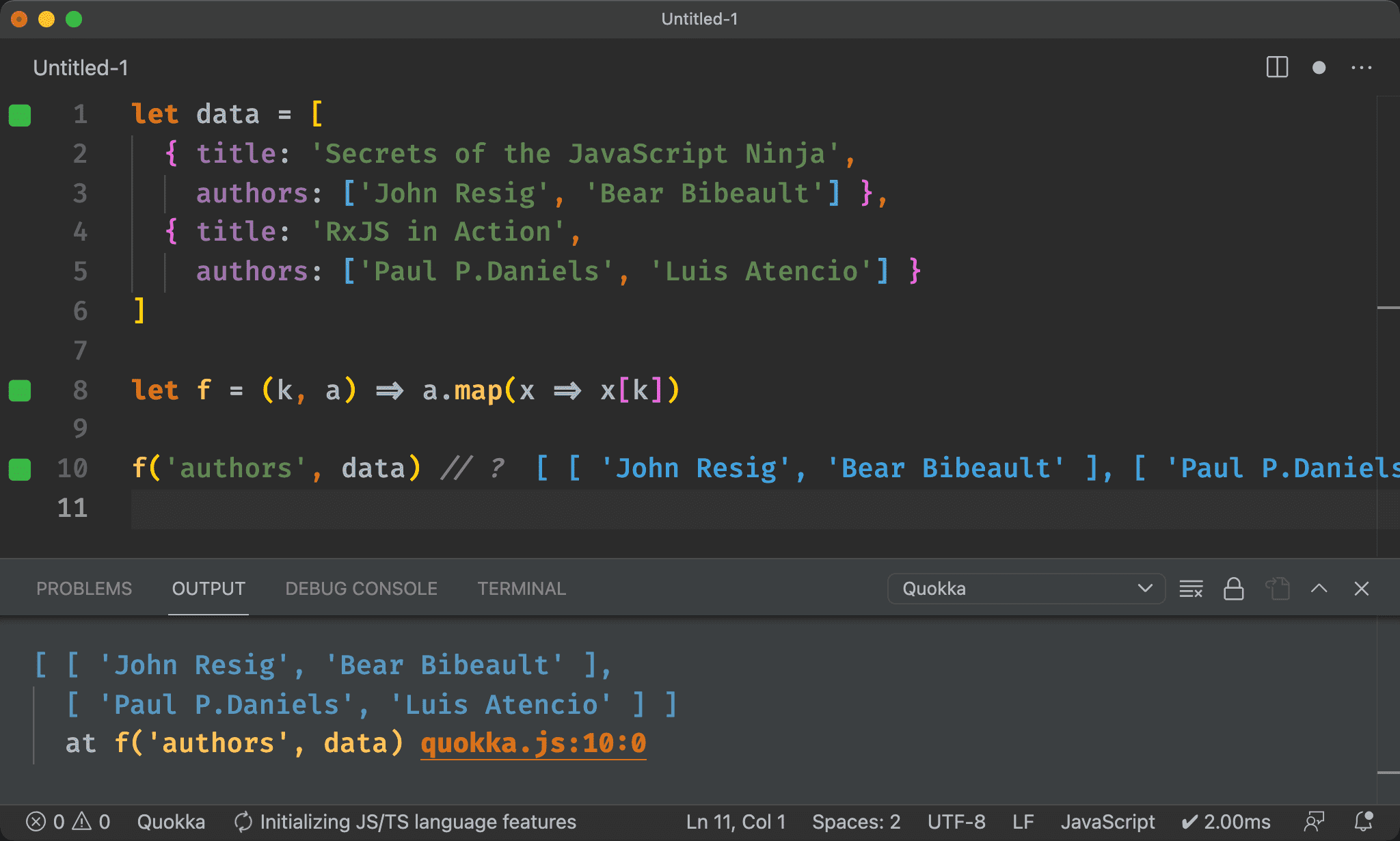
Array.prototype.flat()
let data = [
{ title: 'Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja',
authors: ['John Resig', 'Bear Bibeault'] },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action',
authors: ['Paul P.Daniels', 'Luis Atencio'] }
]
let f = (k, a) => a.map(x => x[k]).flat()
f('authors', data) // ?
