ECMAScript 5 無論是 Function Declaration 或 Anonymous Function,都可以使用 this 搭配 call()、apply() 與 bind() 動態改變 this,ECMAScript 2015 支援了 Arrow Function 後,這對原本的 this 、call() 、apply() 與 bind() 有任何影響嗎 ?
Version
macOS Catalina 10.15
VS Code 1.38.1
Quokka 1.0.254
ECMAScript 5
ECMAScript 2015
ECMAScript 5
let counter = {
count: 0,
increment() {
setInterval(function() {
console.log(++this.count);
}, 1000);
},
};
counter.increment();
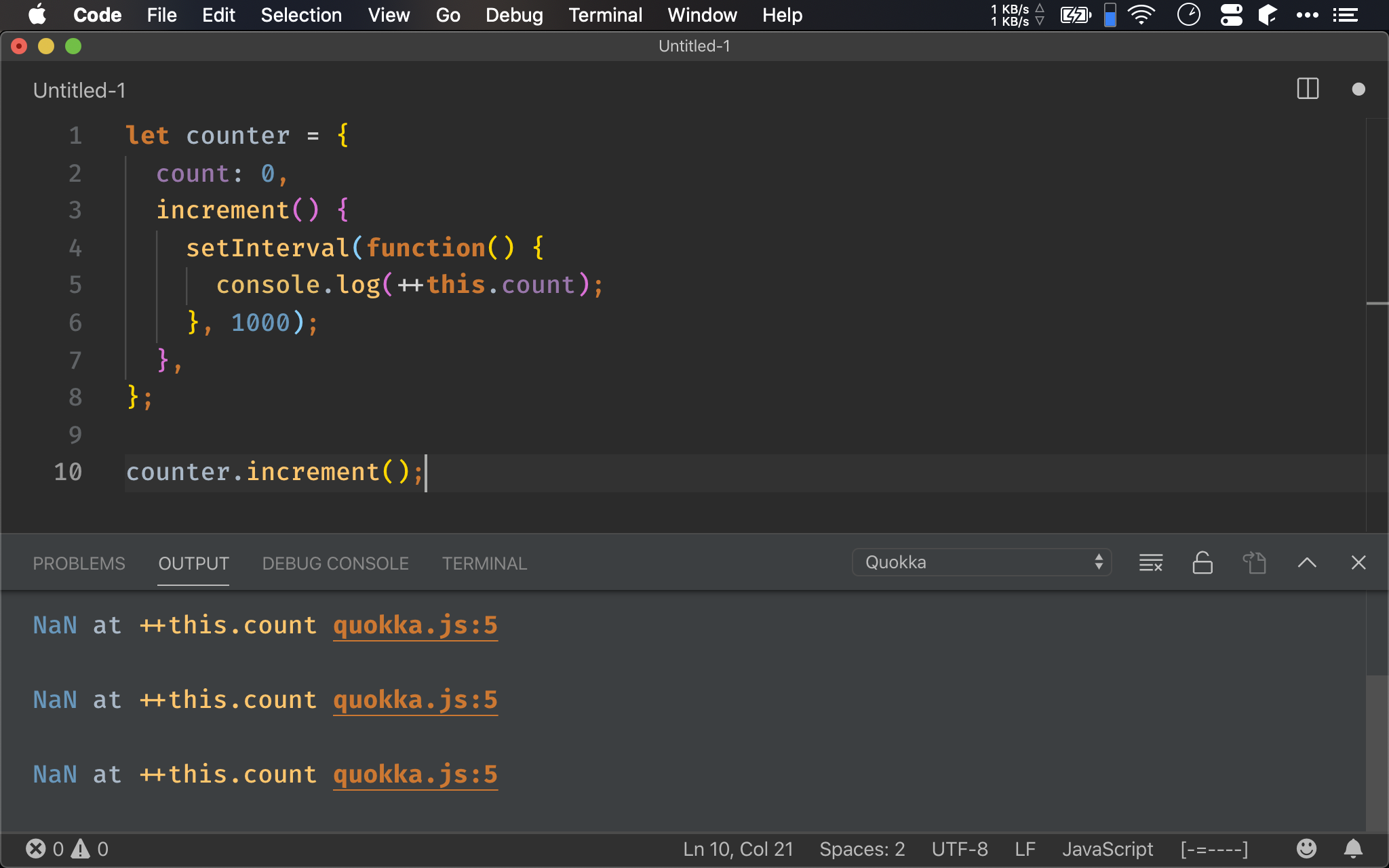
一個常見的應用,在 counter object 定義 increment() method,在其內呼叫 setInterval(),由於被要求傳入 callback,因此以 anonymous function 傳入 setInterval()。
由於 anonymous function 想對 counter property 做累加,很直覺的就寫出 ++this.count。
Why Not ?
