Functor 的 Composition Law 是重構 Functor 常見技巧,但可惜 Monad 並不存在 Composition Law,但仍可使用 Function 都有的 Associativity Law 與 Monad 特有的 Associativity Law 來組合。
Version
Fantasy Land 5.0.0
chain
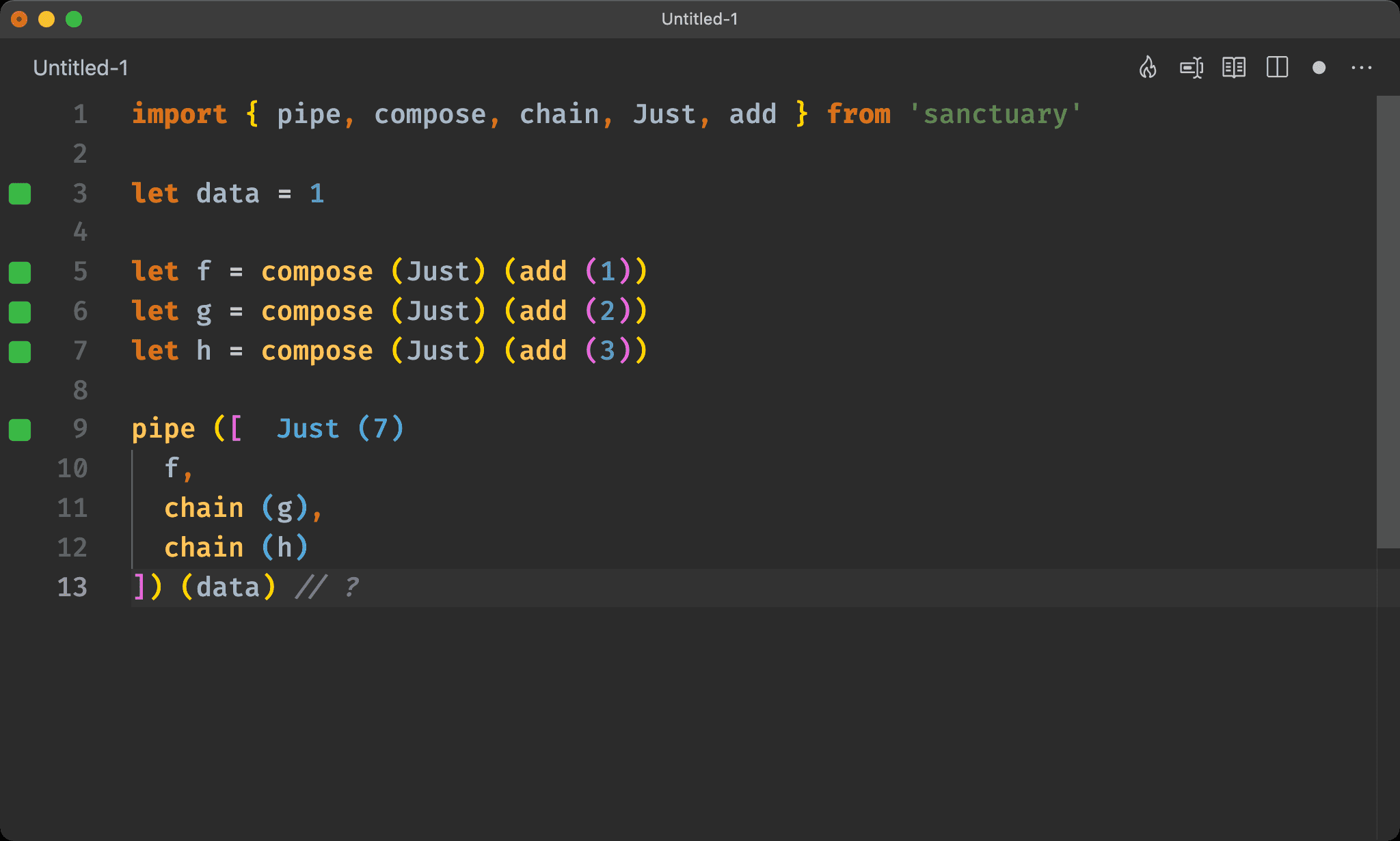
import { pipe, compose, chain, Just, add } from 'sanctuary'
let data = 1
let f = compose (Just) (add (1))
let g = compose (Just) (add (2))
let h = compose (Just) (add (3))
pipe ([
f,
chain (g),
chain (h)
]) (data) // ?