ES2019 新增 Array.prototype.flat(),可將多層 Array 攤平,相當於 Ramda 的 flatten()。
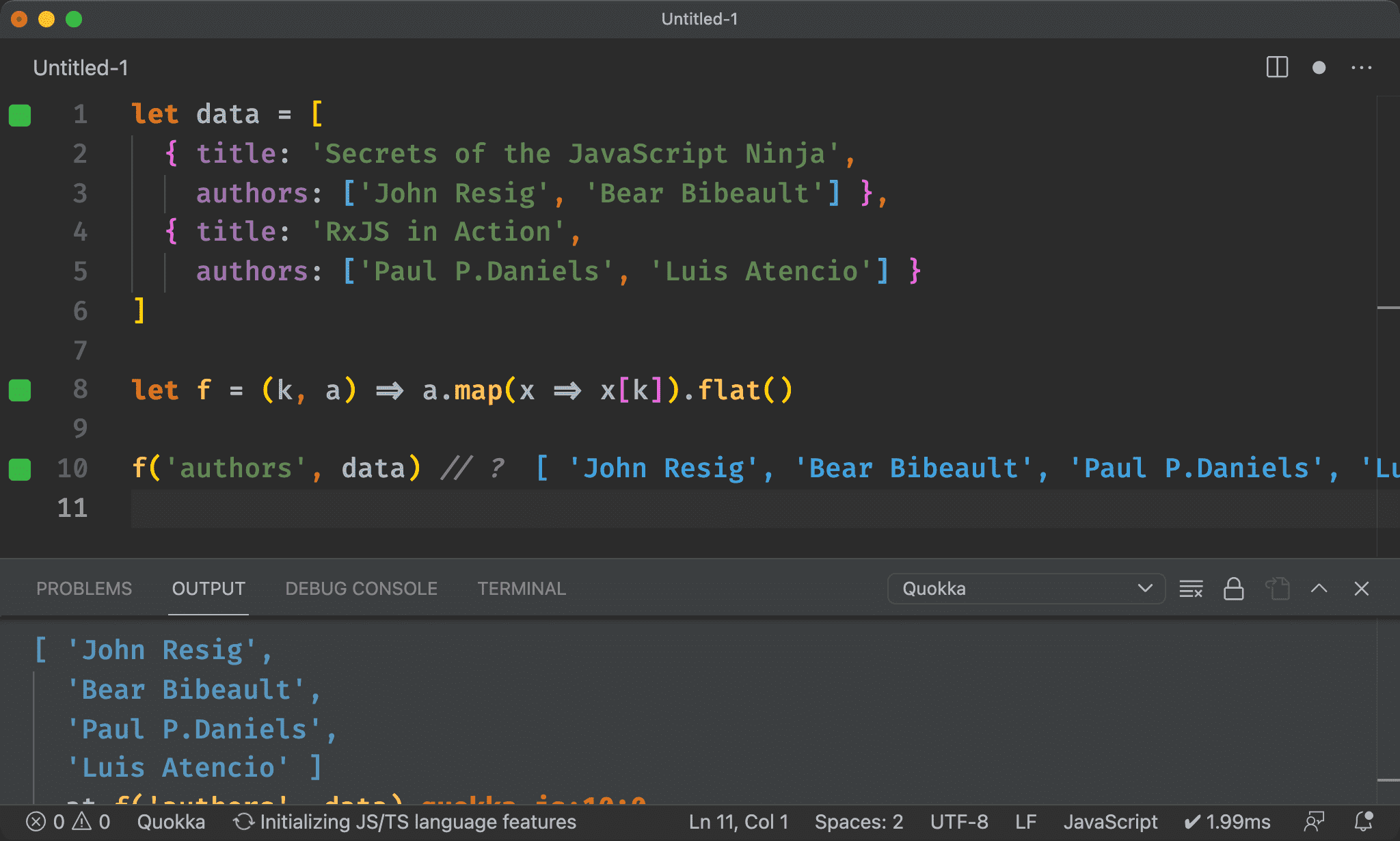
Array.prototype.flatMap()
let data = [
{ title: 'Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja',
authors: ['John Resig', 'Bear Bibeault'] },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action',
authors: ['Paul P.Daniels', 'Luis Atencio'] }
]
let f = (k, a) => a.flatMap(x => x[k])
f('authors', data) // ?
