ECMAScript 雖然是 Dynamic Type Language,但並不代表 Variable 沒有 Type,只是其內建獲得 Type 方法包含太多 驚喜,成為備受爭議部分。本文整理出 4 種獲得 Type 方式,各有其優缺點,最後自訂 typeof_(),可判斷各種 Type。
Version
macOS Mojave 10.14.5
VS Code 1.36.1
Quokka 1.0.236
ECMAScript 5
Ramda 0.26.1
Type
本文將介紹 5 種獲得 Type 方式:
- 內建的
typeof - 內建的
instanceof - 內建的
Object.prototype.toString() - Ramda 的
is() - 自訂
typeof_()
Number
Number 共有 3 種建立方法:
- Number literal
- Number function
- Number constructor
實務上最常使用 number literal,轉型時會使用 number function (或使用 +),但 number constructor 實務上不建議使用。
import { is } from 'ramda';
/** typeof */
typeof 1; // ?
typeof Number(1); // ?
typeof new Number(1); // ?
/** instanceof */
1 instanceof Number; // ?
Number(1) instanceof Number; // ?
new Number(1) instanceof Number; // ?
/** Object.prototype.toString() */
Object.prototype.toString.call(1); // ?
Object.prototype.toString.call(Number(1)); // ?
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Number(1)); // ?
/** is() */
is(Number, 1); // ?
is(Number, Number(1)); // ?
is(Number, new Number(1)); // ?
typeof
- 對於 literal 或 function 所產生的 number 判斷如預期,會回傳
number - 對於 constructor 所產生的 number,會回傳
object,這是比較困擾之處
instanceof
- 對於 literal 或 function 所產生的 number 判斷如預期,會回傳
false - 對於 constructor 所產生的 number 判斷如預期,會回傳
true
instanceof邏輯理論上沒錯,但typeof與instanceof都有其不足,無法同時判斷 literal、function 與 constructor 所建立的 number,實務上並不好用
Object.prototype.toString()
- 無論對於 literal、function、constructor 所產生的 number,都回傳
number
Ramda 之 is()
- 無論對於 literal、function、constructor 所產生的 number,都回傳
true
Object.prototype.toString()與is()都能同時判斷 literal、function 與 constructor 所產生的 number,實務上比較好用
String
String 共有 3 種建立方法:
- String literal
- String function
- String constructor
實務上最常使用 string literal,轉型時會使用 string function (或使用 + ''),但 string constructor 實務上不建議使用。
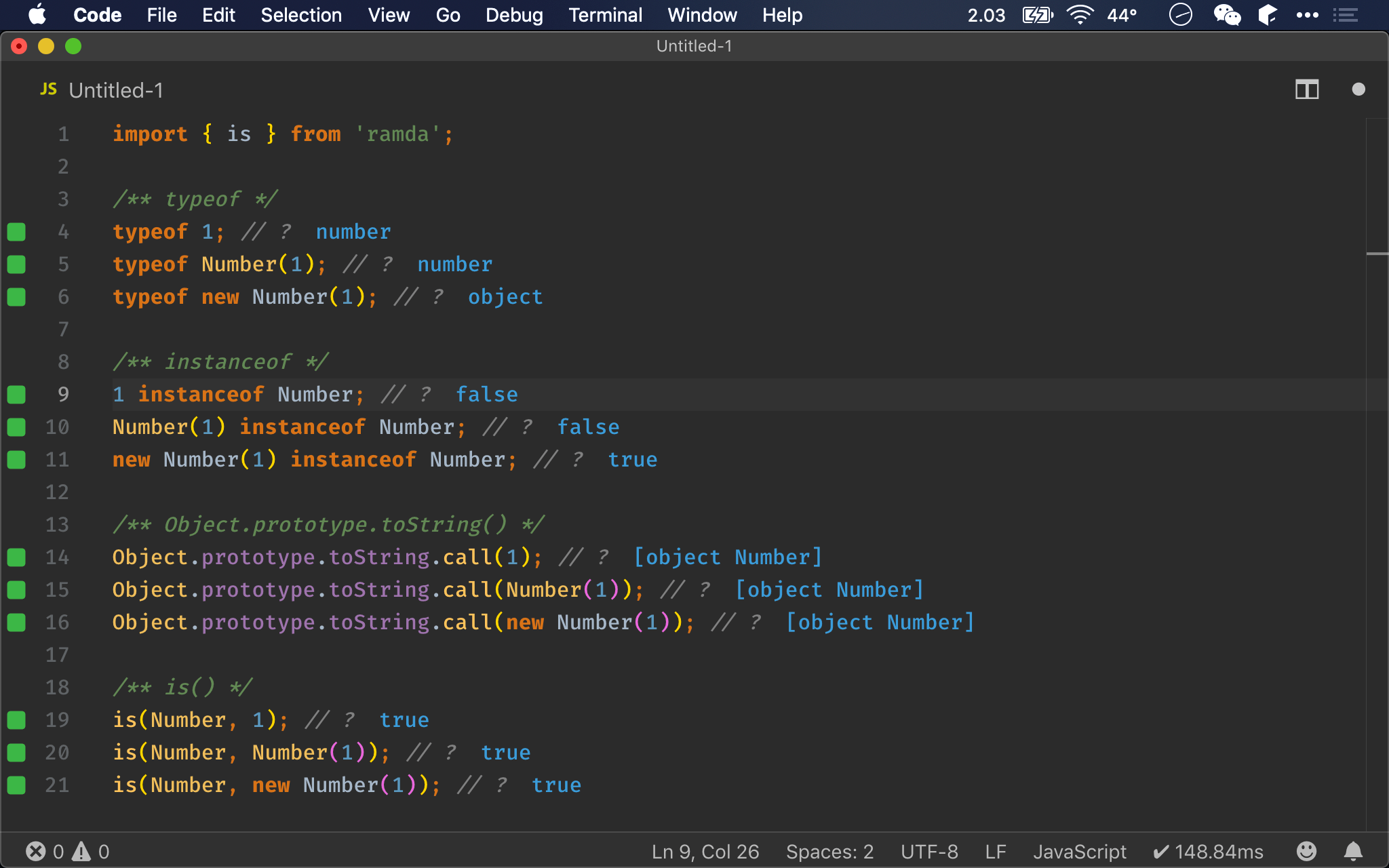
import { is } from 'ramda';
/** typeof */
typeof 'abc'; // ?
typeof String('abc'); // ?
typeof new String('abc'); // ?
/** instanceof */
'abc' instanceof String; // ?
String('abc') instanceof String; // ?
new String('abc') instanceof String; // ?
/** Object.prototype.toString() */
Object.prototype.toString.call('abc'); // ?
Object.prototype.toString.call(String('abc')); // ?
Object.prototype.toString.call(new String('abc')); // ?
/** is() */
is(String, 'abc'); // ?
is(String, String('abc')); // ?
is(String, new String('abc')); // ?
