after 允許我們動態新增內容,也因為本質是 Element,所以可以設定各種 CSS Property。
Version
CSS 3
after
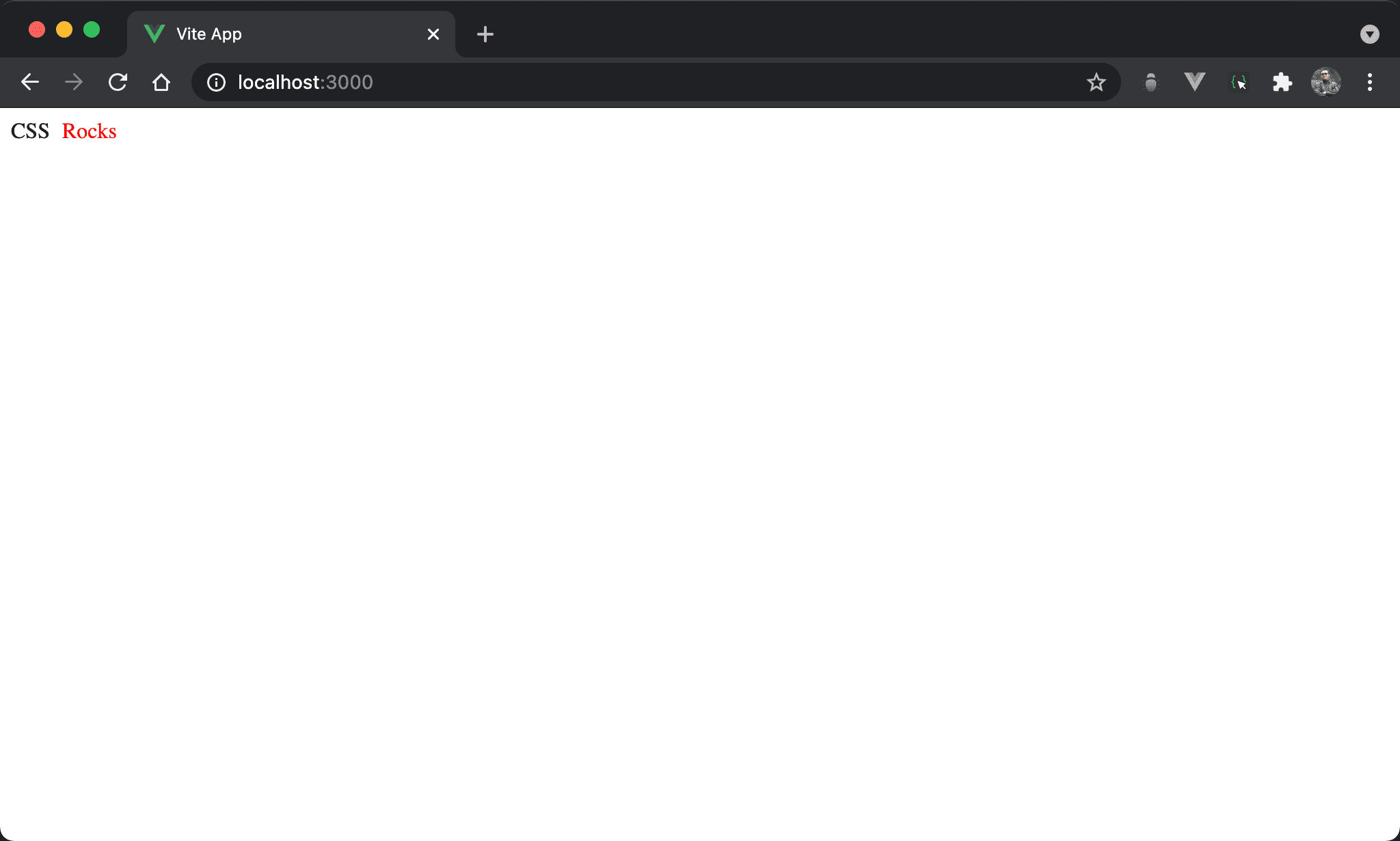
乍看之下會以為 HTML 有 CSS Rocks,只是 Rocks 是由 CSS 所新增。
<template>
<div class="title">
CSS
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
.title:after {
content: 'Rocks';
color: #f00;
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>
第 2 行
<div class="title">
CSS
</div>
HTML 實際上只有 CSS 而已。
第 8 行
.title:after {
content: 'Rocks';
color: #f00;
margin-left: 5px;
}