map() 與 flat() 的組合實在太常使用,ES2019 另外也新增了 Array.prototype.flatMap()。
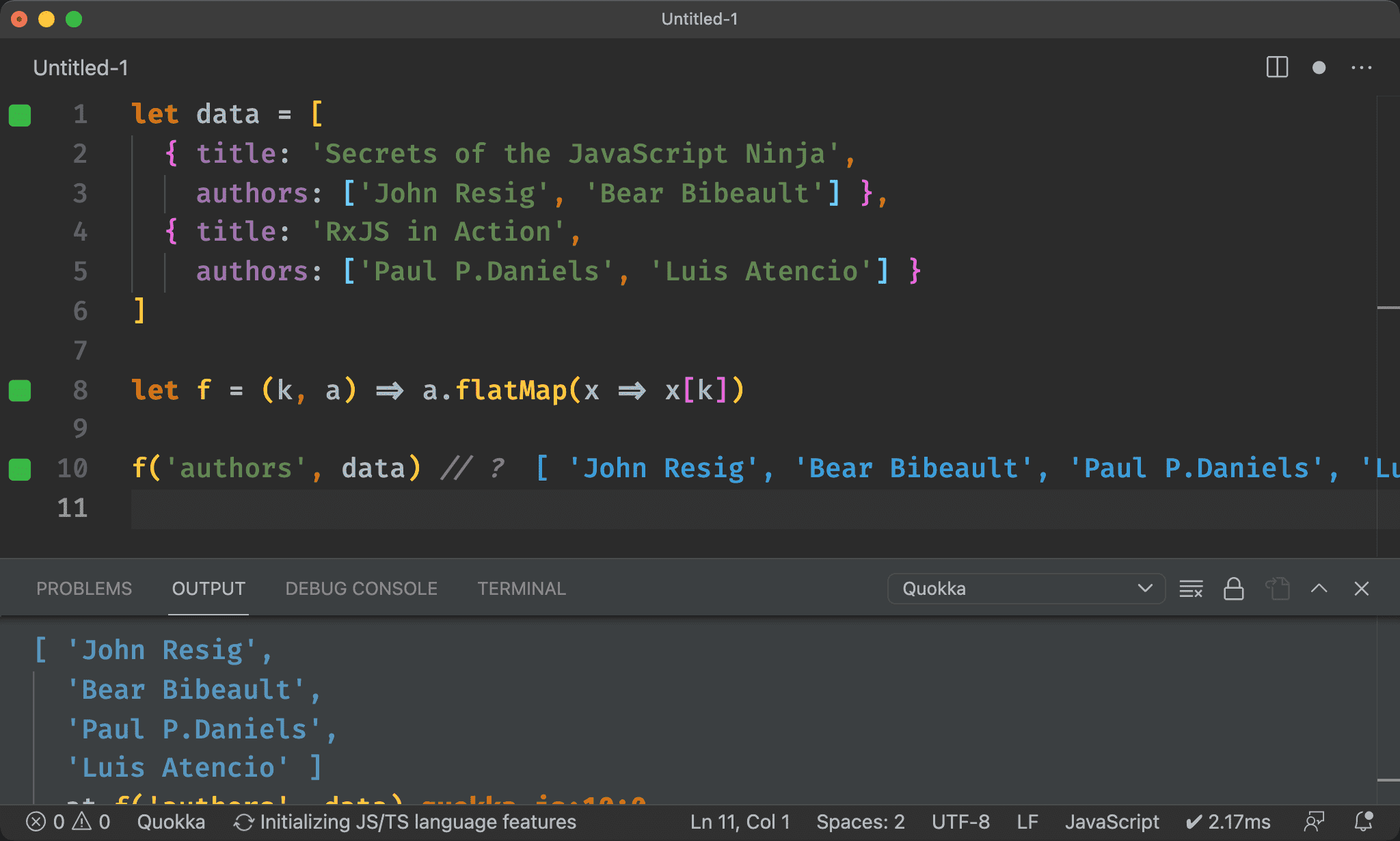
Ramda
map()
import { pipe, map } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja',
authors: ['John Resig', 'Bear Bibeault'] },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action',
authors: ['Paul P.Daniels', 'Luis Atencio'] }
]
let f = k => pipe(
map(x => x[k])
)
f('authors')(data) // ?