typeof
- 對於 literal 或 function 所產生的 string 判斷如預期,會回傳
string - 對於 constructor 所產生的 string,會回傳
object,這是比較困擾之處
instanceof
- 對於 literal 或 function 所產生的 string 判斷如預期,會回傳
false - 對於 constructor 所產生的 string 判斷如預期,會回傳
true
instanceof邏輯理論上沒錯,但typeof與instanceof都有其不足,無法同時判斷 literal、function 與 constructor 所建立的 string,實務上並不好用
Object.prototype.toString()
- 無論對於 literal、function、constructor 所產生的 string,都回傳
string
Ramda 之 is()
- 無論對於 literal、function、constructor 所產生的 string,都回傳
true
Object.prototype.toString()與is()都能同時判斷 literal、function 與 constructor 所產生的 string,實務上比較好用
Boolean
Boolean 共有 3 種建立方法:
- Boolean literal
- Boolean function
- Boolean constructor
實務上最常使用 boolean literal,轉型時會使用 boolean function (或使用 !!,且 ECMAScript 支援 boolean coercion,會自動轉型),但 boolean constructor 實務上不建議使用。
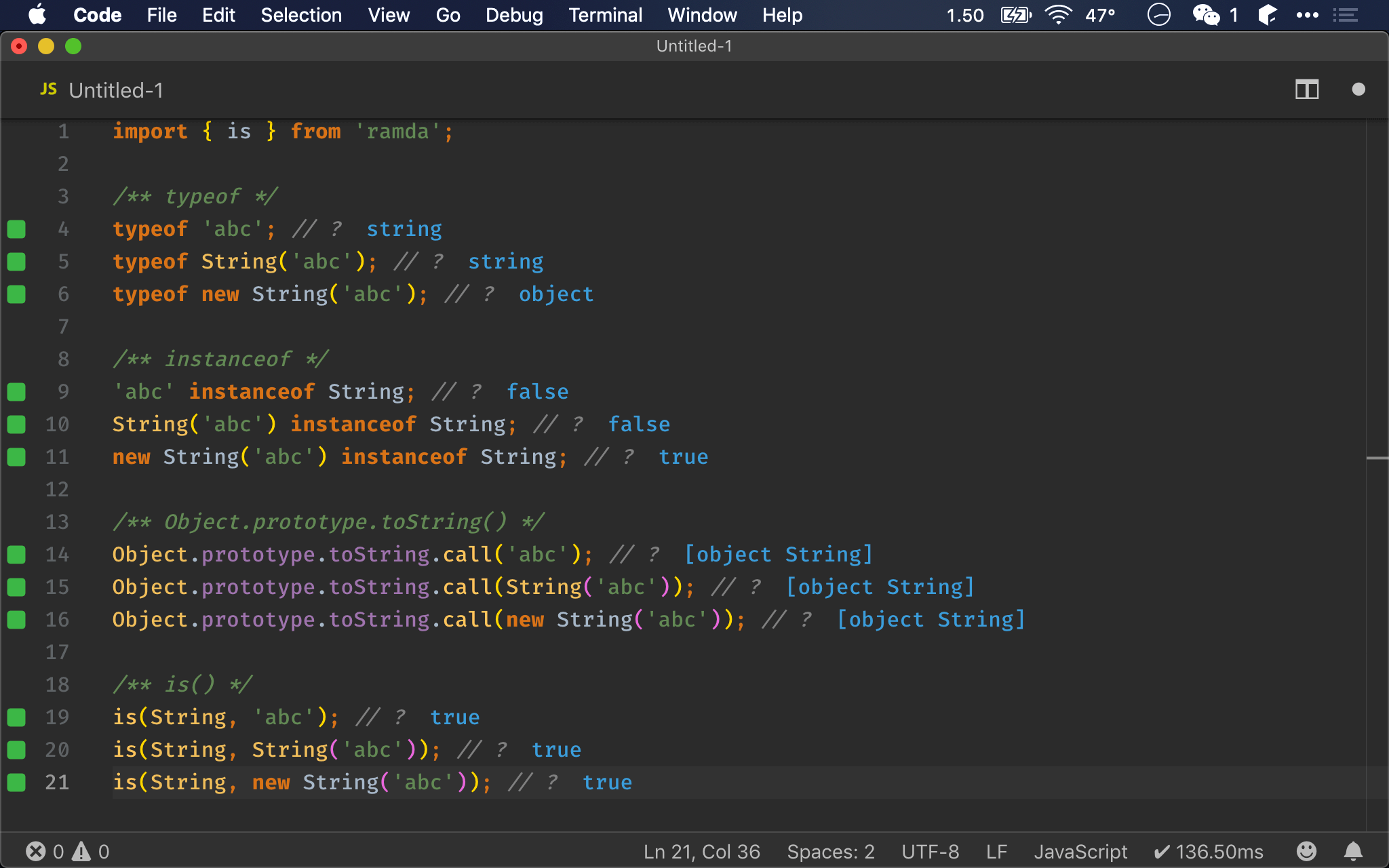
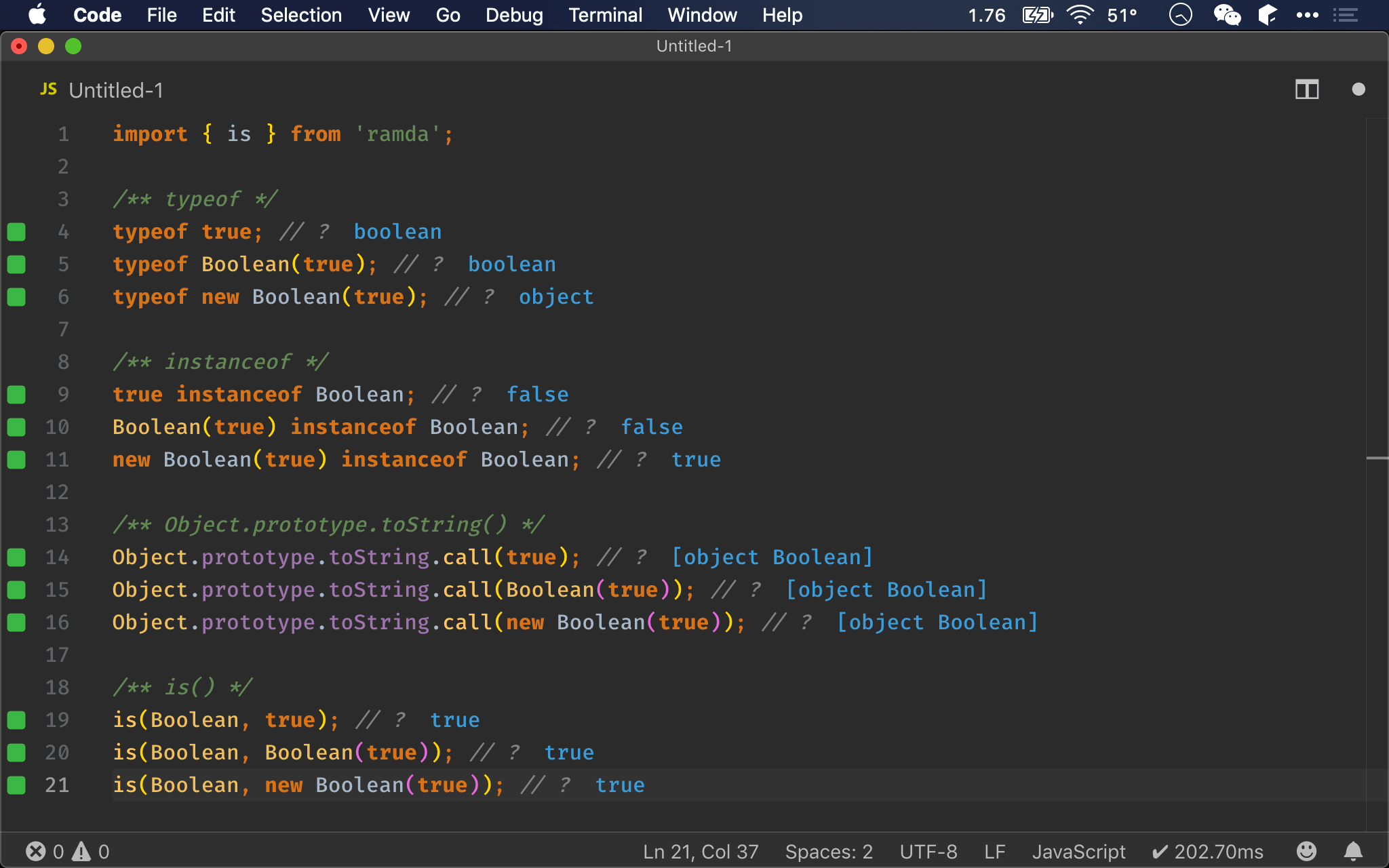
import { is } from 'ramda';
/** typeof */
typeof true; // ?
typeof Boolean(true); // ?
typeof new Boolean(true); // ?
/** instanceof */
true instanceof Boolean; // ?
Boolean(true) instanceof Boolean; // ?
new Boolean(true) instanceof Boolean; // ?
/** Object.prototype.toString() */
Object.prototype.toString.call(true); // ?
Object.prototype.toString.call(Boolean(true)); // ?
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Boolean(true)); // ?