使用 after 動態建立 Rocks:
content:指定要顯示的內容color:由於after本質是 element,因此也能設定 CSS propertymargin-left:設定Awesome的 left margin
after是 pseudo-element,理論上該使用::,但也可簡寫成:
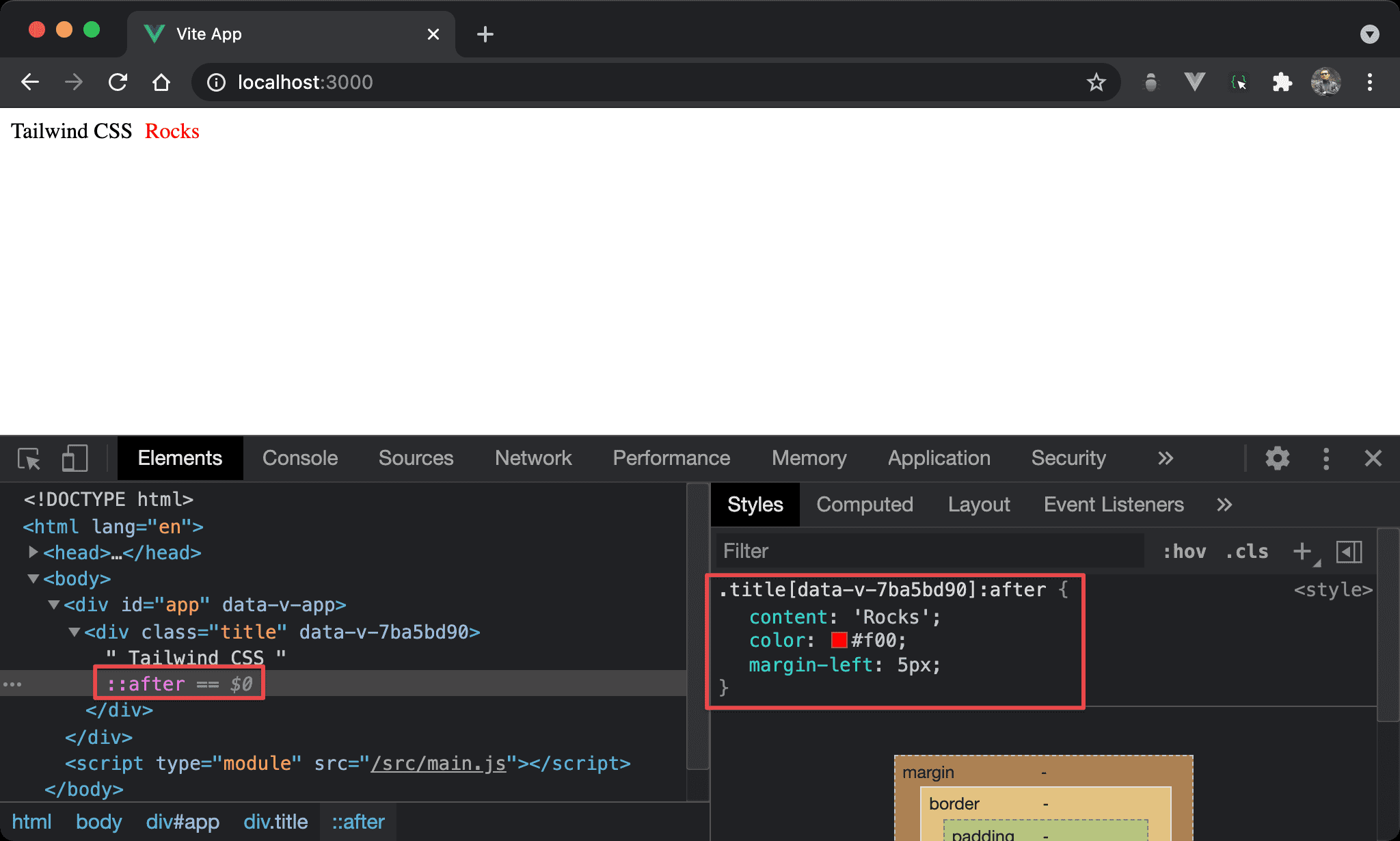
- 直覺會以為
after會新增到原 element 之後,事實上是新增在原 content 之後,但卻是原 element 之內 - 在 DevTools 並不會直接顯示其 property,必須選擇
::after才會顯示
inline-block
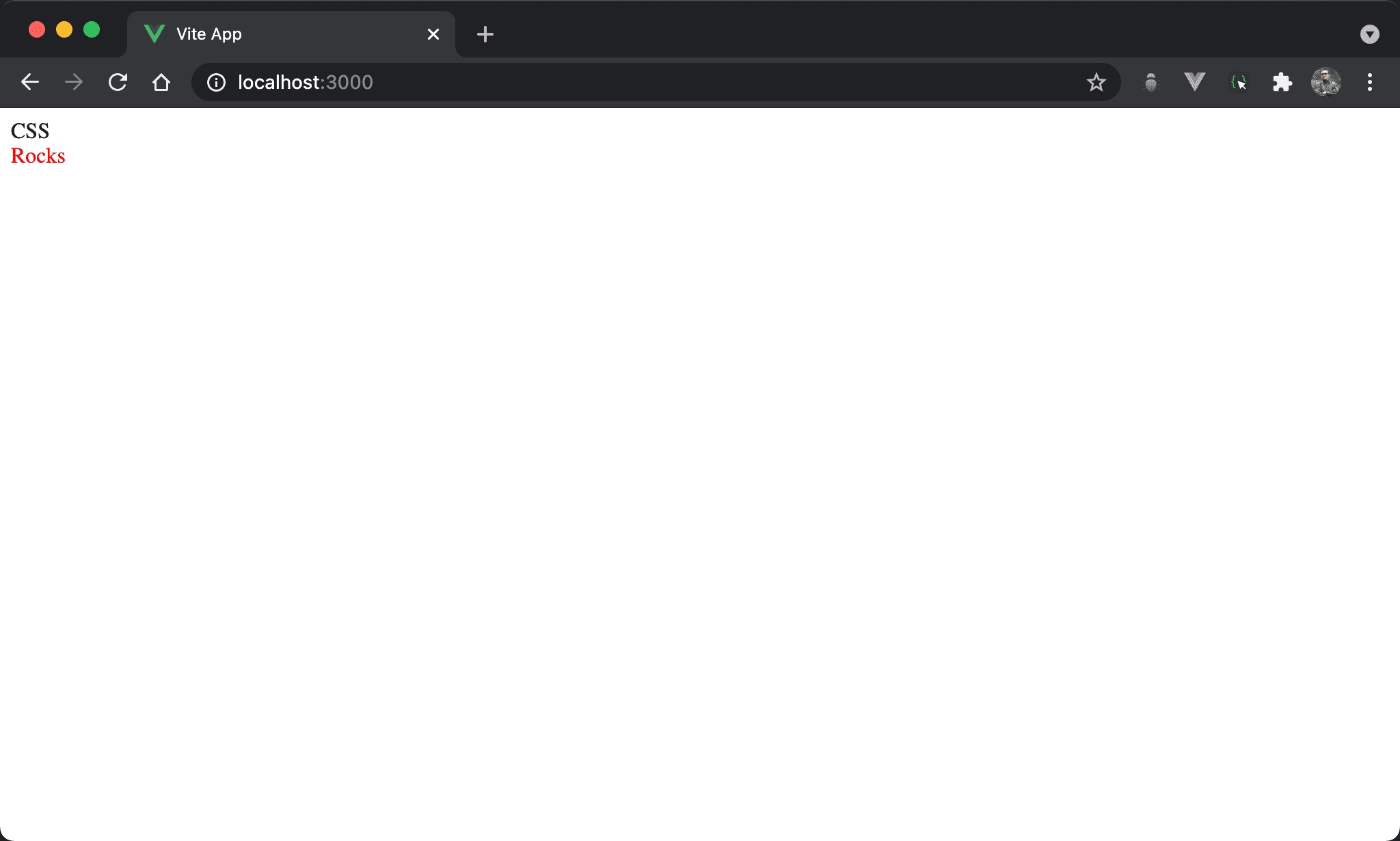
after 預設為 inline-block,欲使其換行必須改成 block。
<template>
<div class="title">
CSS
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
.title:after {
content: ' Rocks';
color: #f00;
display: block;
}
</style>
第 8 行
.title:after {
content: ' Rocks';
color: #f00;
display: block;
}
display: block:為了能讓after與原來內容同一行,所以after預設為 inline-block,若要使其能換行,必須改用display: block。
Conclusion
after是 pseudo-element,理論上該使用::,但也可簡寫成:after一定得搭配contentproperty,否則不會顯示,最少也必須是content: ''after的價值在於不修改 HTML 前提下仍可新增內容,若 component 由自己開發,建議直接使用 real element 增加內容,也有助於 SEO;但若 component 是來自於 package 或其他 framework,由於無法變更 HTML,則可使用after加以新增