Array.prototype 下的 method 是以 OOP 設計,method 掛在 data 上;但 Ramda 以 FP 呈現,全部都是 function,data 則為 function 最後一個 argument,方便 Point-free。
將 Array.prototype.map() 改成 Ramda 的 map(),最後結果也會維持兩層 Array,這顯然不是我們所要的。
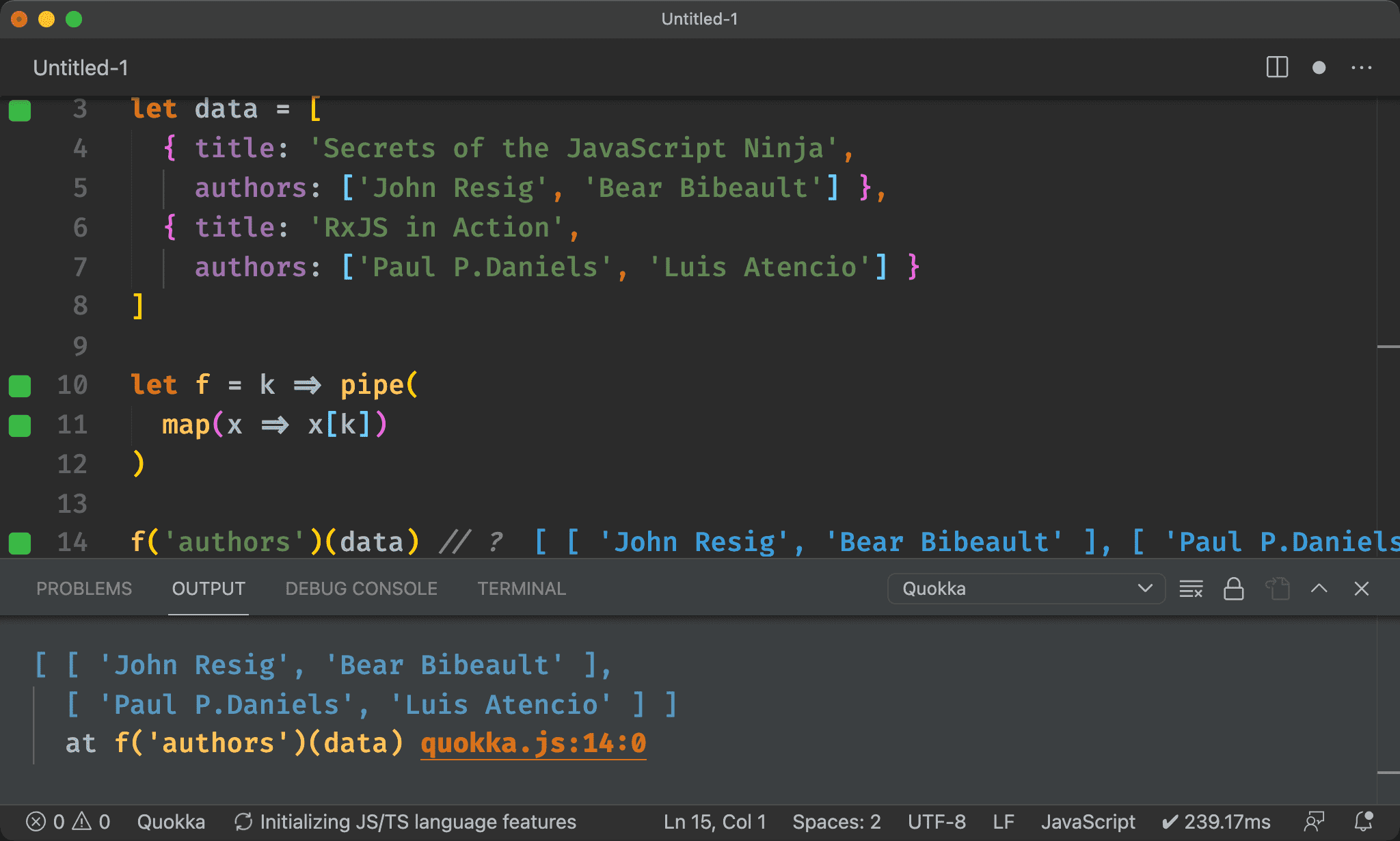
flatten()
import { pipe, map, flatten } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja',
authors: ['John Resig', 'Bear Bibeault'] },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action',
authors: ['Paul P.Daniels', 'Luis Atencio'] }
]
let f = k => pipe(
map(x => x[k]),
flatten,
)
f('authors')(data) // ?