/** is() */
is(Boolean, true); // ?
is(Boolean, Boolean(true)); // ?
is(Boolean, new Boolean(true)); // ?
typeof
- 對於 literal 或 function 所產生的 boolean 判斷如預期,會回傳
boolean - 對於 constructor 所產生的 boolean,會回傳
object,這是比較困擾之處
instanceof
- 對於 literal 或 function 所產生的 boolean 判斷如預期,會回傳
false - 對於 constructor 所產生的 boolean 判斷如預期,會回傳
true
instanceof邏輯理論上沒錯,但typeof與instanceof都有其不足,無法同時判斷 literal、function 與 constructor 所建立的 boolean,實務上並不好用
Object.prototype.toString()
- 無論對於 literal、function、constructor 所產生的 boolen,都回傳
boolean
Ramda 之 is()
- 無論對於 literal、function、constructor 所產生的 boolean,都回傳
true
Object.prototype.toString()與is()都能同時判斷 literal、function 與 constructor 所產生的 boolean,實務上比較好用
Undefined
Undefined 在 ECMAScript 已獨立成一個 type,其值是 undefined。
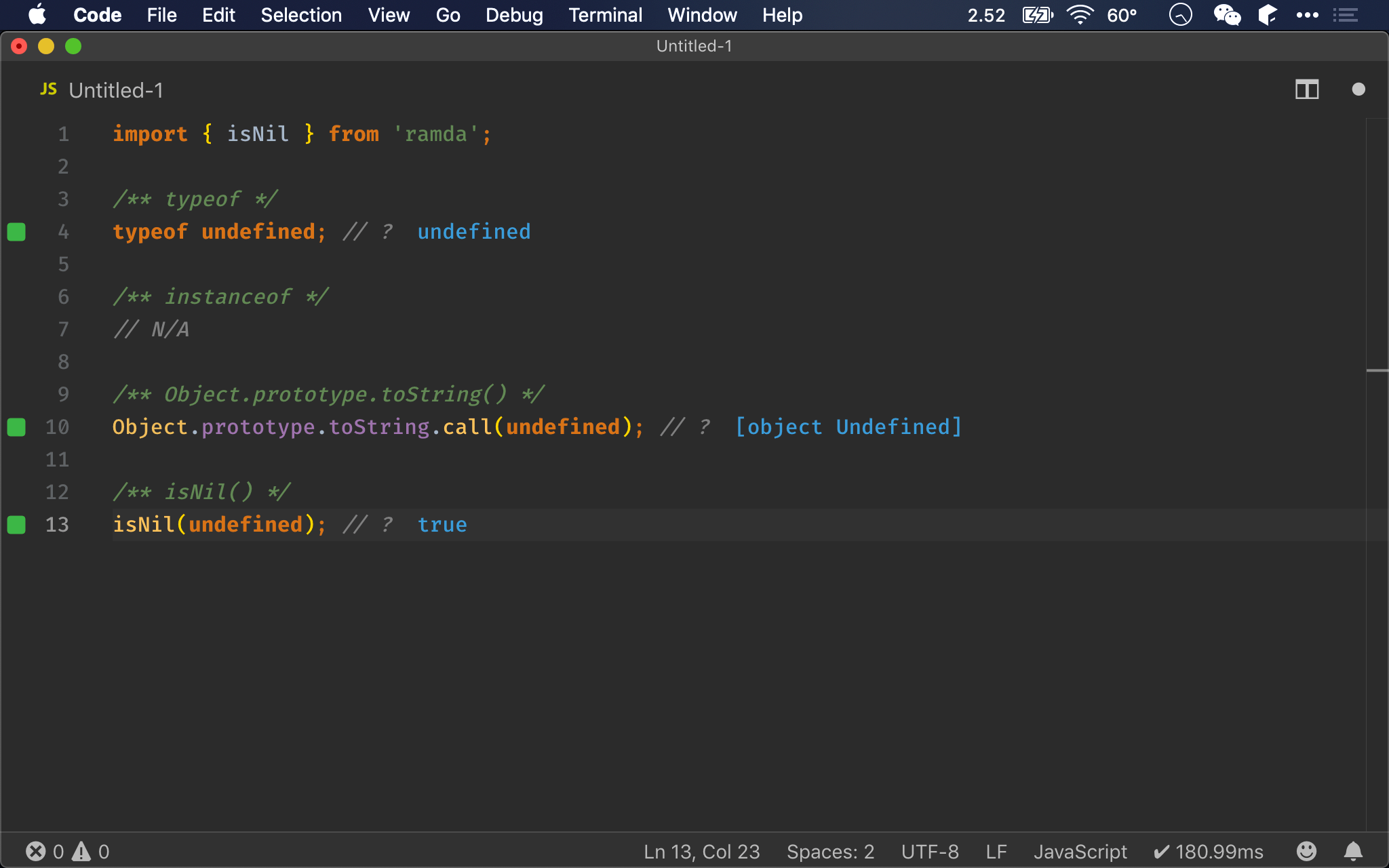
import { isNil } from 'ramda';
/** typeof */
typeof undefined; // ?
/** instanceof */
// N/A
/** Object.prototype.toString() */
Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined); // ?
/** isNil() */
isNil(undefined); // ?
typeof
- 判斷
undefined會如預期回傳undefined
instanceof
- 無法判斷
undefined,因為不存在 undefined constructor
Object.prototype.toString()
- 判斷
undefined會如預期回傳undefined
isNil()
is()無法判斷undefined,要改用isNil(),如預期回傳true
Ramda 使用
isNil()使得 type 判斷分裂成兩個 function,實務上沒那麼好用,目前只有Object.prototype.toString()能達到單一 function 判斷所有 type
Null
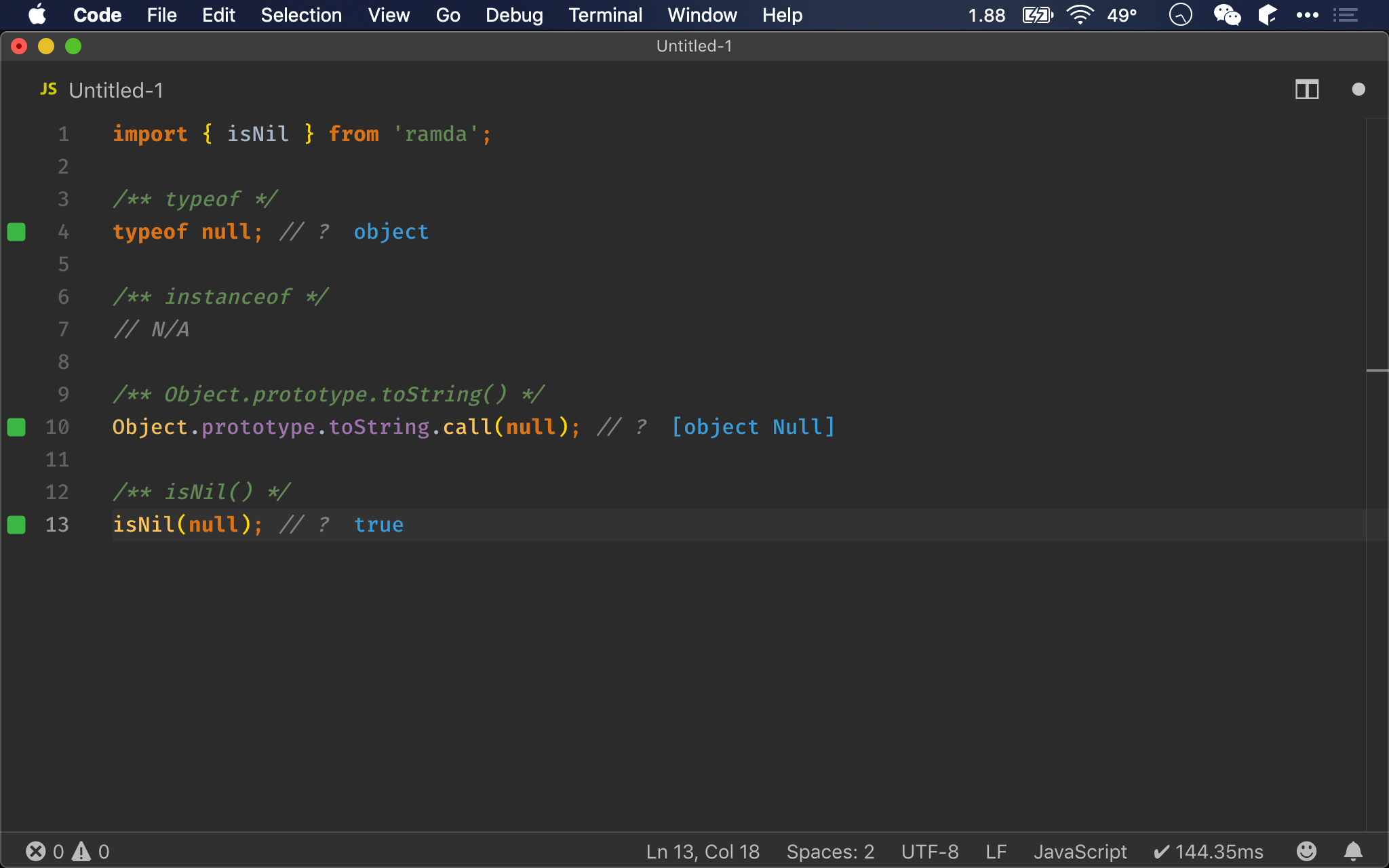
Null 在 ECMAScript 已獨立成一個 type,其值是 null。
import { isNil } from 'ramda';
/** typeof */
typeof null; // ?