f、g 與 h 都是回傳 Maybe 的 function,若要將依序套用這 3 個 function,可使用 pipe 組合 f、g 與 h。
唯 3 個 funciton 都回傳 Maybe,因此必須使用 chain 將 Maybe 與回傳 Maybe 的 function 綁定。
Composition
import { pipe, compose, chain, Just, add } from 'sanctuary'
let data = 1
let f = compose (Just) (add (1))
let g = compose (Just) (add (2))
let h = compose (Just) (add (3))
let t = pipe ([
g,
h
])
pipe ([
f,
chain (t)
]) (data) // ?
第 9 行
let t = pipe ([
g,
h
])
根據使用 map 的經驗,直覺會想將在 chain 內的 g 與 h 先組合起來。
14 行
pipe ([
f,
chain (t)
]) (data) // ?
然後一次傳給 chain,這就是 Functor 的 composition。
Composition Law
fmap f . fmap g = fmap (f . g)
多次map相當於先組合 function 再一次傳入map
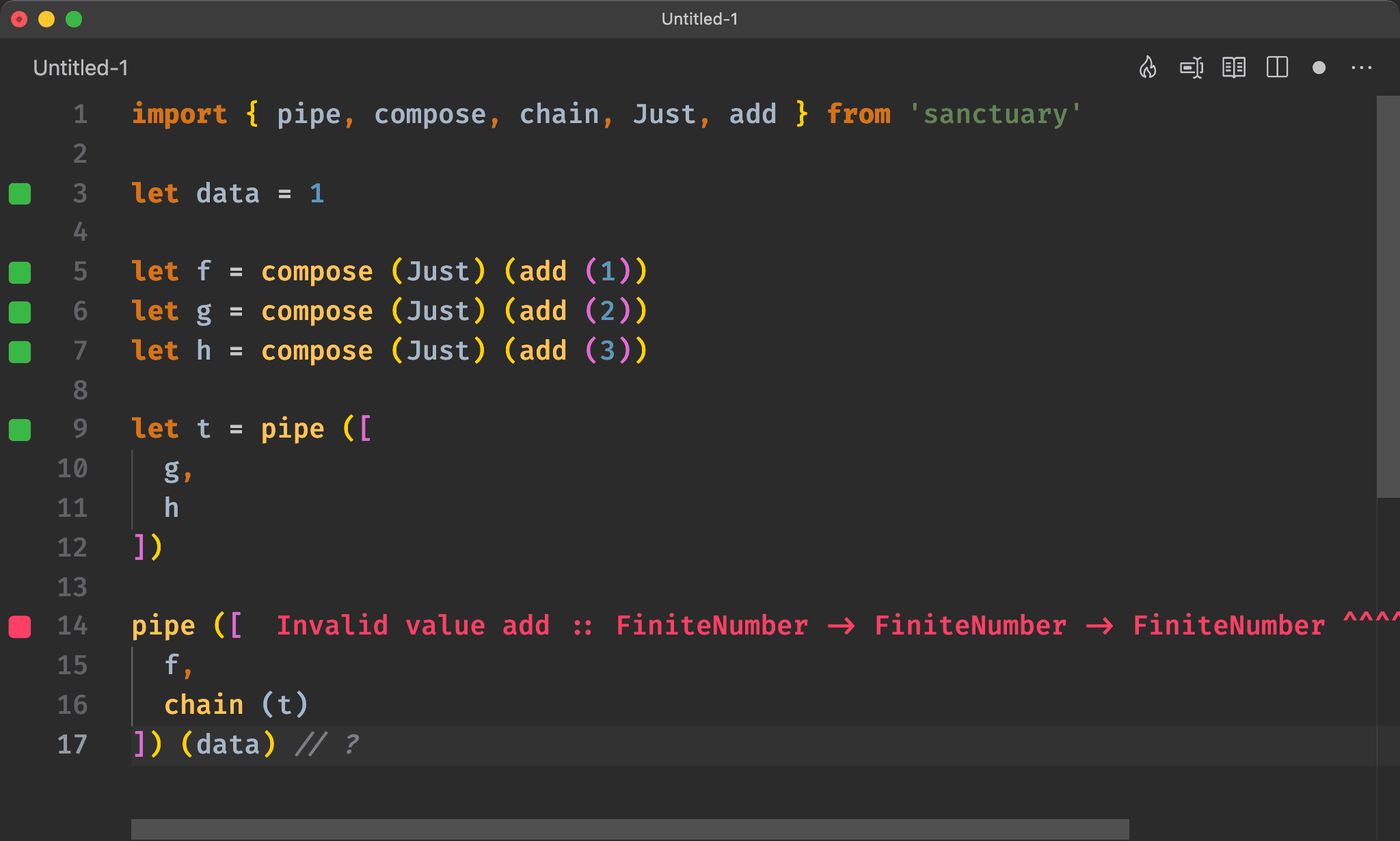
但會發現 Sanctuary 會抱怨 type 不合而無法組合,因為 Monad 並不存在 composition law,因此 chain 無法如 map 那樣組合。
Associativity
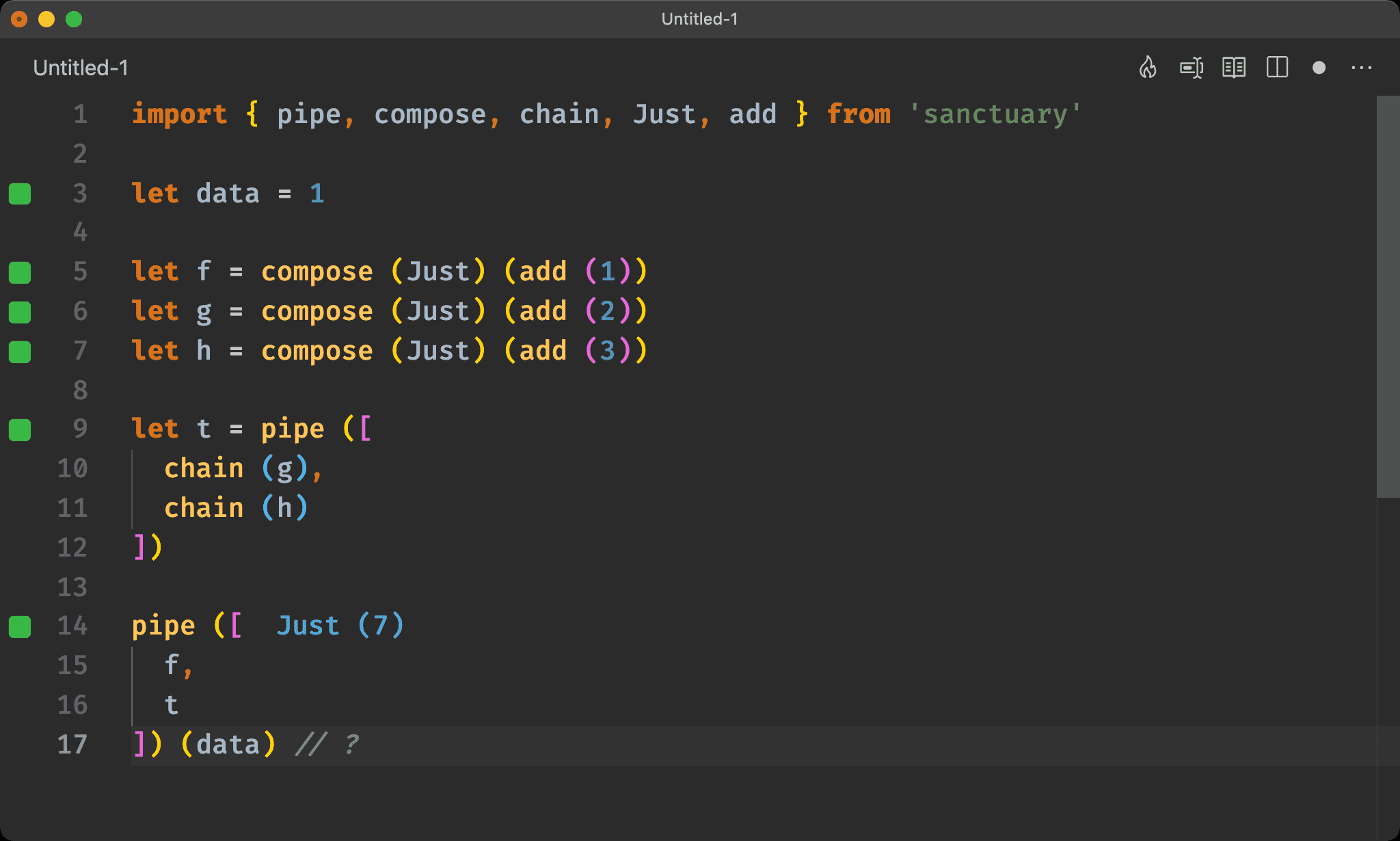
import { pipe, compose, chain, Just, add } from 'sanctuary'
let data = 1
let f = compose (Just) (add (1))
let g = compose (Just) (add (2))
let h = compose (Just) (add (3))
let t = pipe ([
chain (g),
chain (h)
])
pipe ([
f,
t
]) (data) // ?
第 9 行
let t = pipe ([
chain (g),
chain (h)
])
一樣組合 g 與 h,但改用 function 都支援的 associativity law,因此 chain 也要帶進 pipe。
14 行
pipe ([
f,
t
]) (data) // ?