Ramda 另提供 flatten(),將多層 Array 攤平成一層 Array,這就是我們所要的結果。
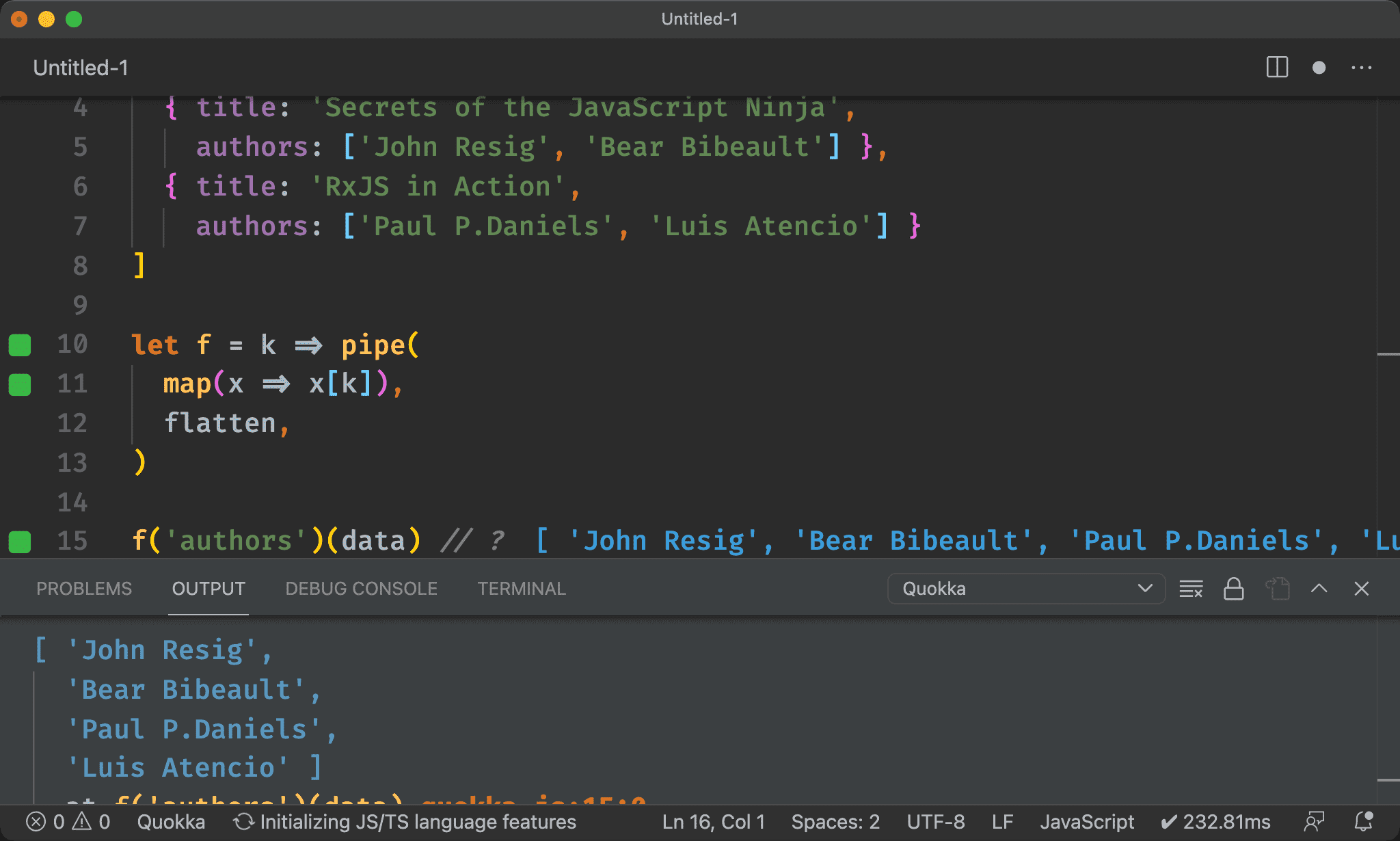
prop()
import { pipe, map, flatten, prop } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja',
authors: ['John Resig', 'Bear Bibeault'] },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action',
authors: ['Paul P.Daniels', 'Luis Atencio'] }
]
let f = k => pipe(
map(prop(k)),
flatten,
)
f('authors')(data) // ?