/** instanceof */
// N/A
/** Object.prototype.toString() */
Object.prototype.toString.call(null); // ?
/** isNil() */
isNil(null); // ?
typeof
- 判斷
null會如預期回傳object,這是已知的 bug,但因為歷史因素,無法修改,已成 feature
instanceof
- 無法判斷
null,因為不存在 null constructor
Object.prototype.toString()
- 判斷
null會如預期回傳null
isNil()
is()無法判斷null,要改用isNil(),如預期回傳true
Ramda 使用
isNil()使得 type 判斷分裂成兩個 function,實務上沒那麼好用,目前只有Object.prototype.toString()能達到單一 function 判斷所有 type
Object
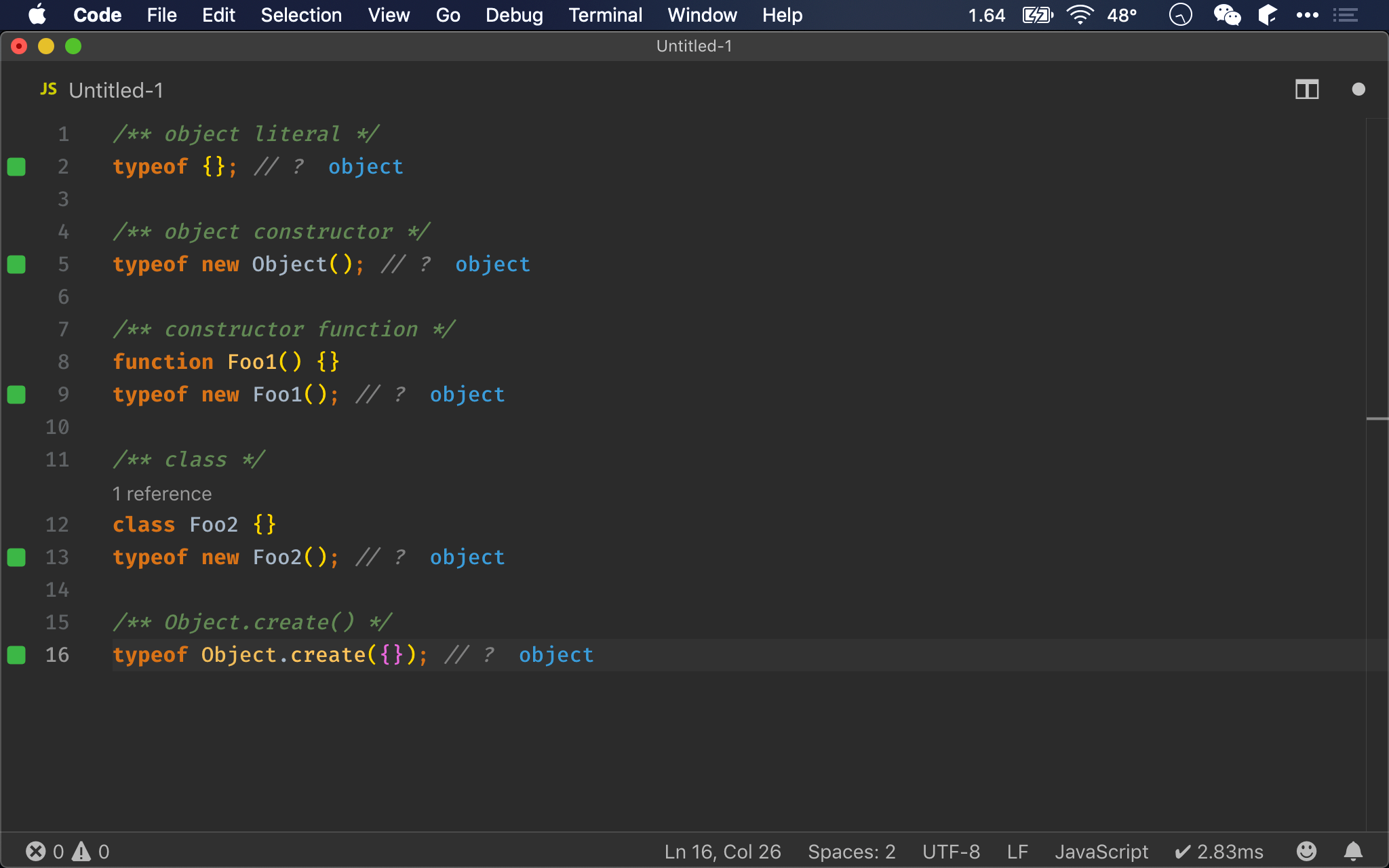
Object 共有 5 種建立方法:
- Object literal
- Object constructor
- Constructor function
- Class
- Object.create()
實務上最常使用 object literal,而 constructor function、class 與 Object.create() 都有其適用時機,但 object constructor 實務上不建議使用。
/** object literal */
typeof {}; // ?
/** object constructor */
typeof new Object(); // ?
/** constructor function */
function Foo1() {}
typeof new Foo1(); // ?
/** class */
class Foo2 {}
typeof new Foo2(); // ?
/** Object.create() */
typeof Object.create({}); // ?
typeof
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 object,都會如預期回傳
object
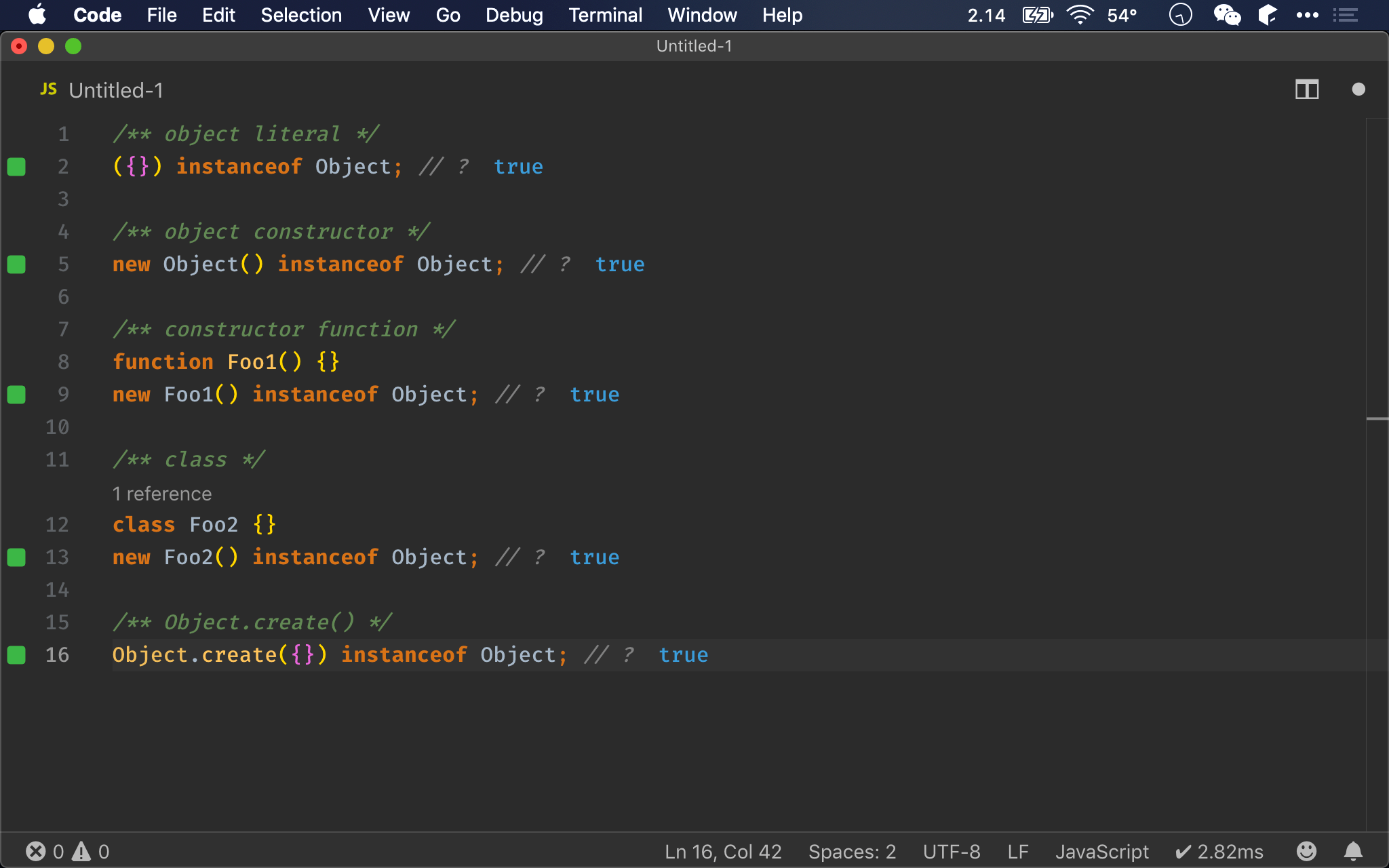
/** object literal */
({}) instanceof Object; // ?
