除了一般語言都有的 Global Scope 與 Local Scope 外, ECMAScript 還有一個很特殊的 Lexical Scope,這導致了 Closure 與日後 Functional Programming 發展。
Version
ECMAScript 2015
Lexical Scope
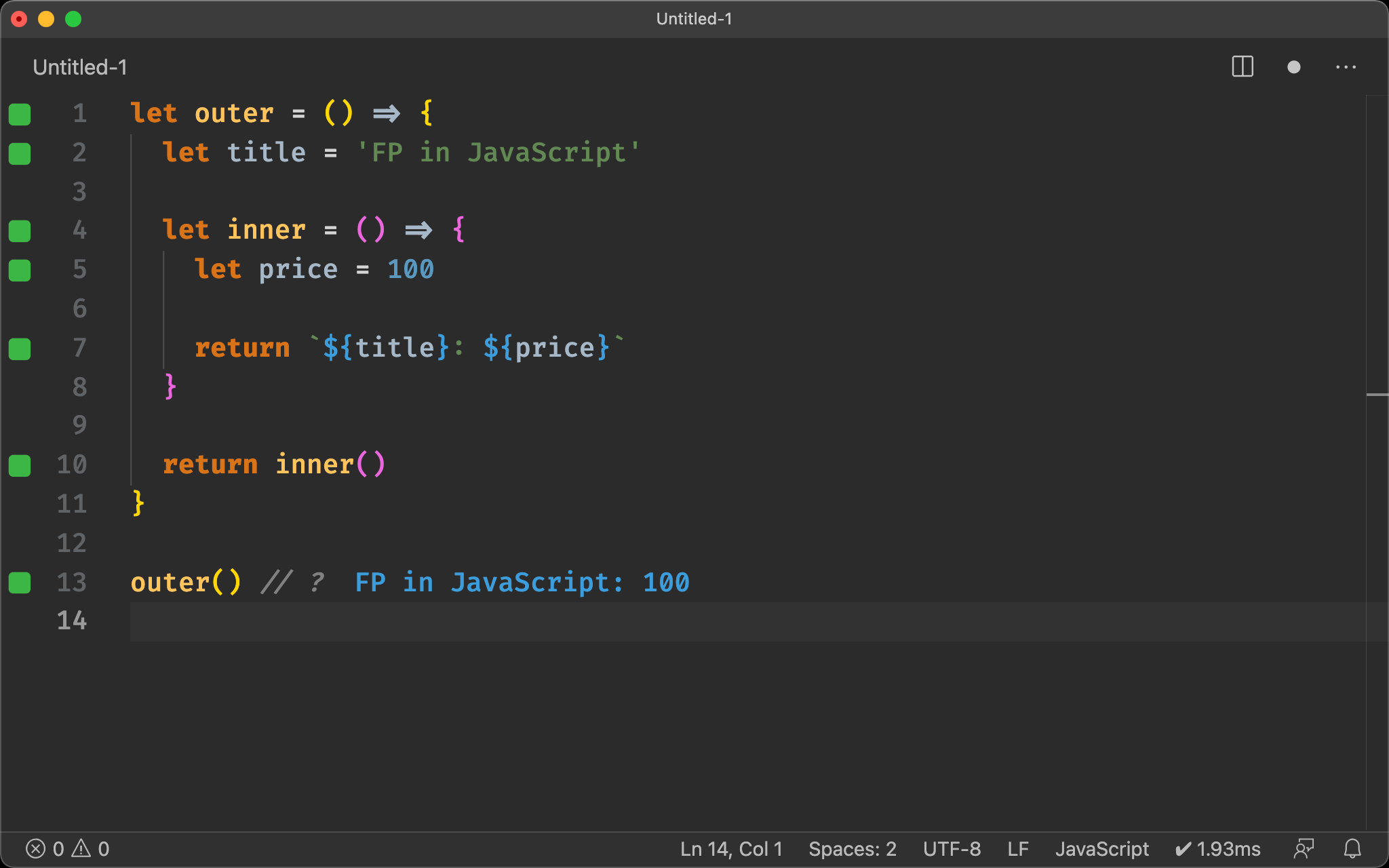
let outer = () => {
let title = 'FP in JavaScript'
let inner = () => {
let price = 100
return `${title}: ${price}`
}
return inner()
}
outer() // ?
使用 arrow function 定義 function 與 let 定義 variable。
當執行 outer() 時,會先定義 title,然後再定義 inner()。
在 outer() 內執行 inner() 時,會發現 inner() 的 local scope 只有 price 但沒有 title,且 global scope 也沒有 title。
ECMAScript 除了 local scope 與 global scope 外,另有獨特的 lexical scope。
Q:為何稱為 lexical 呢 ?
ECMAScript 在執行前,會將整個 code 都 parse 一遍,而不是如普通 script 簡單地一行一行執行,此稱為 lexing phase。
inner() 為在 outer() 內定義的 inner function,而 outer() 為 inner() 的 outer function。
在 lexing phase 時會將 outer function 的 variable 賦予 inner function 存取能力,稱為 lexical scope,因此 inner() 能存取 title。
由此可發現 lexical scope 是在 ECMAScript 執行前的 lexing phase 就決定,有別於 this 在 runtime 才決定的 dynamic scope。
Lexical scope 可簡單使用以下公式表示:
Outer function 的 local scope === Inner function 的 lexical scope
也就是 inner function 可不必透過 argument 傳遞,就能直接存取 outer function 的 variable,稱為 lexical scope。
Conclusion
- 由別於其他語言,ECMAScript 常在 function 內定義小 function 增加可讀性,而這些小 function 不需透過 argument 傳遞就可讀取 function 外的 variable,都是拜 lexical scope 之賜
- Inner function 除了透過 lexical scope 讀取 outer function 的 variable 外,甚至還能將其記住,這就進化成 closure 了
Reference
MDN, Lexical scoping
Tim Holt, What is Lexical Scope Anyway ?