也可使用 prop() 使 map() 的 callback 也 Point-free。
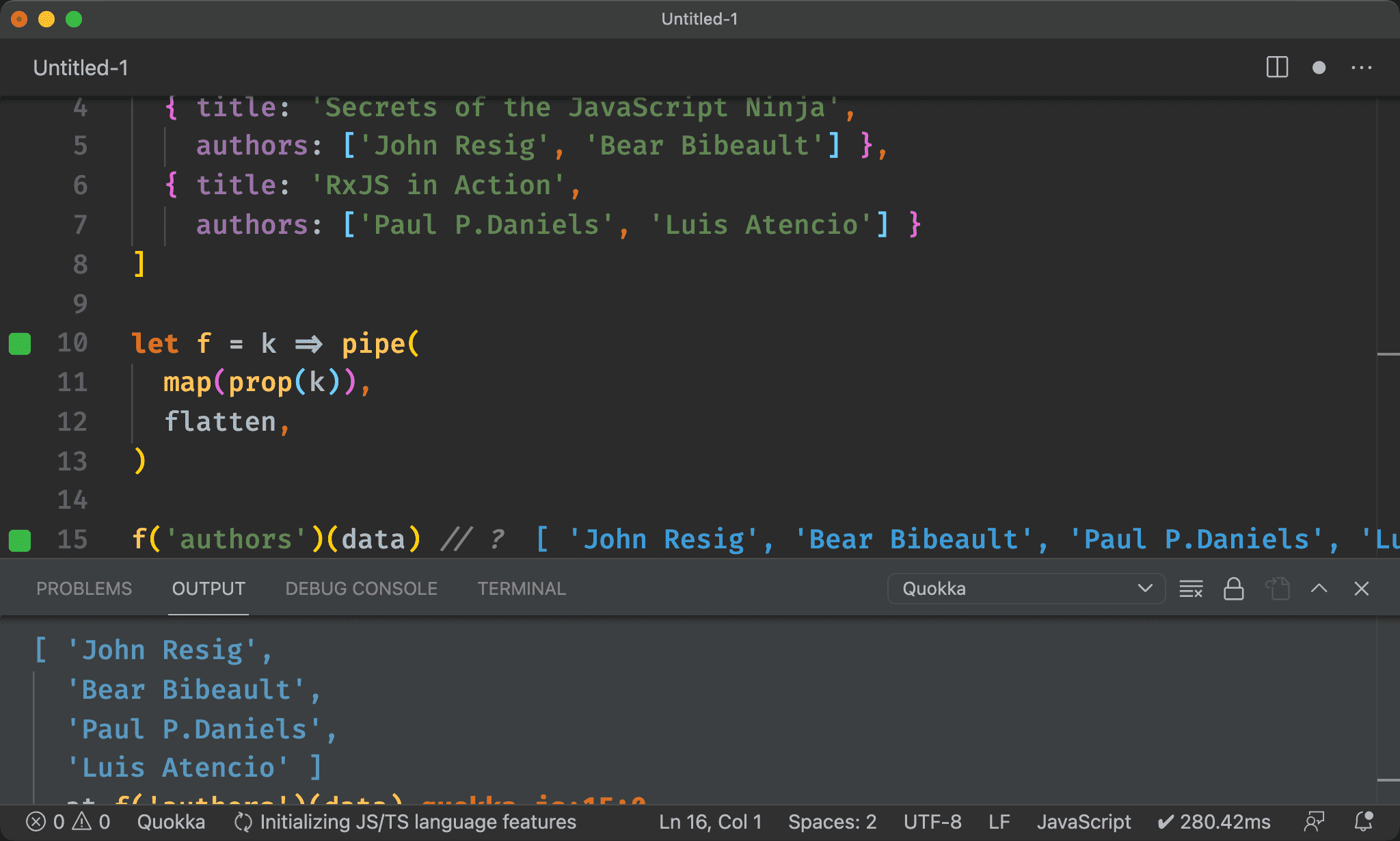
chain()
import { pipe, chain, prop } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja',
authors: ['John Resig', 'Bear Bibeault'] },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action',
authors: ['Paul P.Daniels', 'Luis Atencio'] }
]
let f = k => pipe(
chain(prop(k))
)
f('authors')(data) // ?