/** object constructor */
new Object() instanceof Object; // ?
/** constructor function */
function Foo1() {}
new Foo1() instanceof Object; // ?
/** class */
class Foo2 {}
new Foo2() instanceof Object; // ?
/** Object.create() */
Object.create({}) instanceof Object; // ?
instanceof
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 object,都會如預期回傳
true
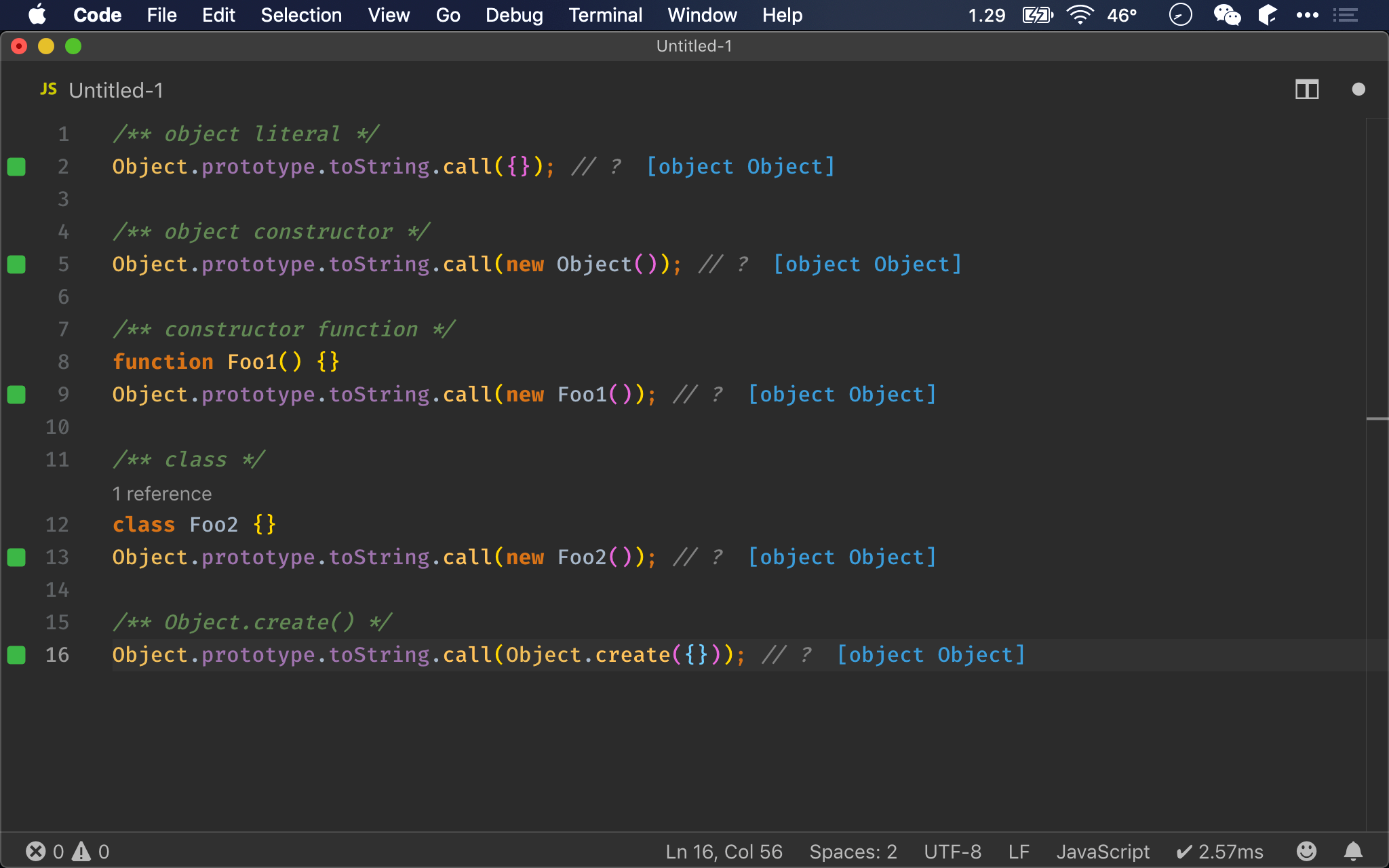
/** object literal */
Object.prototype.toString.call({}); // ?
/** object constructor */
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Object()); // ?
/** constructor function */
function Foo1() {}
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Foo1()); // ?
/** class */
class Foo2 {}
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Foo2()); // ?
/** Object.create() */
Object.prototype.toString.call(Object.create({})); // ?
Object.prototype.toString()
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 object,都會如預期回傳
object
import { is } from 'ramda';
/** object literal */
is(Object, {}); // ?
/** object constructor */
is(Object, new Object()); // ?
/** constructor function */
function Foo1() {}
is(Object, new Foo1()); // ?
/** class */
class Foo2 {}
is(Object, new Foo2()); // ?
/** Object.create() */
is(Object, Object.create({})); // ?
is()
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 object,都會如預期回傳
true
對於 object,無論使用
typeof、instanceof、Object.prototype.toString()或is(),都可以如預期判斷出 object
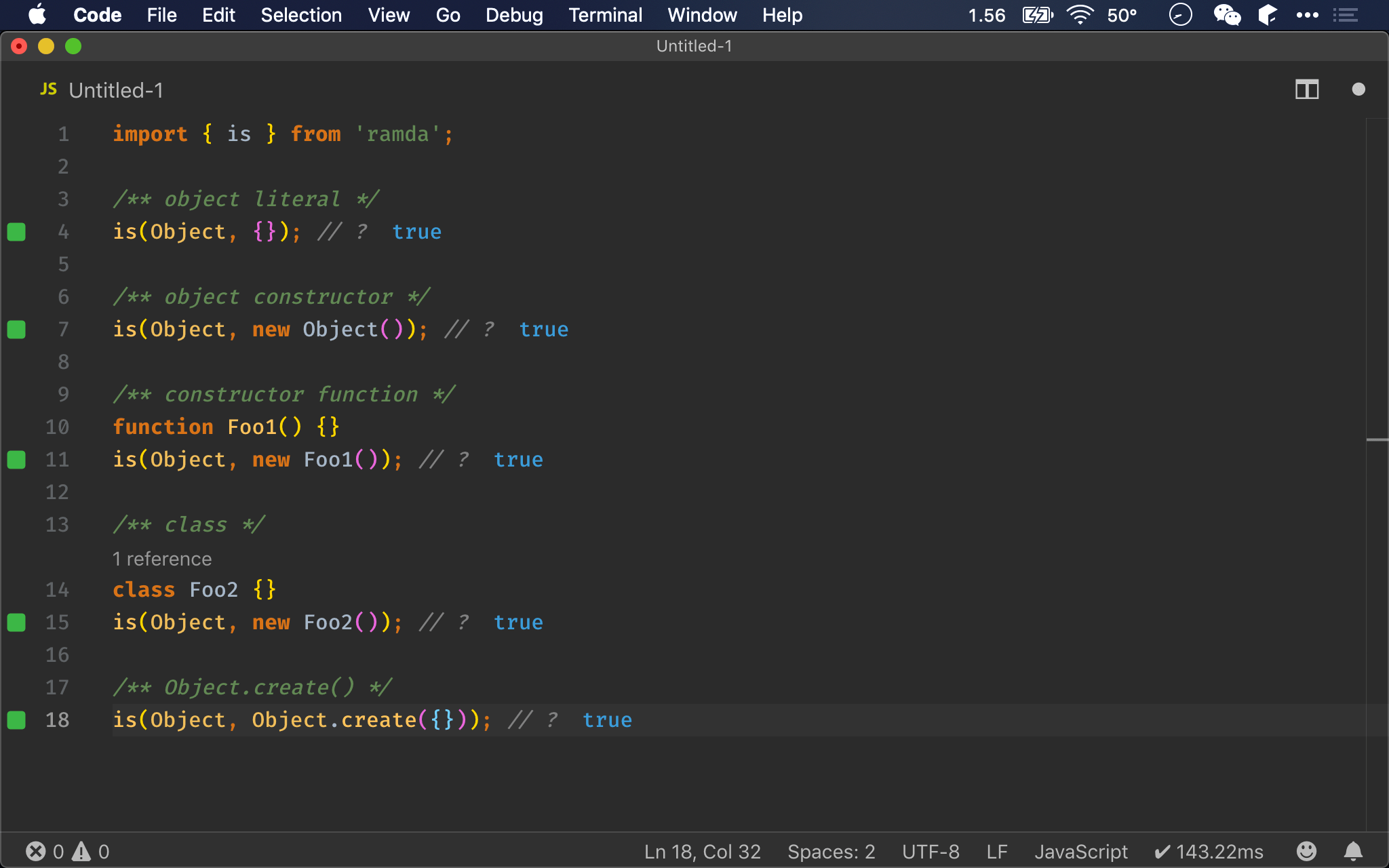
Array
Array 共有 3 種建立方法:
- Array literal
- Array function
- Array constructor
實務上最常使用 array literal,建立 empty array 時會使用 array function,但 array constructor 實務上不建議使用 (因為效果與 array function 一樣)。
import { is } from 'ramda';
/** typeof */
typeof []; // ?