setInterval(function() {
console.log(++this.count);
}, 1000);
對每個 function 而言,它都有自己的 this,當 function 成為 object 的 method 時,this 指向 object,但 anonymous function 並非 object 的 method,因此 this 並不是指向 object。
這與 class-based OOP 的 this 永遠指向 object 不同,因為 ECMAScript 是以 function 為主體,所以 this 也是以 function 為考量,而非以 object 考量。
Self
let counter = {
count: 0,
increment() {
self = this;
setInterval(() => {
console.log(++self.count);
}, 1000);
},
};
counter.increment();
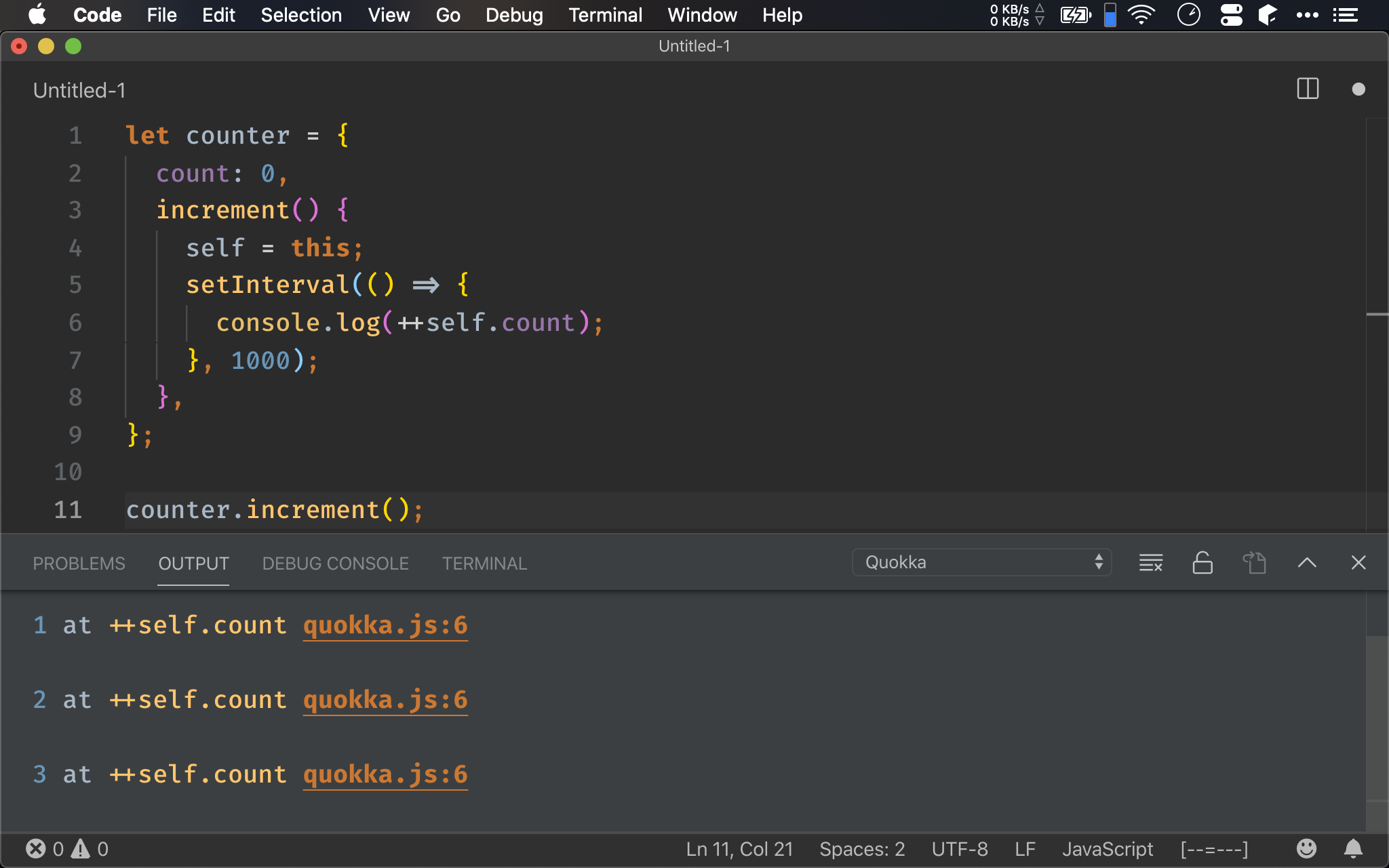