如此將 t 一次傳進 pipe 即可。
但可發現
f明明也是回傳 Maybe 的 function,卻沒有一起組合
import { pipe, compose, chain, Just, add } from 'sanctuary'
let data = 1
let f = compose (Just) (add (1))
let g = compose (Just) (add (2))
let h = compose (Just) (add (3))
let t = pipe ([
f,
chain (g),
chain (h)
])
t (data) // ?
第 9 行
let t = pipe ([
f,
chain (g),
chain (h)
])
也可繼續使用 associativity 將 f 也整進 pipe。
但這樣似乎跟沒 refactoring 一樣,又回到原點
Monad’s Associativity
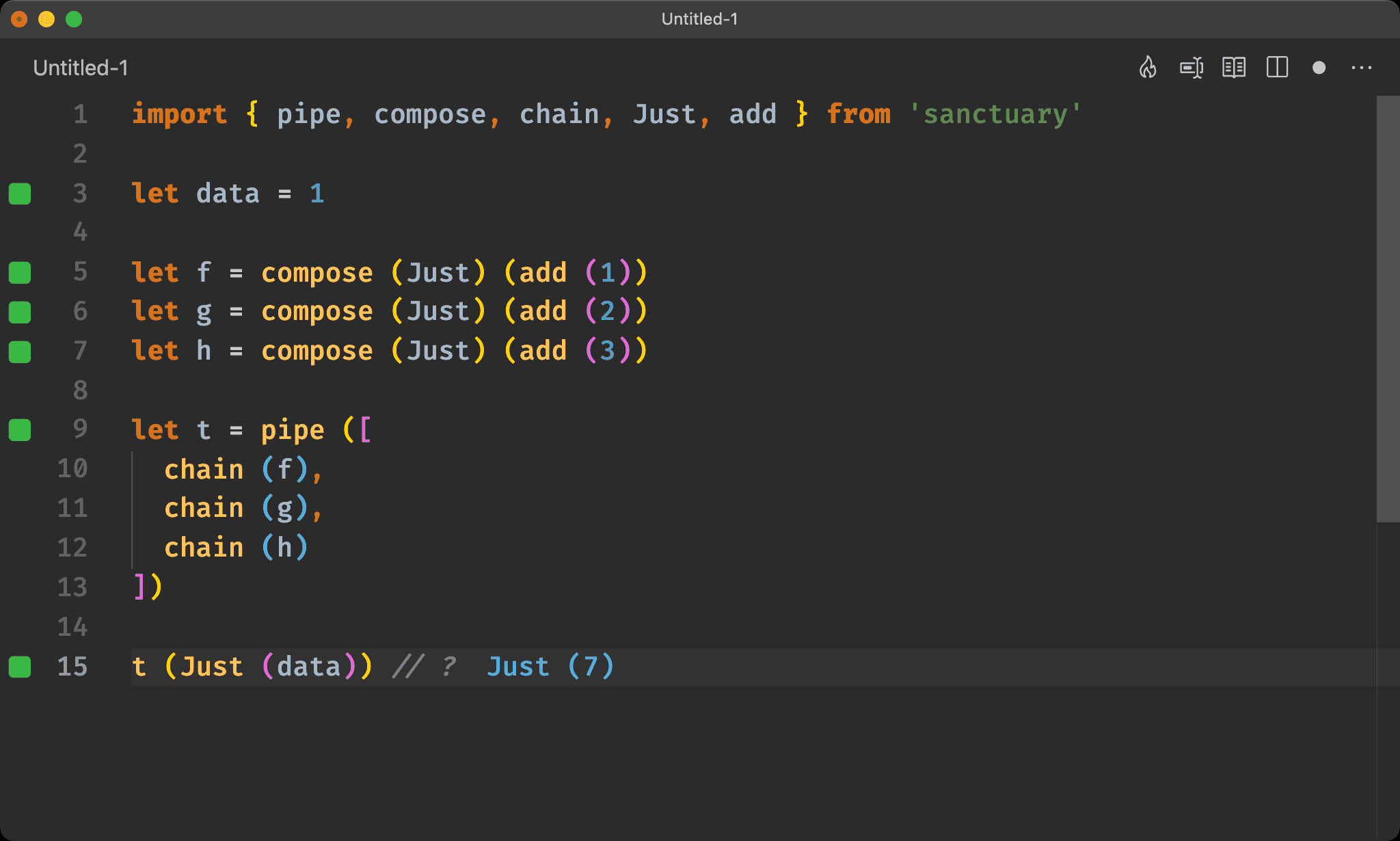
import { pipe, compose, chain, Just, add } from 'sanctuary'
let data = 1
let f = compose (Just) (add (1))
let g = compose (Just) (add (2))
let h = compose (Just) (add (3))
let t = pipe ([
chain (f),
chain (g),
chain (h)
])
t (Just (data)) // ?
第 9 行
let t = pipe ([
chain (f),
chain (g),
chain (h)
])
由於 Maybe 也是 Monad,因此也可使用 Monad 的 associativity law 來組合 f、g 與 h。
Associativity
(m >>= f) >>= g === m >>= (\x -> f x >>= g)
先將 value 包進 Monad 再連續使用chain與 function 綁定,與 value 先經過 function 運算最後包進 Monad 結果相同
15 行
t (Just (data)) // ?
唯 data 必須先包進 Maybe 內。
Conclusion
- 不見得只能使用 composition 組合 function,事實上 associativity 也能組合 function
- Monad 並不存在 Functor 那樣的 composition law,但仍可用 function 共通的 associatively law 或 Monad 的 associativity law 來組合