typeof Array(0); // ?
typeof new Array(0); // ?
/** instanceof */
[] instanceof Array; // ?
Array(0) instanceof Array; // ?
new Array(0) instanceof Array; // ?
/** Object.prototype.toString() */
Object.prototype.toString.call([]); // ?
Object.prototype.toString.call(Array(0)); // ?
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Array(0)); // ?
/** is() */
is(Array, []); // ?
is(Array, Array(0)); // ?
is(Array, new Array(0)); // ?
typeof
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 array,都無法如預期回傳
array,而是回傳object,這是比較困擾之處
instanceof
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 object,都會如預期回傳
true
Object.prototype.toString()
- 無論對於 literal、function、constructor 所產生的 array,都回傳
array
Ramda 之 is()
- 無論對於 literal、function、constructor 所產生的 array,都回傳
true
instanceof、Object.prototype.toString()與is()都能同時判斷 literal、function 與 constructor 所產生的 array,實務上比較好用,但typeof則完全誤判為 object
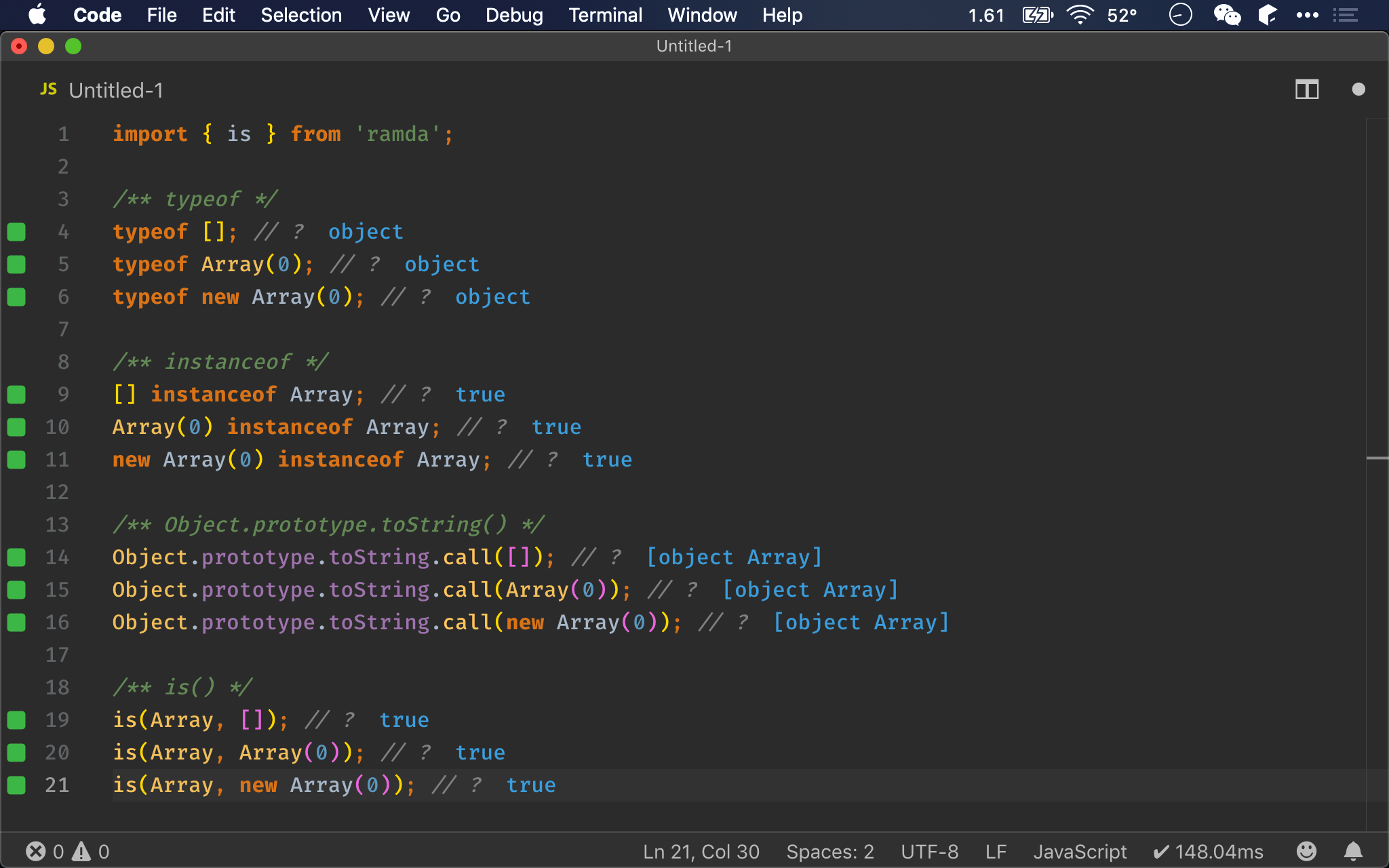
Function
Function 共有 4 種建立方法:
- Function declaration
- Function expression
- Function constructor
- Arrow function
實務上最常使用 function expression 與 arrow function,function declaration 則漸漸較少使用,但 function constructor 使用機會更少,除非想在 runtime 動態湊出 function。
/** function declaration */
function fun() {}
typeof fun; // ?
/** function expression */
typeof function() {}; // ?
/** function constructor */
typeof new Function(); // ?
/** arrow function */
typeof (() => {}); // ?