最傳統的解法,就是將用 self = this,然後再利用 lexical scope 特性,讓 callback 得到正確的 this。
Function.prototype.bind()
let counter = {
count: 0,
increment() {
setInterval(function() {
console.log(++this.count);
}.bind(this), 1000);
},
};
counter.increment();
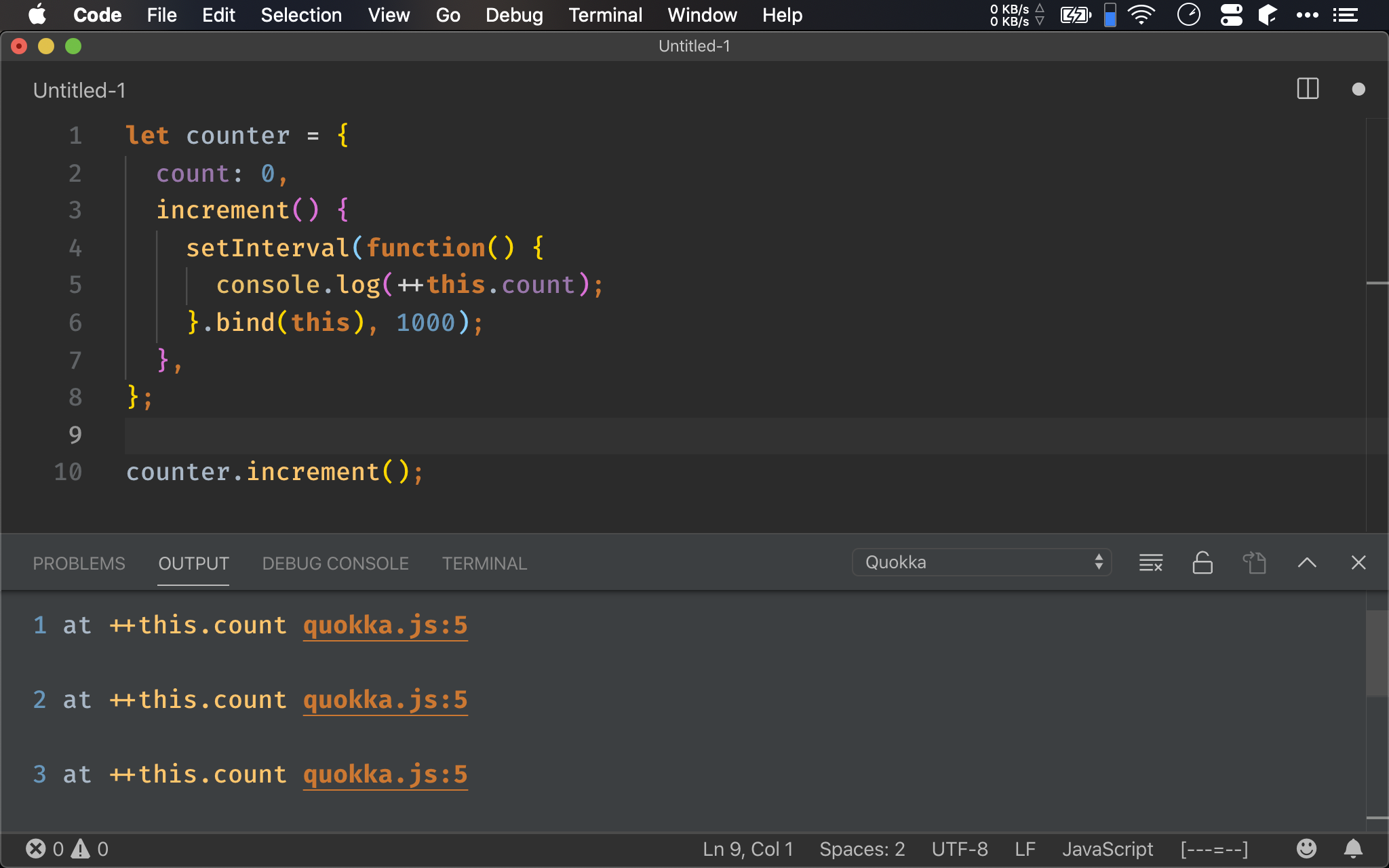
也可透過 bind() 強迫將 this 綁定進 callback 的 this。
Arrow Function
let counter = {
count: 0,
increment() {
setInterval(() => {
console.log(++this.count);
}, 1000);
},
};
counter.increment();
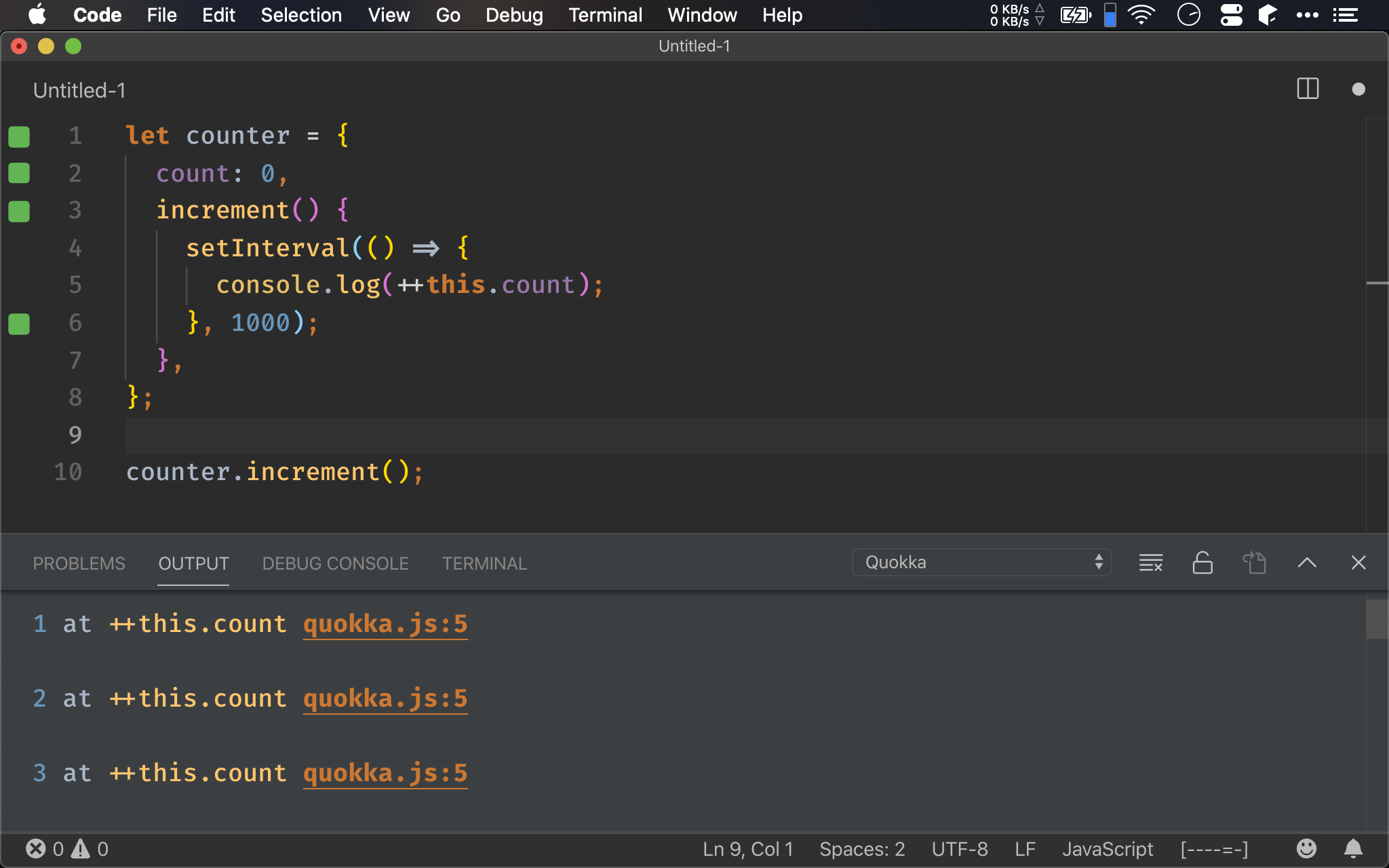
FP 適合以 callbck 傳入 function,因此 ECMAScript 2015 特別支援 arrow function,這比 anonymous function 可讀性更高。
也由於 arrow function 在實務上常常要以 this 讀取 object 的 property,為了讓 arrow function 更好用,不必再使用 bind(this),arrow function 對於 this 有 2 項特色:
- 將以 parent scope 的
this為this this不能夠被改變,因此無法使用call()、apply()與bind()
Conclusion
- Arrow function 並沒有要取代 function declaration 與 anonymous function
- 若
有使用call()、apply()與bind()改變this的需求,就要使用 function Declaration 或 anonymous Function - 若
沒有使用call()、apply()與bind()改變this的需求,就可使用 arrow function
Reference
Egghead.io, Understanding JavaScript’s this Keyword in Depth