pipe(map, flatten) 實在太常使用,Ramda 另外提供了 chain()。
chain()
(a → b) → [a] → [b]
相當於flatten()與map()組合
(a -> b):相當於 map function
[a]:data 為 Array
[b]:回傳攤平後的 Array
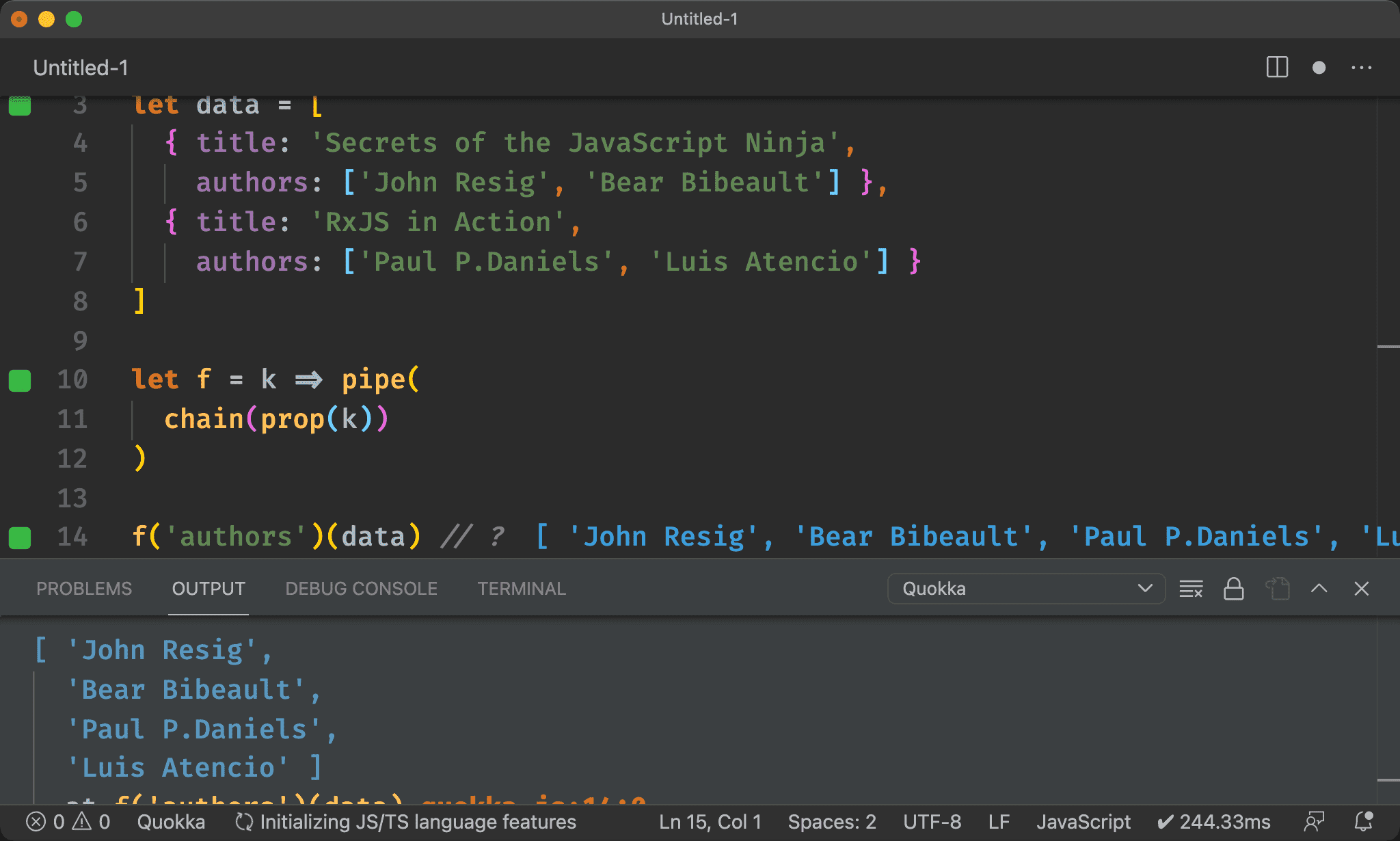
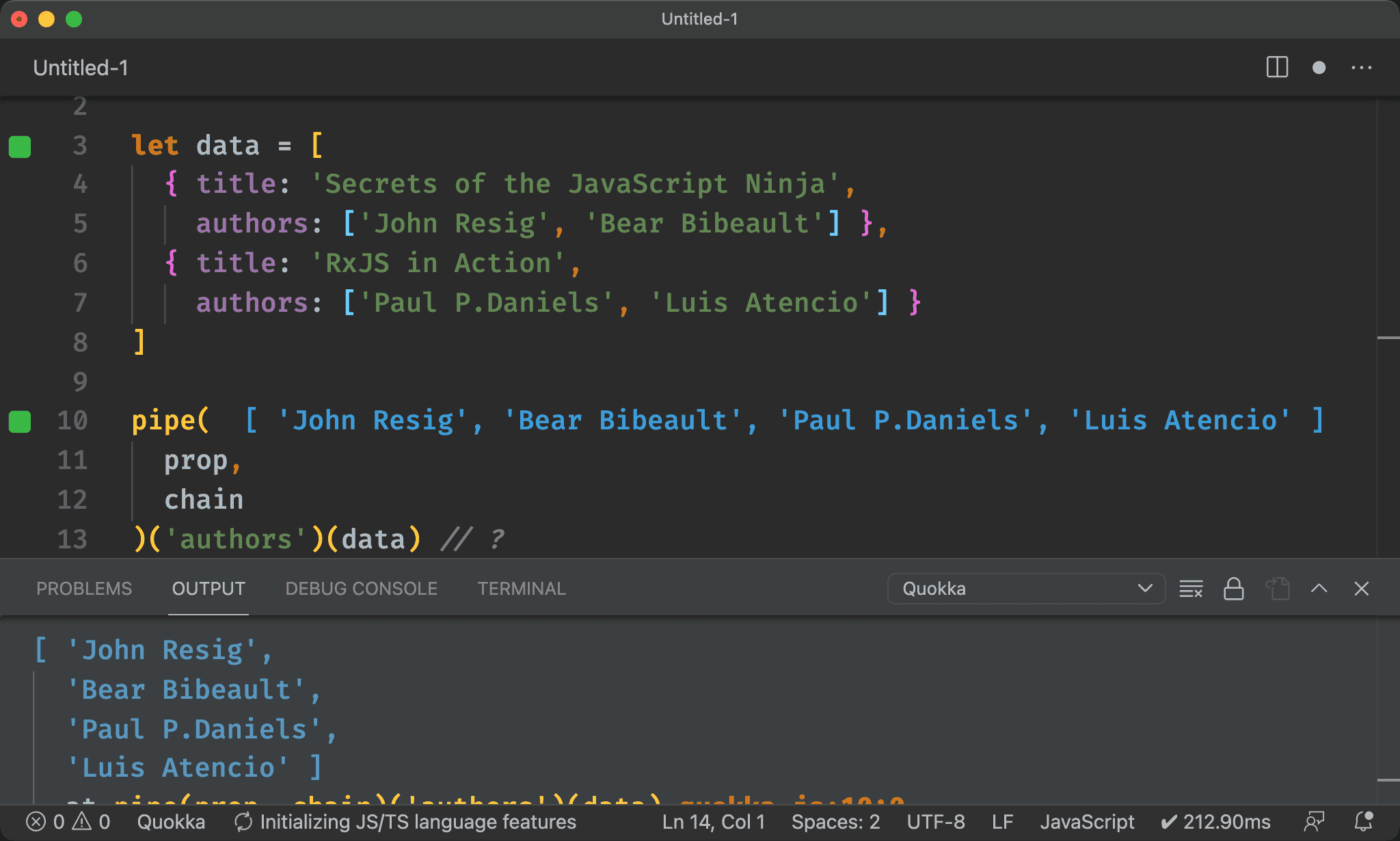
Point-free
import { pipe, chain, prop } from 'ramda'
let data = [
{ title: 'Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja',
authors: ['John Resig', 'Bear Bibeault'] },
{ title: 'RxJS in Action',
authors: ['Paul P.Daniels', 'Luis Atencio'] }
]
pipe(
prop,
chain
)('authors')(data) // ?
也可使用 pipe() 將 prop() 與 chain() 組合起來完全 Point-free。
Conclusion
- 當
chain()搭配 Array 時,與 ES2019 的flatMap()完全相同,都可將 Nested Array 攤平