typeof
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 function,都會如預期回傳
function
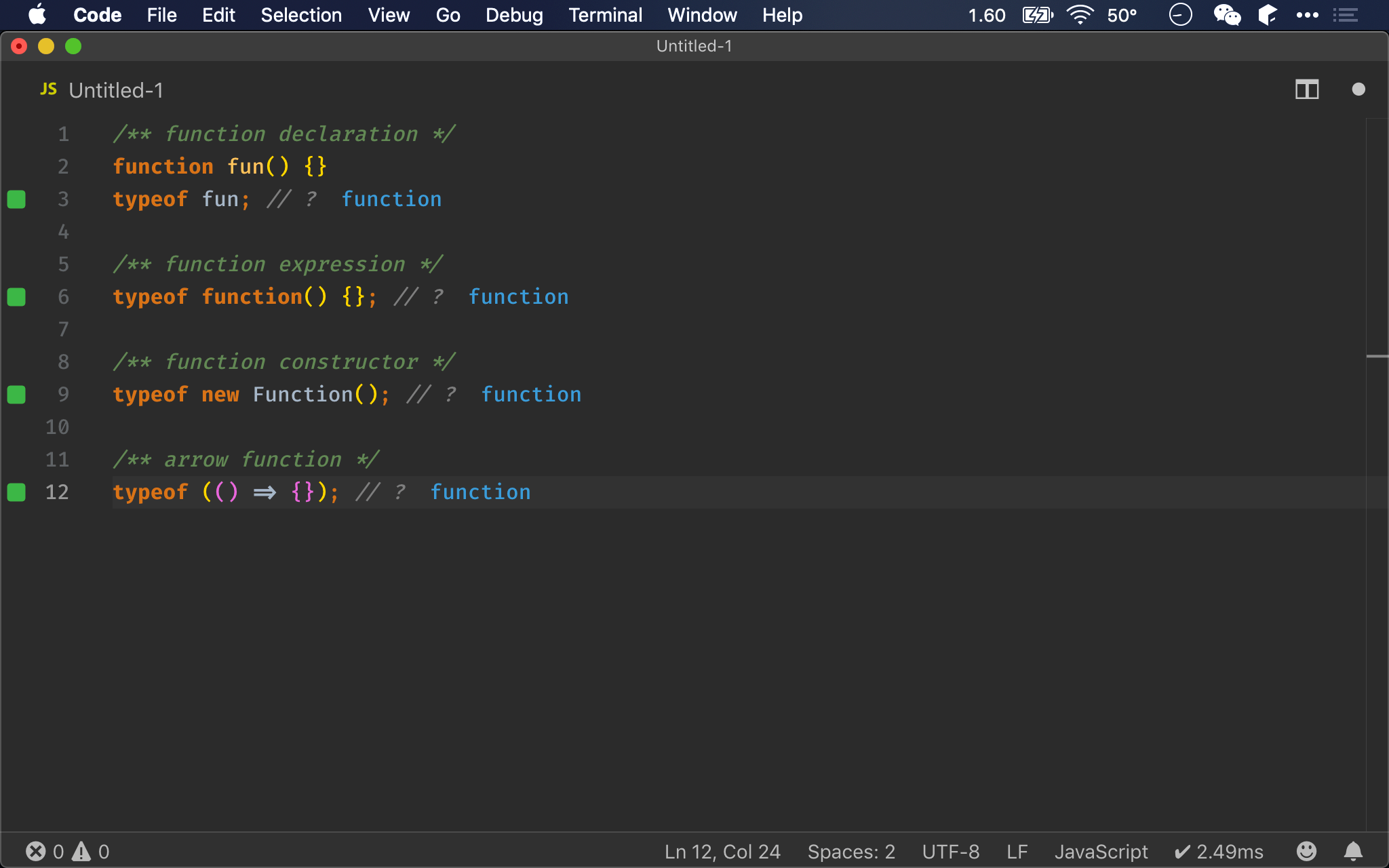
/** function declaration */
function fun() {}
fun instanceof Function; // ?
/** function expression */
(function() {}) instanceof Function; // ?
/** function constructor */
new Function() instanceof Function; // ?
/** arrow function */
(() => {}) instanceof Function; // ?
instanceof
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 function,都會如預期回傳
true
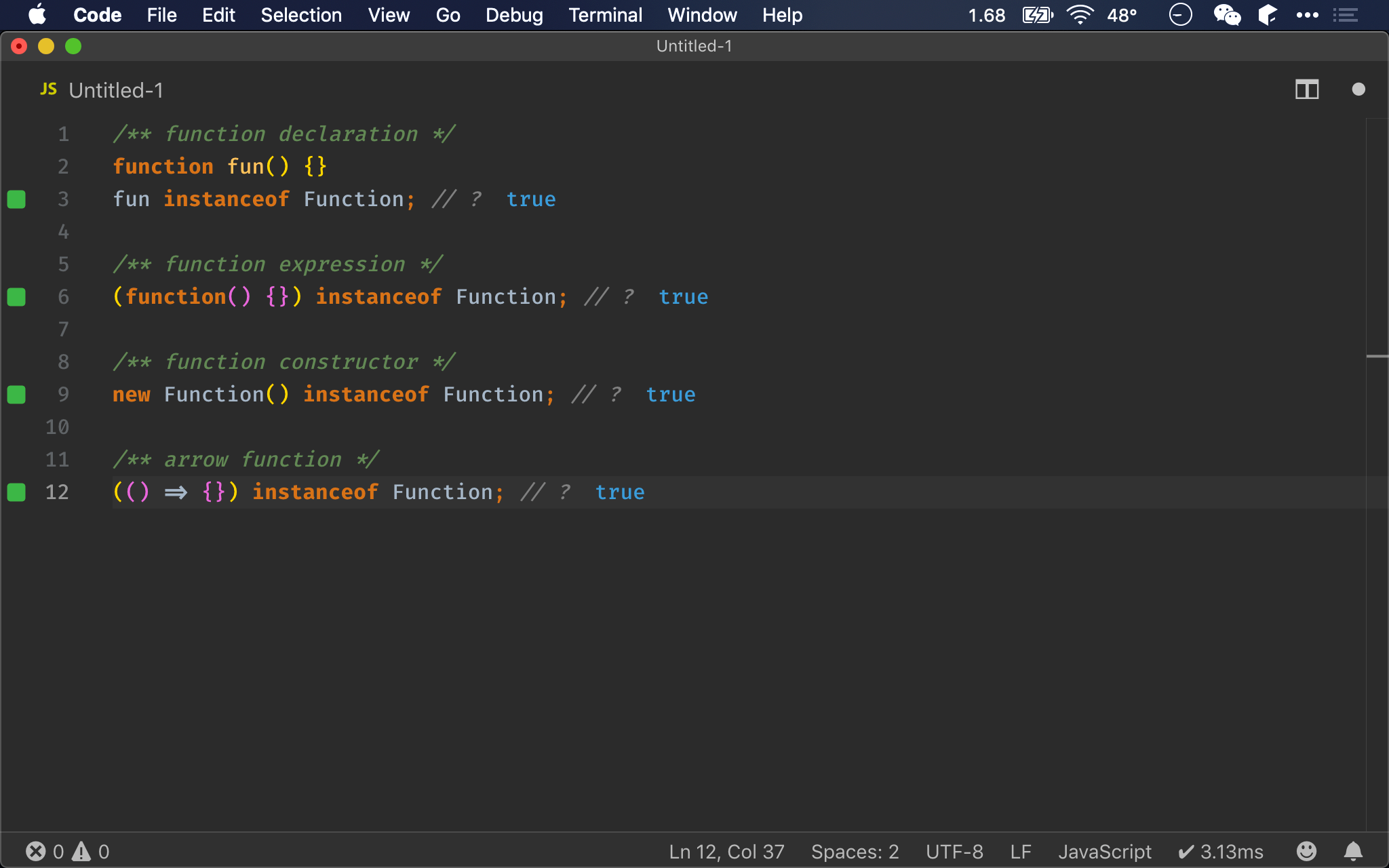
/** function declaration */
function fun() {}
Object.prototype.toString.call(fun); // ?
/** function expression */
Object.prototype.toString.call(function() {}); // ?
/** function constructor */
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Function()); // ?
/** arrow function */
Object.prototype.toString.call(() => {}); // ?
Object.prototype.toString()
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 function,都會如預期回傳
function
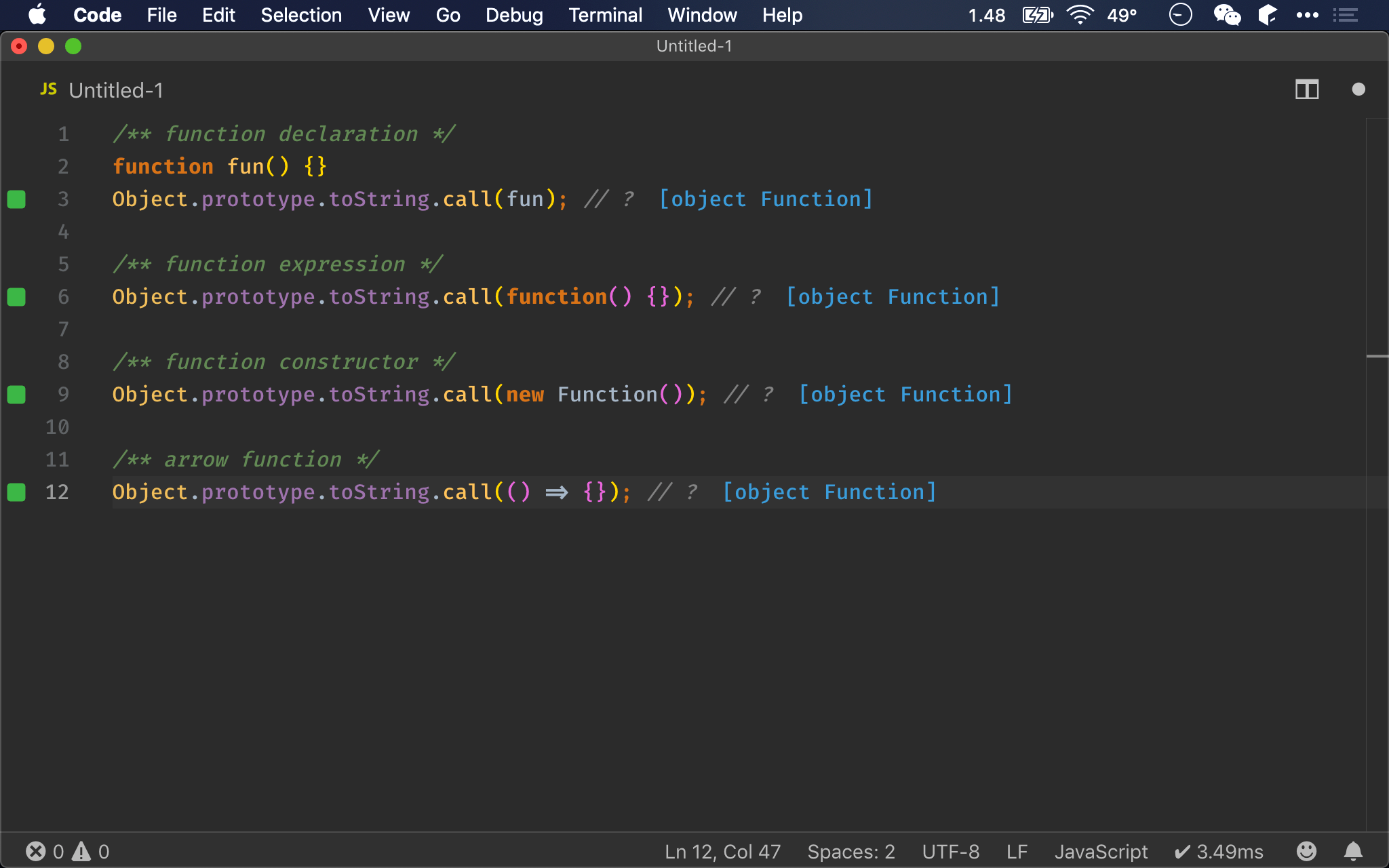
import { is } from 'ramda';
/** function declaration */
function fun() {}
is(Function, fun); // ?
/** function expression */
is(Function, function() {}); // ?
/** function constructor */
is(Function, new Function()); // ?
/** arrow function */
is(Function, () => {}); // ?
is()
- 無論使用哪一種方式建立 function,都會如預期回傳
true
對於 function,無論使用
typeof、instanceof、Object.prototype.toString()或is(),都可以如預期判斷出 function
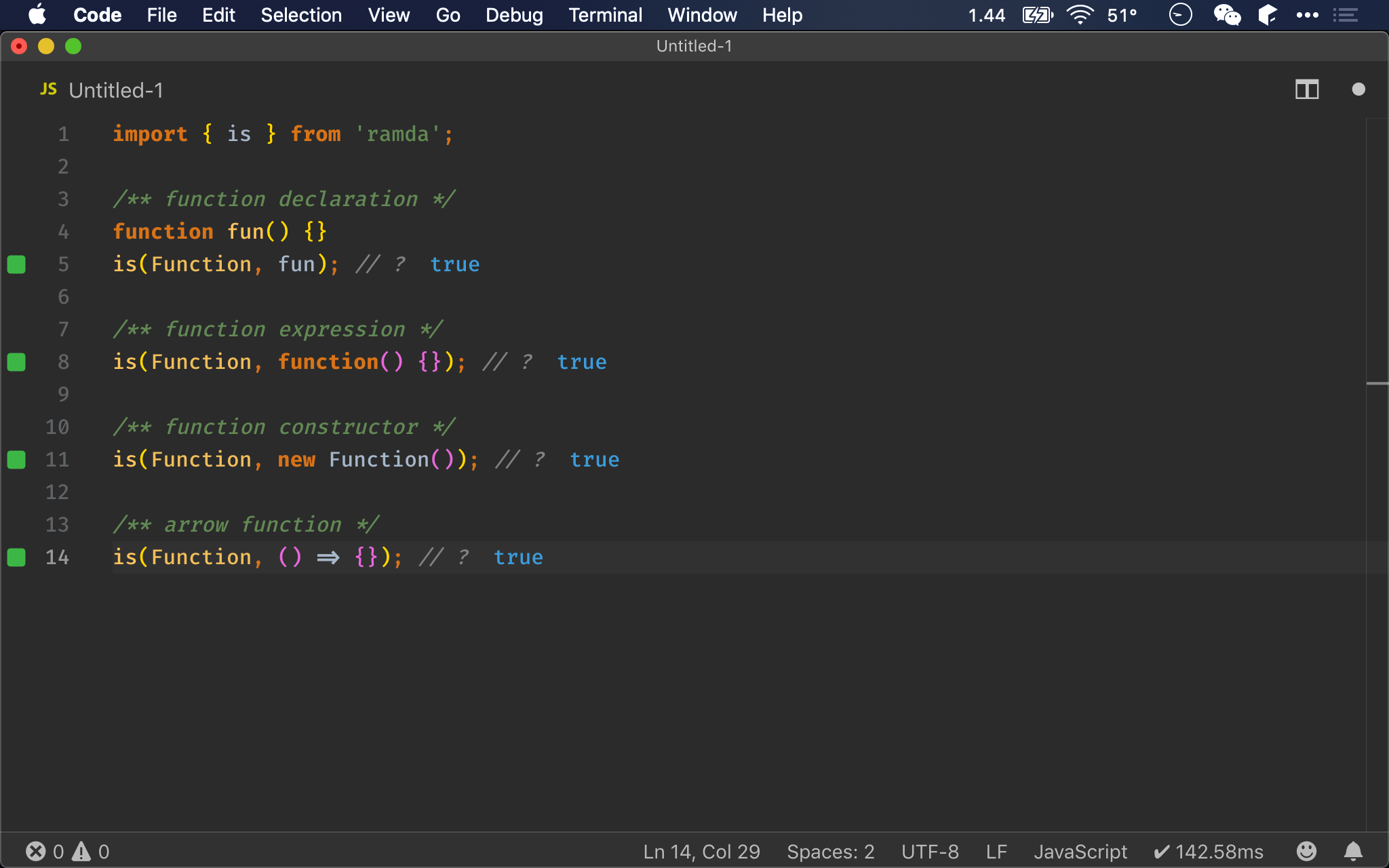
typeof_()
// typeof_ :: * -> String
let typeof_ = data => Object.prototype.toString.call(data).slice(8, -1).toLowerCase();
typeof_(1); // ?
typeof_(new Number(1)); // ?
typeof_(new String('abc')); // ?
typeof_(new String('abc')); // ?
typeof_(true); // ?
typeof_(new Boolean(true)); // ?
typeof_(undefined); // ?
typeof_(null); // ?
typeof_({}); // ?
typeof_([]); // ?
typeof_(()=>{}); // ?
根據以上經驗,我們發現只有一種方式能抓到所有 type 都正確,那就是 Object.prototype.toString(),但其回傳還包含 [Object ] 等不需要部分,且 type 是第一個字大寫,因此只要稍作加工,就可以與 typeof 完全一樣。
第 1 行
// typeof_ :: * -> String
let typeof_ = data => Object.prototype.toString.call(data).slice(8, -1).toLowerCase();
一樣使用 Object.prototype.toString(),利用 slice() 抓到我們要的部分,最後再 toLowerCase() 轉成全小寫。
Conclusion
- 使用 literal 或 function 建立的 data,推薦使用
typeof,但typeof無法判斷null(可判斷nudefined) 與以 constructor 建立的 data,也無法判斷 array - 使用 constructor 建立的 data,推薦使用
instanceof,使用typeof只會傳回object instanceof無法測試null與undefined,因為沒有 constructor- Ramda 的
is()無法測試undefind與null,nullable (undefined與null) 必須使用isNil(),因此也無法達成單一 function 判斷所有 type Object.prototype.toString().call()最完整,單一 function 可以判斷所有 typetypeof null是 ECMAScript 有名的 bug,已成為 feature- 自己寫的
typeof_(),則是以Object.prototype.toString()為基礎,再搭配slice()與toLowerCase(),打造出全型別判斷的typeof_()
Reference
MDN, typeof
MDN, instanceof
MDN, Object.prototype.toString()
MDN, String.prototype.slice()
MDN, String.prototype.toLowerCase()
Ramda, is()
Ramda, isNil()